Lessons from 2025: Evolving Tactics in AI-Driven Cyber Attacks Highlight Persistent Vulnerabilities
Published on: 2026-01-13
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: What Should We Learn From How Attackers Leveraged AI in 2025
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
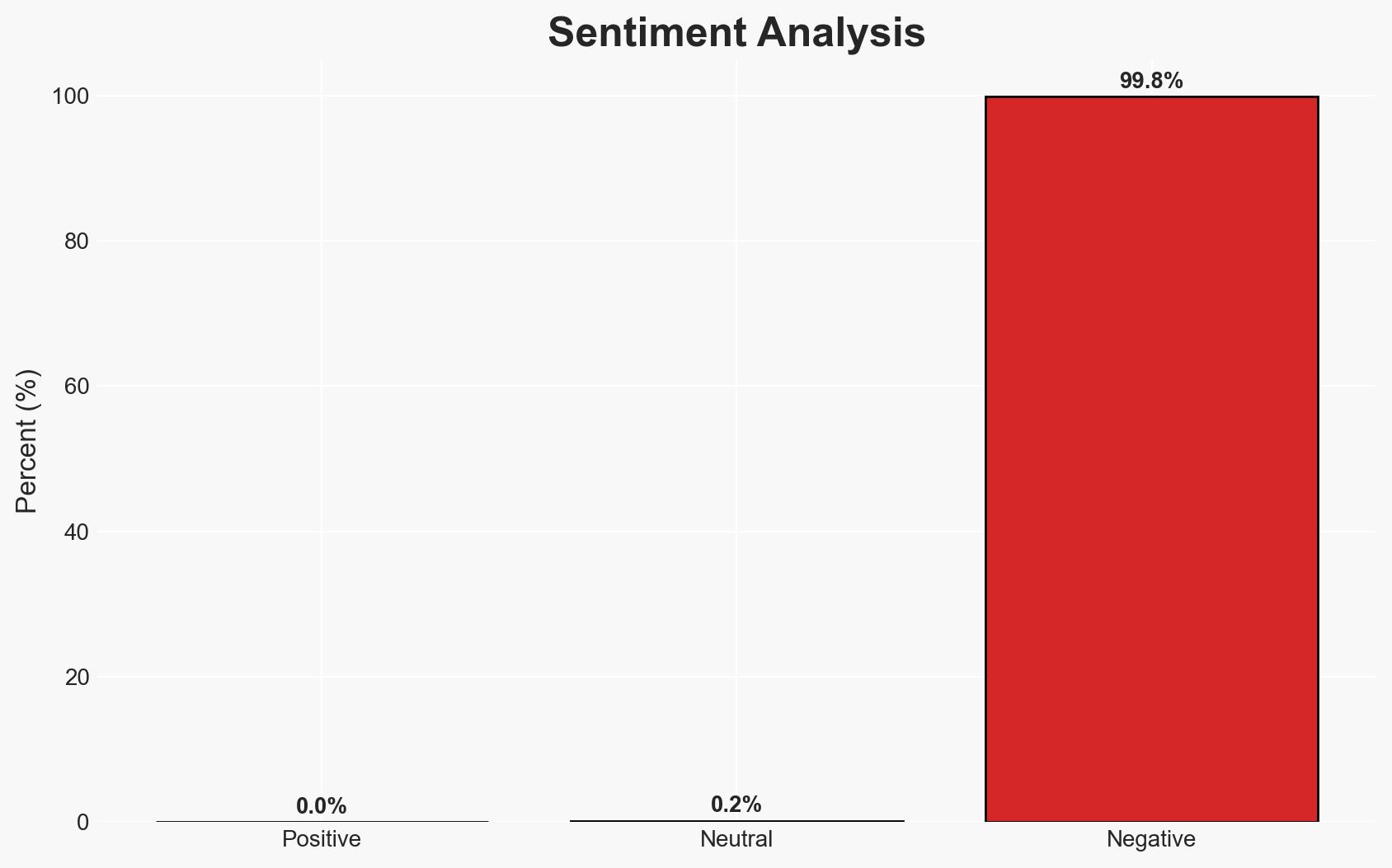
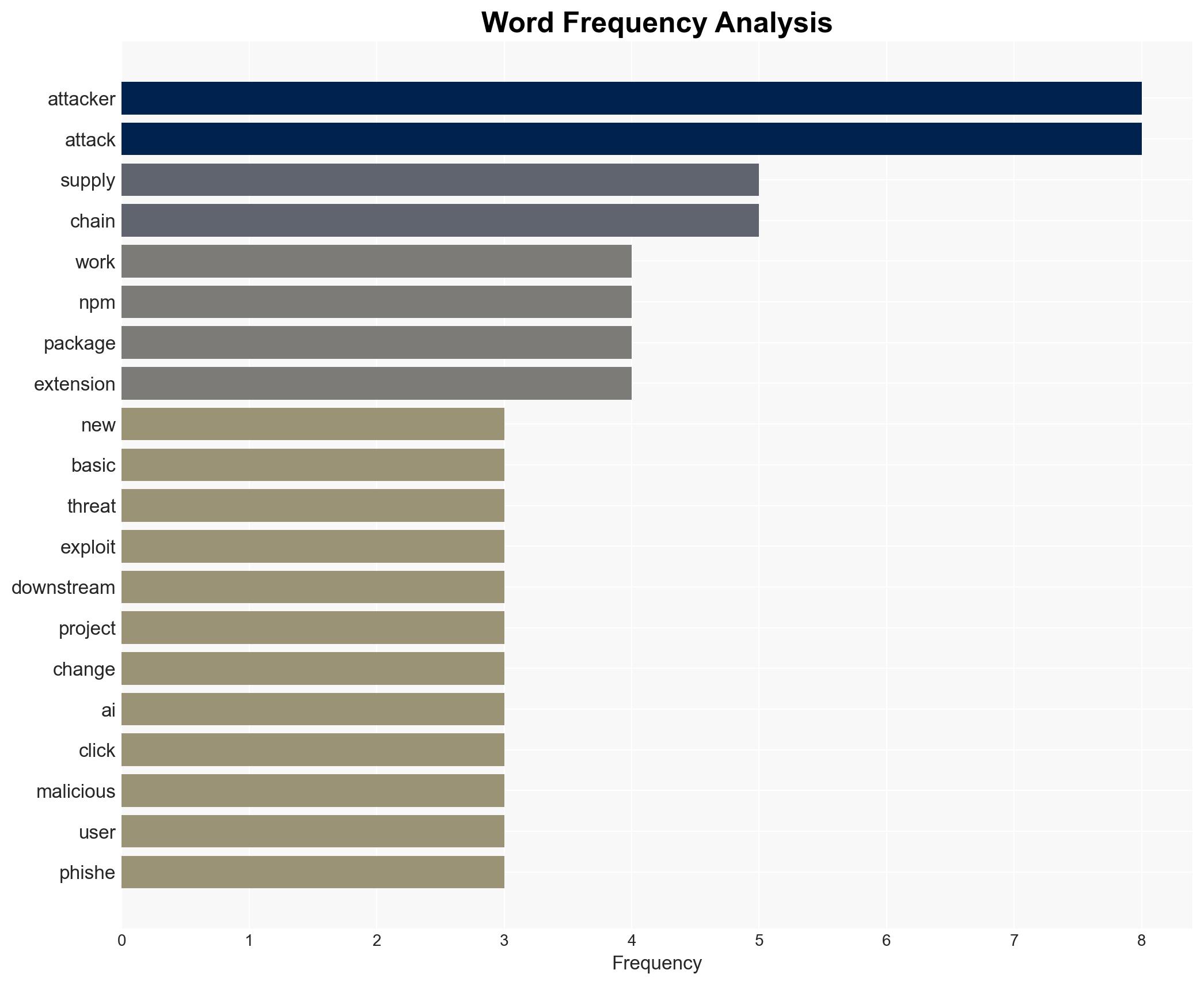
The integration of AI into cyber-attacks has enhanced the efficiency of traditional attack vectors, notably supply chain compromises and phishing. This evolution poses significant risks to software security and user data integrity. The most likely hypothesis is that AI will continue to lower the barrier for individual attackers, increasing the frequency and scale of attacks. This assessment is made with moderate confidence due to existing information gaps regarding the full extent of AI’s role in these attacks.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: AI has fundamentally changed the nature of cyber-attacks, allowing for new types of attacks that were not possible before. While AI has indeed improved efficiency, evidence suggests that attackers are primarily optimizing existing methods rather than creating entirely new ones. Key uncertainties include the potential for undiscovered AI-driven attack methods.
- Hypothesis B: AI is primarily enhancing existing attack vectors, making them more efficient and scalable. This is supported by the continued effectiveness of traditional attacks like phishing and supply chain compromises, albeit executed with greater precision and reach. Contradicting evidence might emerge if new AI-specific attack vectors are identified.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported, as the evidence indicates that AI is being used to refine and scale existing attack methodologies rather than invent new ones. Indicators that could shift this judgment include the discovery of novel AI-driven attack techniques.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI capabilities will continue to advance and be accessible to attackers; traditional attack vectors will remain relevant; defenders will not significantly outpace attackers in AI application.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the specific AI tools and techniques used by attackers; comprehensive analysis of AI’s role in recent large-scale attacks.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in overestimating AI’s role due to its current prominence in discourse; risk of deception from attackers exaggerating AI use to create fear and uncertainty.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The continued use of AI to enhance traditional cyber-attacks could lead to increased frequency and impact of security breaches, affecting both public and private sectors. This evolution may strain existing cybersecurity frameworks and necessitate new strategies.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased state-sponsored cyber operations leveraging AI, leading to geopolitical tensions.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment as AI enables more sophisticated and widespread attacks.
- Cyber / Information Space: Greater difficulty in detecting and mitigating attacks, necessitating advanced AI-driven defense mechanisms.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic disruptions from compromised supply chains and loss of consumer trust in digital platforms.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of AI-driven attack indicators; prioritize patching and securing supply chain vulnerabilities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with AI research entities to improve defensive capabilities; invest in AI-driven threat detection and response systems.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: AI is effectively integrated into defensive strategies, reducing attack success rates.
- Worst: AI-driven attacks overwhelm current defenses, leading to widespread breaches.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in both attack and defense capabilities, maintaining a dynamic threat landscape.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, AI in cybercrime, supply chain attacks, phishing, digital threats, information security, cyber defense
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us