Meteorite Hunters Scour the Sahara for Riches From Outer Space – Financial Post
Published on: 2025-11-14
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Meteorite Hunters Scour the Sahara for Riches From Outer Space – Financial Post
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
With a moderate confidence level, the most supported hypothesis is that the meteorite hunting activity in Morocco is primarily driven by economic incentives and is likely to continue growing due to the high market value of meteorites and the relatively lenient regulatory environment. Strategic recommendations include monitoring the impact on local communities and ecosystems, and considering the development of a regulatory framework to manage the trade sustainably.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The surge in meteorite hunting in Morocco is primarily driven by economic incentives, with hunters motivated by the high market value of meteorites and the potential for significant financial gain.
Hypothesis 2: The increase in meteorite hunting is largely a result of scientific interest and the desire to contribute to planetary science, with economic gain being a secondary factor.
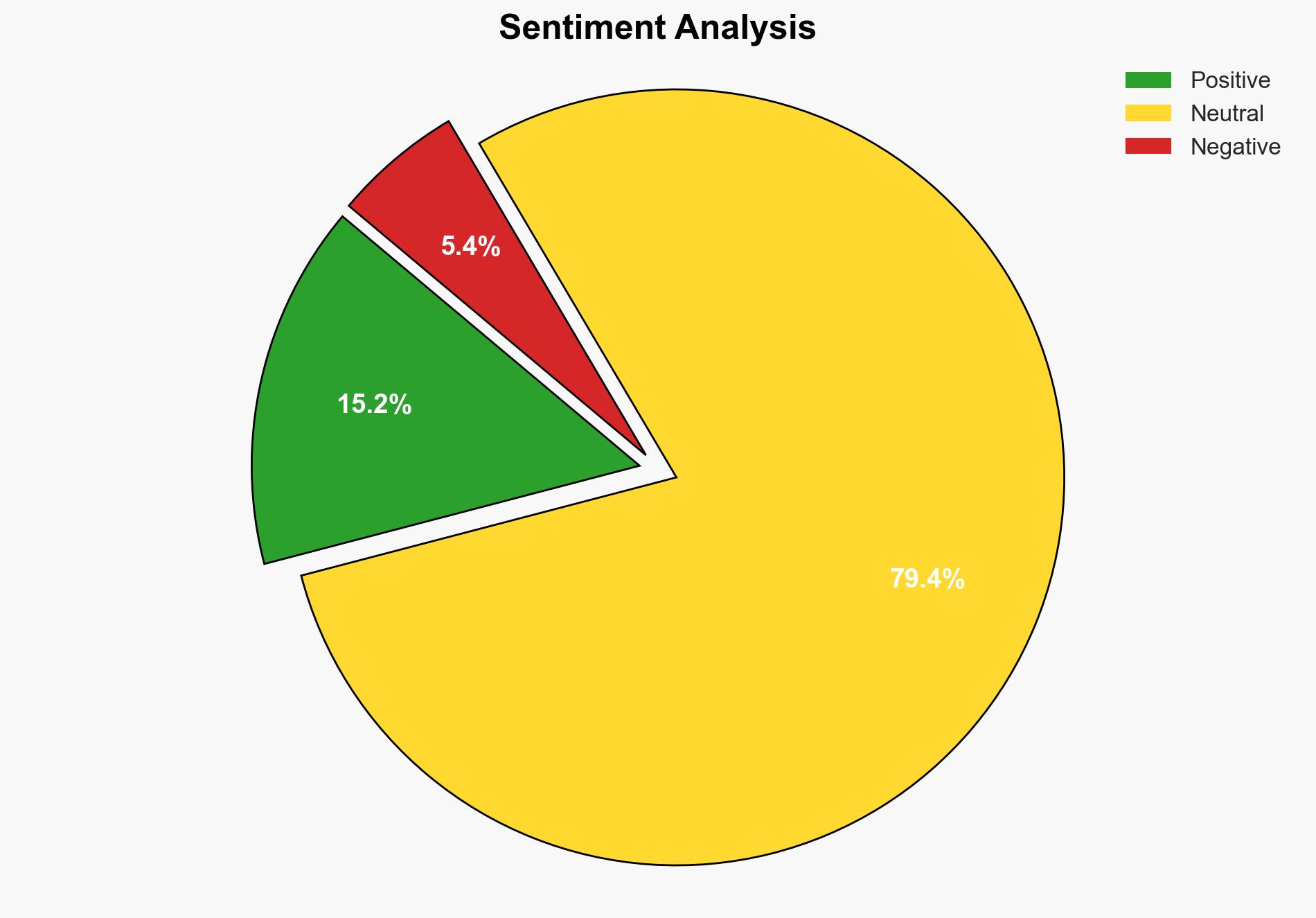
Evidence supports Hypothesis 1 as more likely due to the emphasis on financial transactions, the involvement of international auction houses, and the mention of tourism and revenue generation. Hypothesis 2 is less supported as the scientific interest appears to be a secondary benefit rather than the primary driver.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: It is assumed that the current regulatory environment in Morocco will remain unchanged, allowing for continued meteorite hunting and trade. It is also assumed that the market demand for meteorites will remain strong.
Red Flags: Potential for regulatory changes in Morocco or international pressure to regulate the trade more strictly. Economic dependency on meteorite hunting could lead to unsustainable practices.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The continuation and potential expansion of meteorite hunting could lead to environmental degradation and disruption of local communities. Economically, over-reliance on meteorite hunting could make regions vulnerable to market fluctuations. Politically, there may be increased scrutiny and pressure to regulate the trade, which could impact local economies.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Monitor the impact of meteorite hunting on local communities and ecosystems to ensure sustainable practices.
- Consider developing a regulatory framework to manage the trade and protect local interests.
- Best-case scenario: Meteorite hunting is regulated, providing sustainable economic benefits without environmental or social harm.
- Worst-case scenario: Unregulated hunting leads to environmental degradation and economic instability in local communities.
- Most-likely scenario: Continued growth in meteorite hunting with gradual moves towards regulation.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Mohame Benitjit – Local meteorite hunter.
Hasnaa Chennaoui Aoudjehane – Professor of meteoritics and planetary science.
Samira Mizbar – Independent socio-economist specializing in development policy.
Guy Consolmagno – American research astronomer and physicist, head of Vatican Observatory.
7. Thematic Tags
Regional Focus: Morocco, Sahara Desert, Meteorite Trade, Economic Impact, Regulatory Environment
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Regional Focus Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Methodology