Malicious AI Extensions for VS Code with 1.5 Million Installs Compromise Developer Source Code to China
Published on: 2026-01-26
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Malicious VS Code AI Extensions with 15 Million Installs Steal Developer Source Code
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
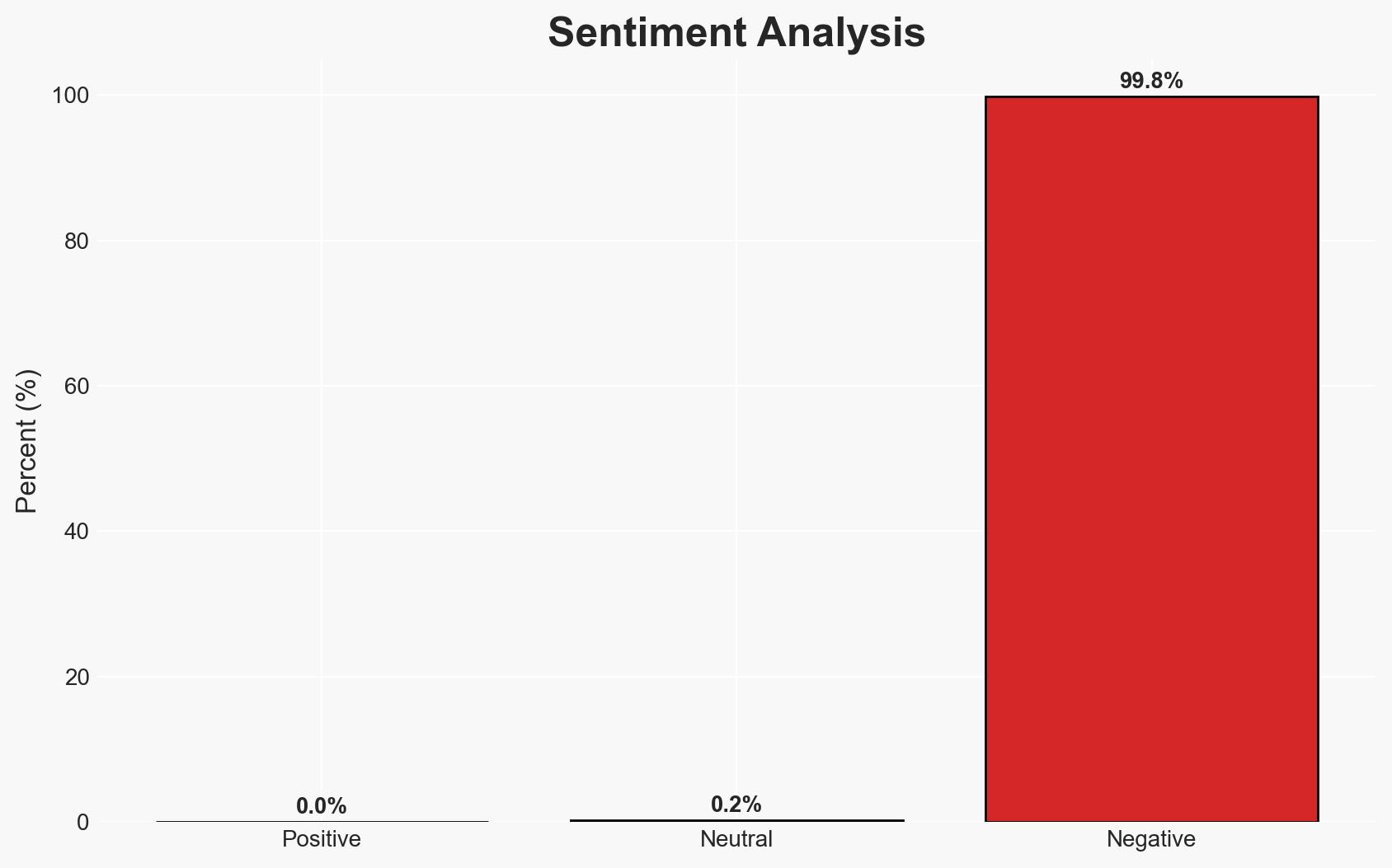
Malicious Visual Studio Code extensions, masquerading as AI-powered coding assistants, have been identified as exfiltrating developer data to China-based servers. This affects developers using these extensions, with potential implications for intellectual property theft and cybersecurity. The most likely hypothesis is state-sponsored cyber-espionage, with moderate confidence due to the sophistication and scale of the operation.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The malicious extensions are part of a state-sponsored cyber-espionage campaign aimed at collecting intellectual property and sensitive data from developers globally. Supporting evidence includes the use of Chinese servers and sophisticated data exfiltration techniques. Key uncertainties involve the direct attribution to state actors.
- Hypothesis B: The extensions are the work of independent cybercriminals seeking to monetize stolen data through industrial espionage or black market sales. This is supported by the potential financial incentives but contradicted by the scale and sophistication of the operation, which suggests state-level resources.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the infrastructure and methods used, which align with known state-sponsored activities. Indicators such as direct attribution to a specific state actor or further technical analysis could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The extensions are primarily targeting intellectual property; the data exfiltrated is of high value; China-based servers imply Chinese state involvement.
- Information Gaps: Direct evidence linking the operation to a specific state actor; detailed analysis of the data being exfiltrated.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Attribution bias towards China due to server location; potential deception in the apparent functionality of the extensions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased scrutiny of software supply chains and heightened tensions in cyber relations between China and affected nations.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential diplomatic friction and calls for international cybersecurity norms.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased vigilance in software supply chain security; potential for retaliatory cyber actions.
- Cyber / Information Space: Enhanced focus on securing development environments; potential for widespread adoption of stricter cybersecurity measures.
- Economic / Social: Possible impact on developer trust in open-source platforms; economic implications for companies whose intellectual property is compromised.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a security audit of installed extensions; monitor for further malicious activity; engage with cybersecurity firms for threat intelligence sharing.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for enhanced cybersecurity collaboration; invest in supply chain security tools and training.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Rapid mitigation and increased security standards; Worst: Escalation in cyber tensions and widespread data breaches; Most-Likely: Gradual improvements in security posture with periodic incidents.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, cyber-espionage, supply chain security, intellectual property theft, state-sponsored cyber activity, software vulnerabilities, China
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us