Loose Wire Blamed for Baltimore Bridge Collapse – Newser
Published on: 2025-11-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report:
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
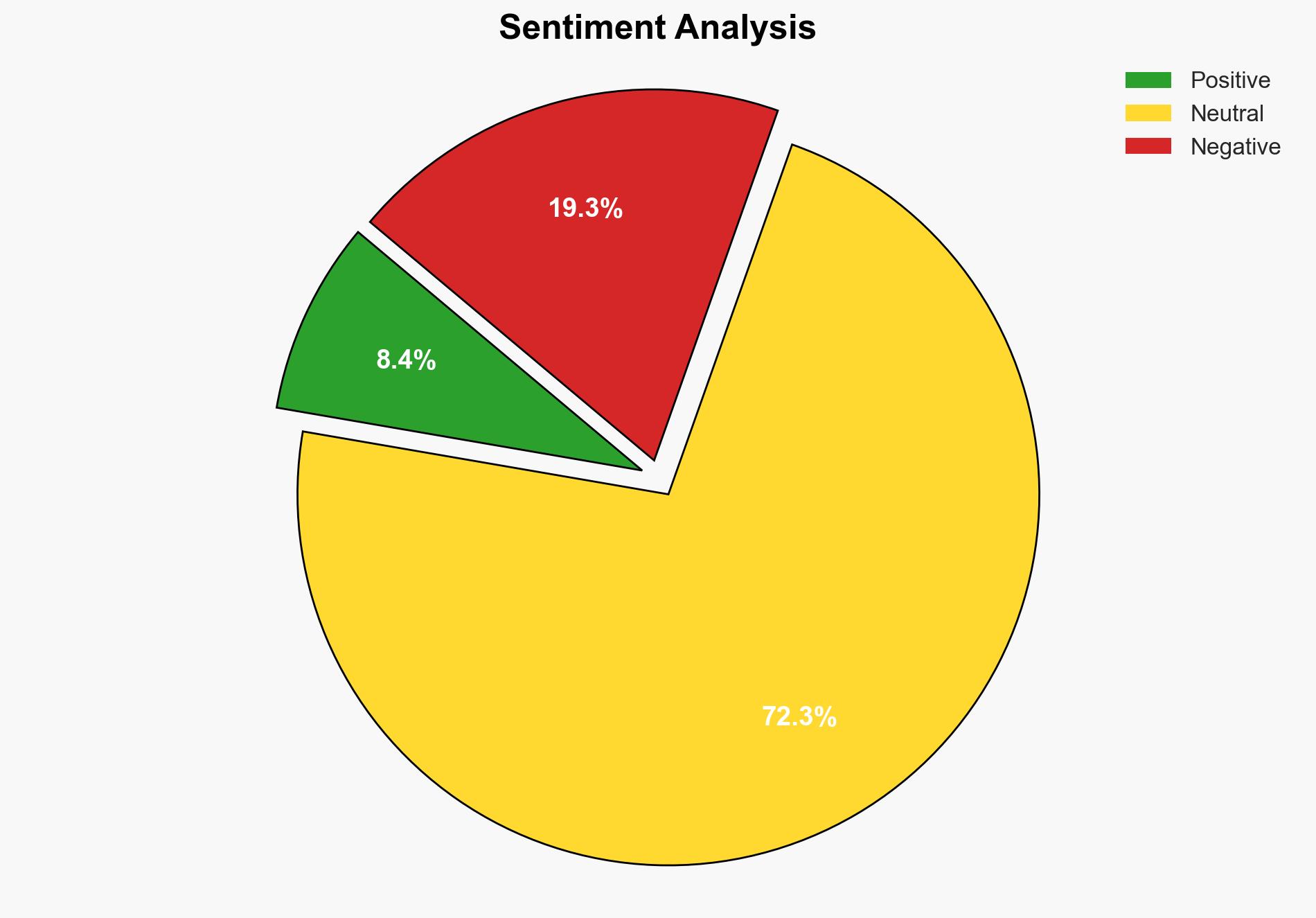
With a moderate confidence level, the most supported hypothesis is that the collapse of the Baltimore Francis Scott Key Bridge was primarily due to systemic oversight failures by Synergy Marine Group, compounded by inadequate response protocols from the Maryland Transportation Authority. Immediate action should focus on enhancing oversight mechanisms and updating safety protocols to prevent similar incidents.
2. Competing Hypotheses
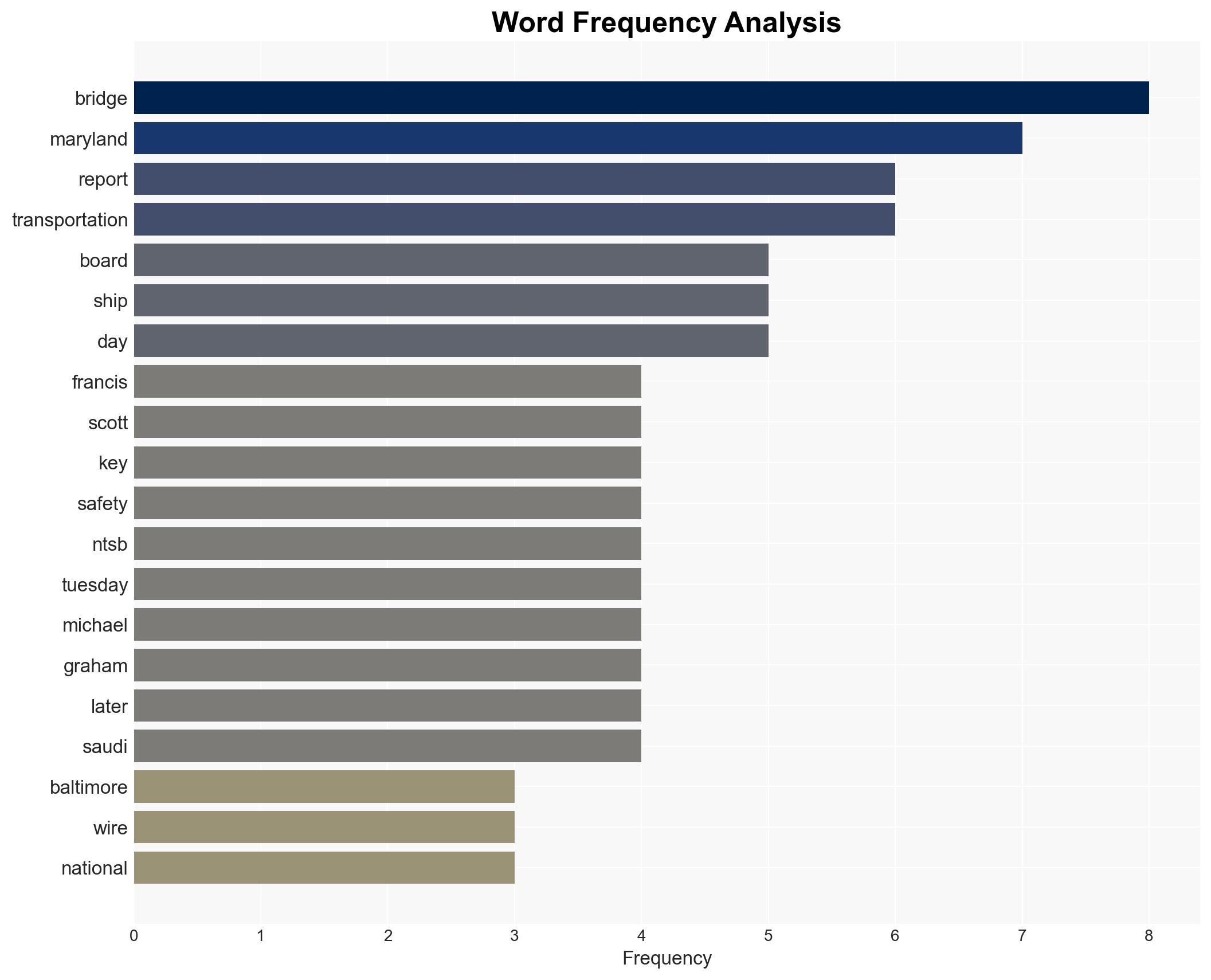
Hypothesis 1: The collapse was primarily caused by a single loose wire, which led to a power failure and subsequent collision with the bridge support pier. This points to a technical failure in the ship’s electrical system.
Hypothesis 2: The collapse resulted from broader systemic failures, including inadequate oversight by Synergy Marine Group and insufficient safety assessments by the Maryland Transportation Authority, which failed to address vulnerabilities and implement NTSB recommendations.
While both hypotheses are plausible, Hypothesis 2 is more likely given the NTSB’s criticism of Synergy Marine Group’s oversight and the Maryland Transportation Authority’s failure to act on previous safety recommendations. The presence of systemic issues suggests a broader pattern of negligence rather than an isolated technical failure.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: It is assumed that the NTSB report accurately reflects the technical and operational conditions leading to the collapse. There is also an assumption that Synergy Marine Group and the Maryland Transportation Authority have not fully implemented past recommendations.
Red Flags: The report’s timing and the focus on a single technical fault may distract from broader systemic issues. The rapid response by the crew, while commendable, may indicate prior awareness of potential vulnerabilities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The incident exposes risks in maritime and infrastructure safety, potentially leading to increased regulatory scrutiny and financial liabilities for involved parties. Politically, it may prompt calls for stricter oversight and funding for infrastructure resilience. Economically, the delay and increased costs of bridge reconstruction could strain state budgets and impact local economies.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Actionable Steps: Enhance oversight of maritime operations and enforce compliance with safety recommendations. Conduct a comprehensive review of infrastructure vulnerabilities and update response protocols.
- Best Scenario: Implementation of improved safety measures prevents future incidents, restoring public confidence and minimizing economic impact.
- Worst Scenario: Continued oversight failures lead to further incidents, resulting in significant economic and political fallout.
- Most-likely Scenario: Incremental improvements in safety protocols and oversight reduce risk, but challenges persist due to budgetary constraints and bureaucratic inertia.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
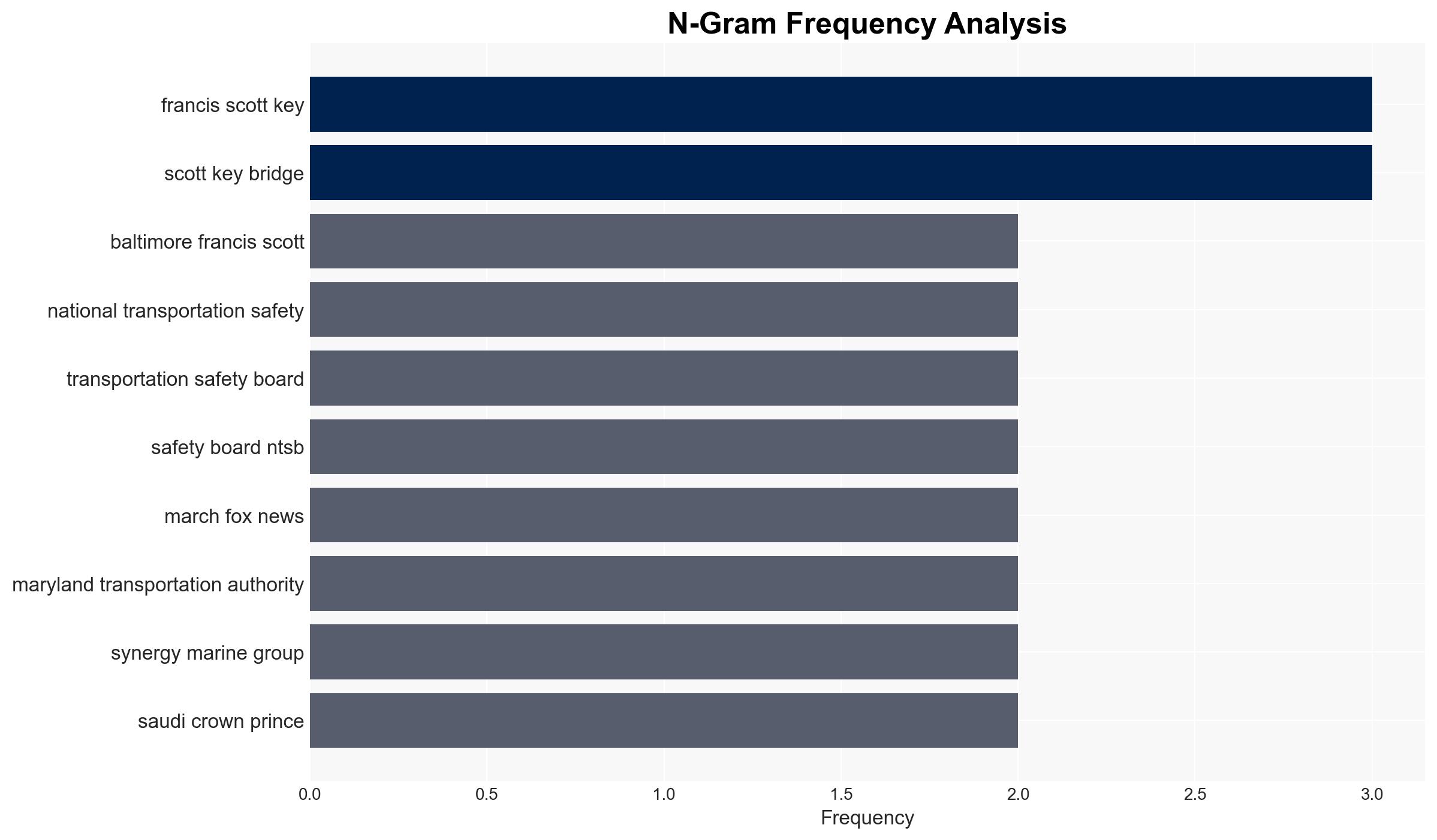
Michael Graham (NTSB Board Member), Synergy Marine Group, Maryland Transportation Authority
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, Infrastructure Safety, Maritime Oversight, Regulatory Compliance, Economic Impact
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us