Microsoft Addresses Six Actively Exploited Zero-Day Vulnerabilities Amid Urgent Security Concerns
Published on: 2026-02-13
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: News brief 6 Microsoft zero days and a warning from CISA
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
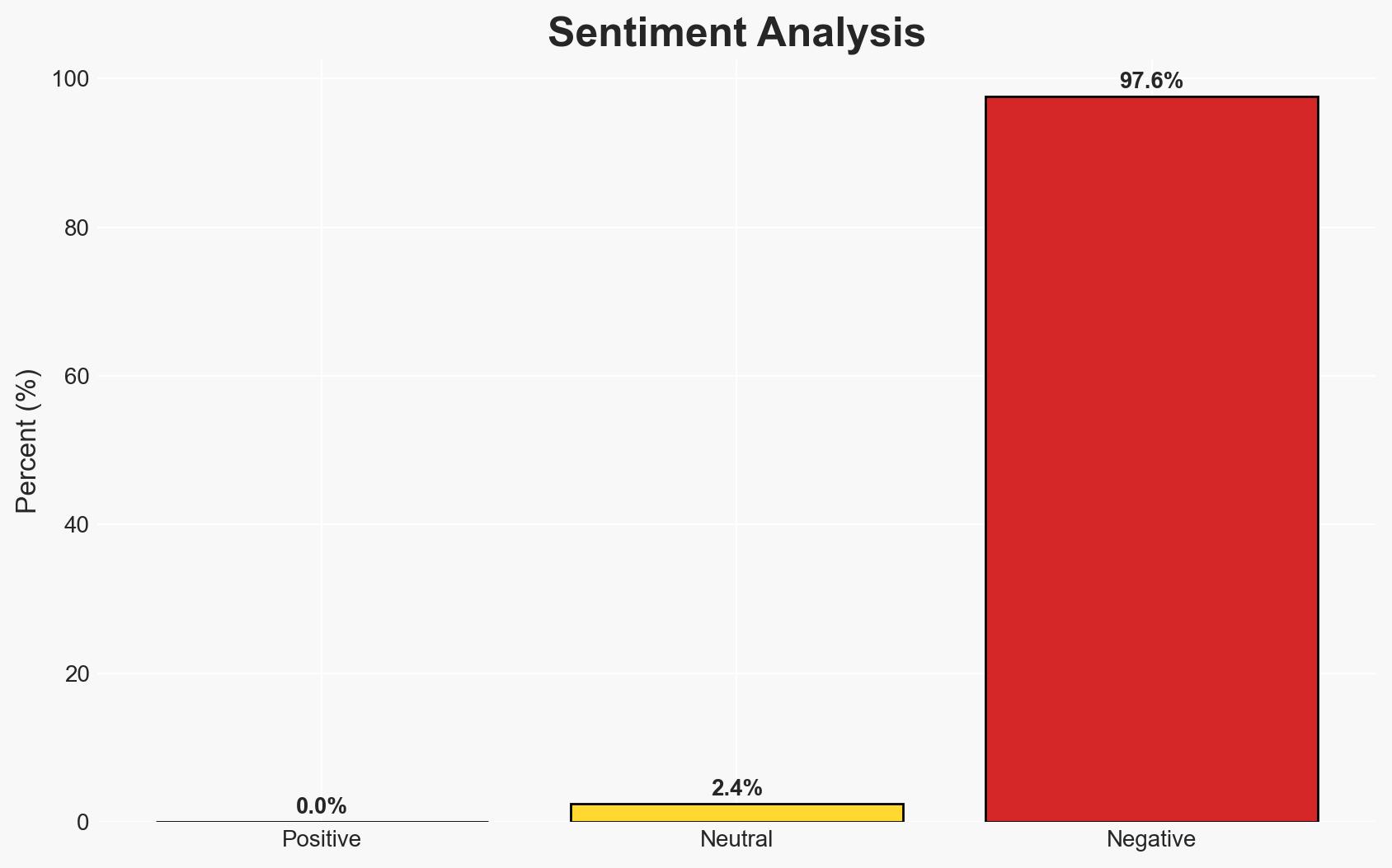
The rapid exploitation of vulnerabilities, as evidenced by the recent Microsoft zero-day patches and CISA’s directive on unsupported devices, highlights a critical need for improved patch management and infrastructure security. The primary concern is the increasing speed of cyber threats outpacing current defense measures, affecting both government and private sectors. Overall, there is moderate confidence in the assessment that immediate action is required to mitigate these risks.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The accelerated exploitation of vulnerabilities is primarily due to increased sophistication and resources of cyber threat actors. This is supported by the reduced time to exploit vulnerabilities and the active exploitation of zero days. However, the exact capabilities and motivations of these actors remain uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The primary driver of increased vulnerability exploitation is inadequate patch management and outdated infrastructure within organizations. This is supported by the average delay in patching critical vulnerabilities and the presence of unsupported devices. The hypothesis is contradicted by the possibility that even with improved management, sophisticated actors could still pose significant threats.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the documented delays in patching and the prevalence of unsupported devices, which provide easy targets for attackers. Indicators such as improved patch management practices and reduced exploitation rates could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Organizations will prioritize patch management; cyber threat actors will continue to exploit vulnerabilities rapidly; CISA’s directives will be implemented effectively.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the specific methods used by attackers to exploit vulnerabilities; comprehensive statistics on patch management practices across sectors.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from cybersecurity firms with vested interests; risk of underestimating the capabilities of threat actors due to lack of visibility into their operations.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ongoing developments in cyber threats and infrastructure vulnerabilities could lead to significant disruptions if not addressed, with potential cascading effects across multiple domains.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased tensions between nations, especially if state-sponsored actors are implicated in cyberattacks.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of cyberattacks on critical infrastructure, potentially affecting national security.
- Cyber / Information Space: Escalation in cyber warfare tactics and increased focus on cybersecurity measures.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic losses from disrupted operations and increased costs for cybersecurity enhancements.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Implement urgent patch management protocols, conduct audits of infrastructure for unsupported devices, and enhance monitoring of cyber threats.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for information sharing, invest in cybersecurity training, and establish robust incident response plans.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid improvement in patch management reduces exploitation rates.
- Worst: Major cyberattack on critical infrastructure due to unpatched vulnerabilities.
- Most-Likely: Continued pressure on organizations to balance patch management with operational demands.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Microsoft
- CISA
- Flashpoint
- Berserk Bear
- Sandworm
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
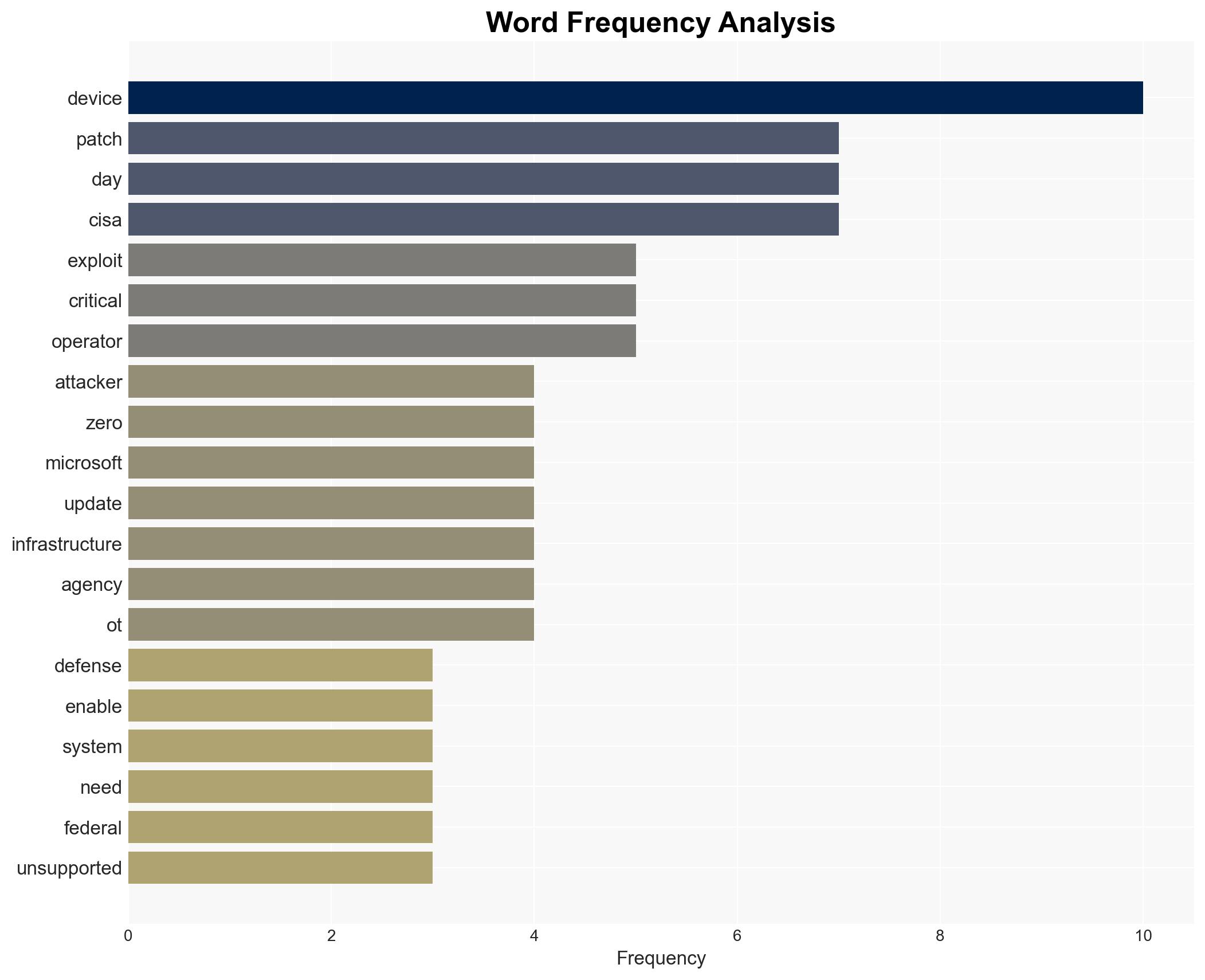
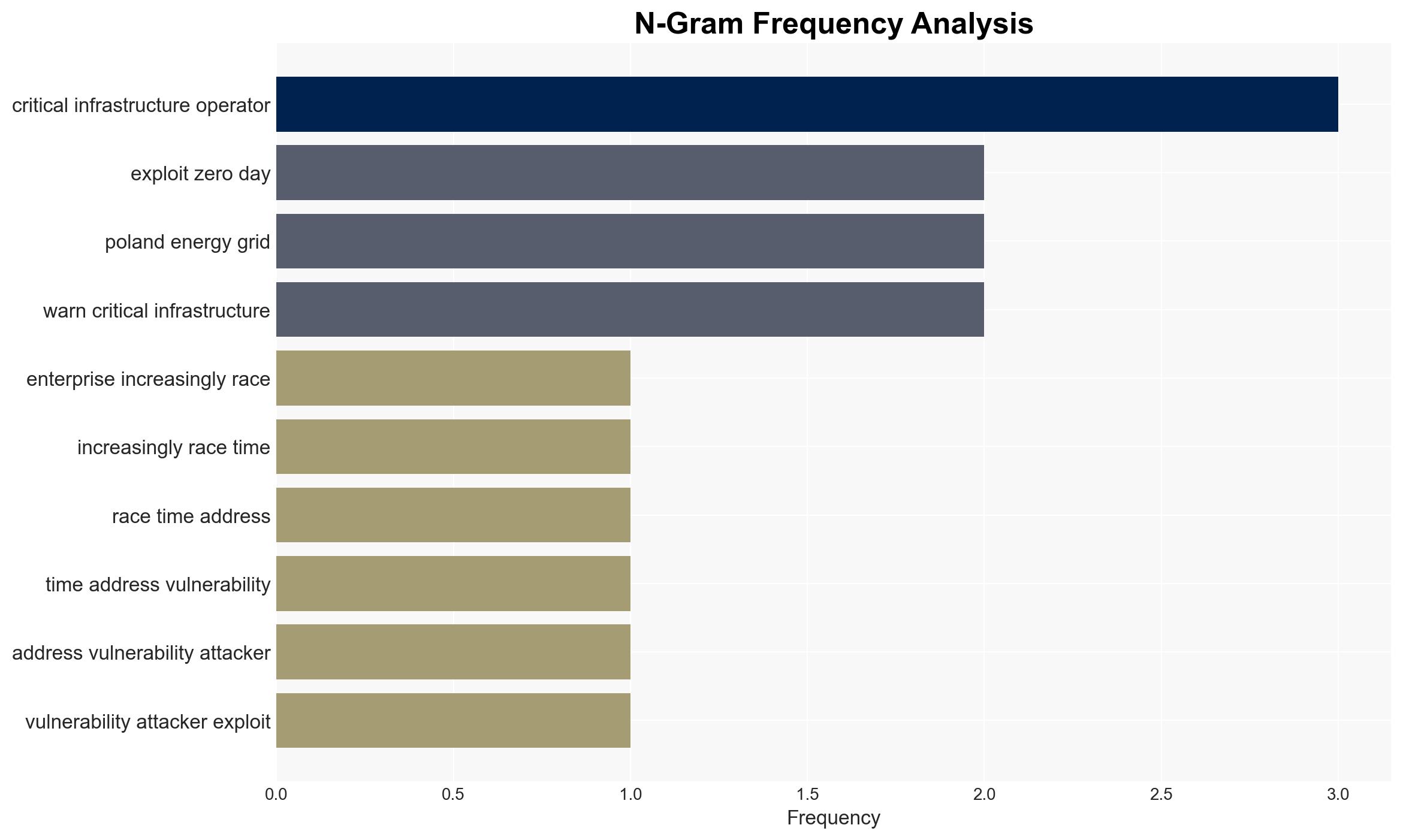
cybersecurity, patch management, zero-day vulnerabilities, critical infrastructure, cyber threats, national security, CISA directives
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us