McDonald’s highlights the risks of using food-related passwords amid rising cybersecurity breaches
Published on: 2026-02-04
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
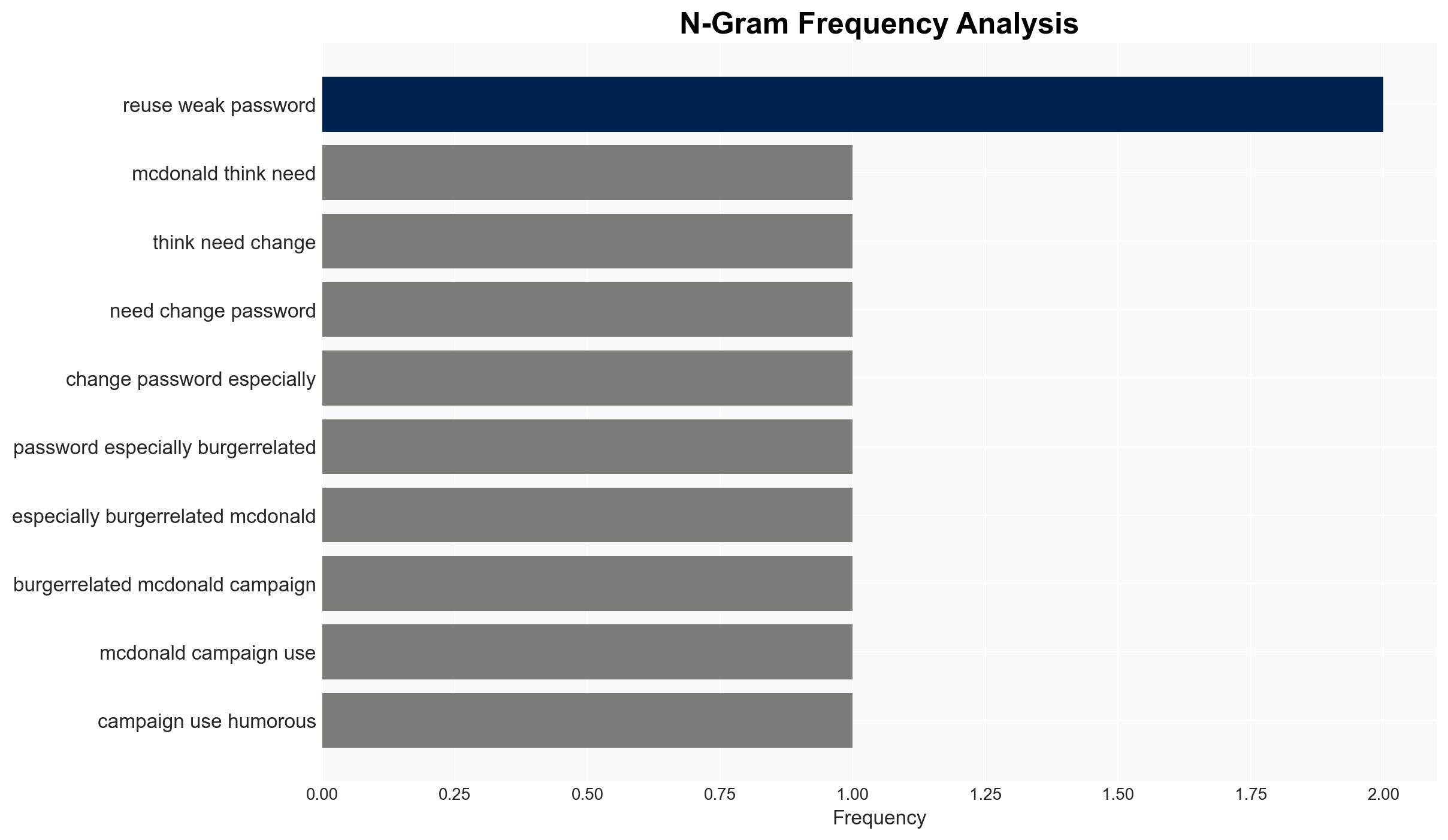
Intelligence Report: Even McDonald’s thinks you need to change your passwords – especially if they’re burger-related
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
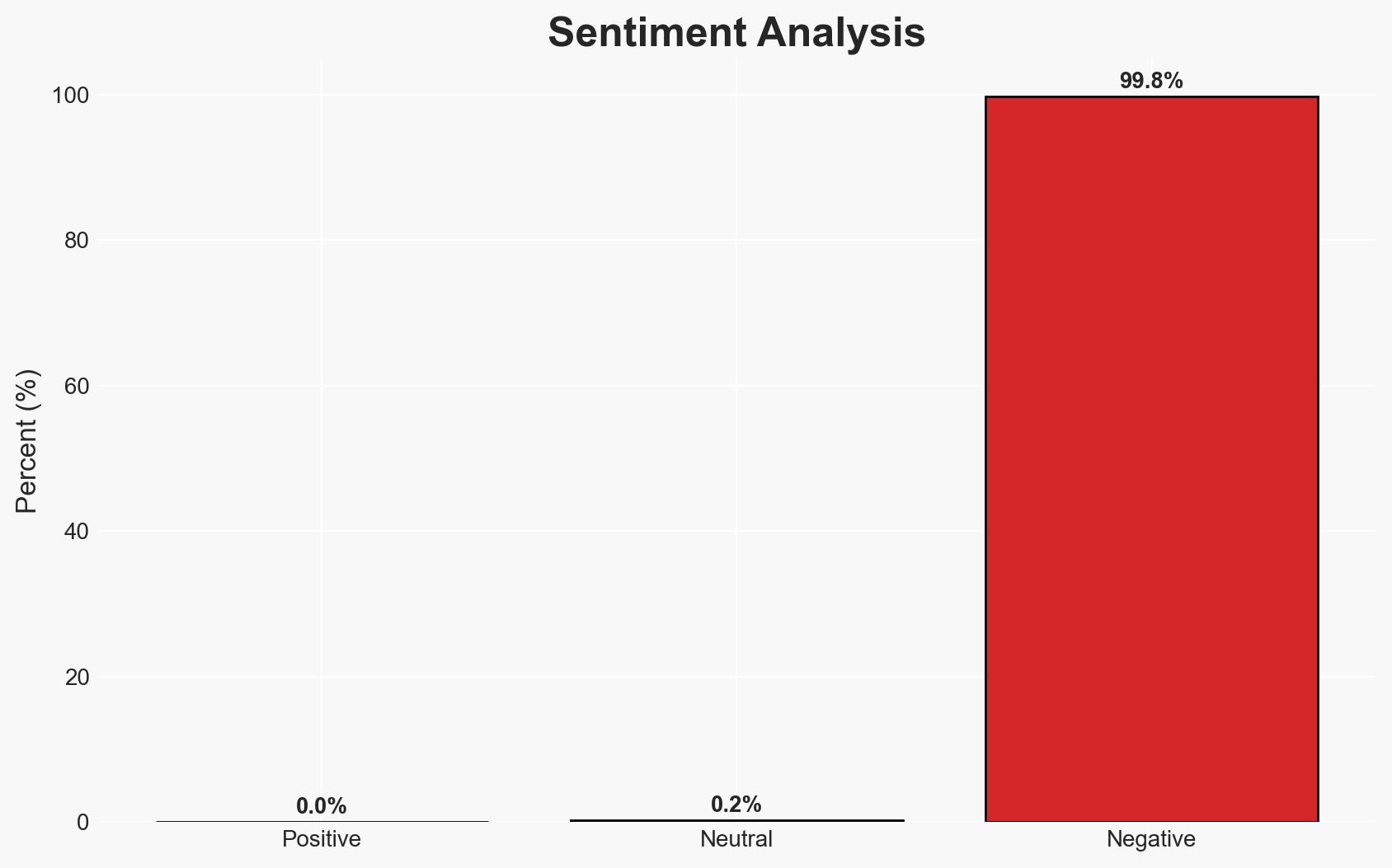
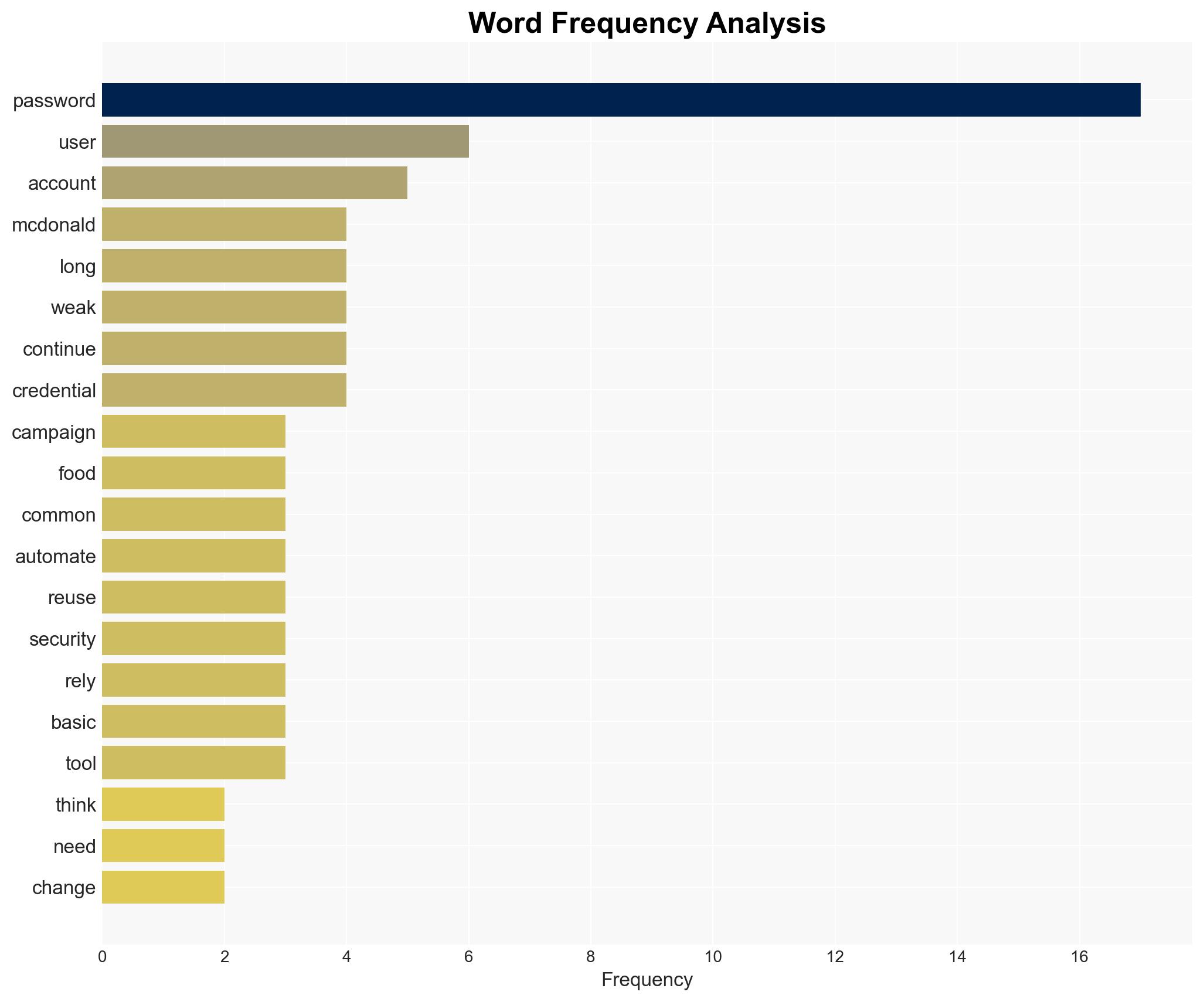
The persistence of weak, food-related passwords, highlighted by McDonald’s campaign, underscores a significant cybersecurity vulnerability affecting both individuals and enterprises. Despite awareness efforts, poor password hygiene remains prevalent, posing risks to personal and organizational security. The most likely hypothesis is that convenience and resistance to change are primary drivers of this behavior. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The continued use of weak, food-related passwords is primarily due to user convenience and resistance to change. Supporting evidence includes the widespread use of such passwords despite awareness campaigns. Contradicting evidence is limited but could include instances where users have adopted stronger practices.
- Hypothesis B: The prevalence of weak passwords is due to a lack of effective cybersecurity education and tools. Supporting evidence includes the limited impact of awareness campaigns and the continued reliance on simple passwords. Contradicting evidence includes the availability of password managers and security tools that are underutilized.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the observed behavior patterns and the limited impact of existing awareness campaigns. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include increased adoption of password managers and a measurable decline in the use of weak passwords.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Users prioritize convenience over security; awareness campaigns have limited reach; enterprises enforce password policies inconsistently; automated attacks are increasingly sophisticated.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the effectiveness of specific cybersecurity education programs; comprehensive statistics on password manager adoption rates.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in data sources such as Have I Been Pwned; humor-based campaigns may downplay the seriousness of the issue.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased vulnerability to cyberattacks, impacting both personal and organizational security. Over time, this may necessitate stronger regulatory measures or technological interventions.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory scrutiny on cybersecurity practices.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Elevated risk of data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased demand for cybersecurity solutions and education; potential rise in cybercrime exploiting weak passwords.
- Economic / Social: Financial losses from breaches; erosion of trust in digital services and platforms.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance public awareness campaigns with a focus on practical tools like password managers; monitor breach data for trends.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with tech companies to promote secure authentication methods; invest in cybersecurity education initiatives.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Widespread adoption of strong password practices reduces breach incidents.
- Worst: Continued reliance on weak passwords leads to significant data breaches.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in password practices with ongoing vulnerabilities.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, password management, data breaches, user behavior, cybersecurity education, enterprise security, digital vulnerability
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us