Microsoft alerts that infostealer malware is increasingly targeting macOS alongside traditional Windows threa…
Published on: 2026-02-04
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Microsoft warns infostealer malware is ‘rapidly expanding beyond traditional Windows-focused campaigns’ and targeting Mac devices
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
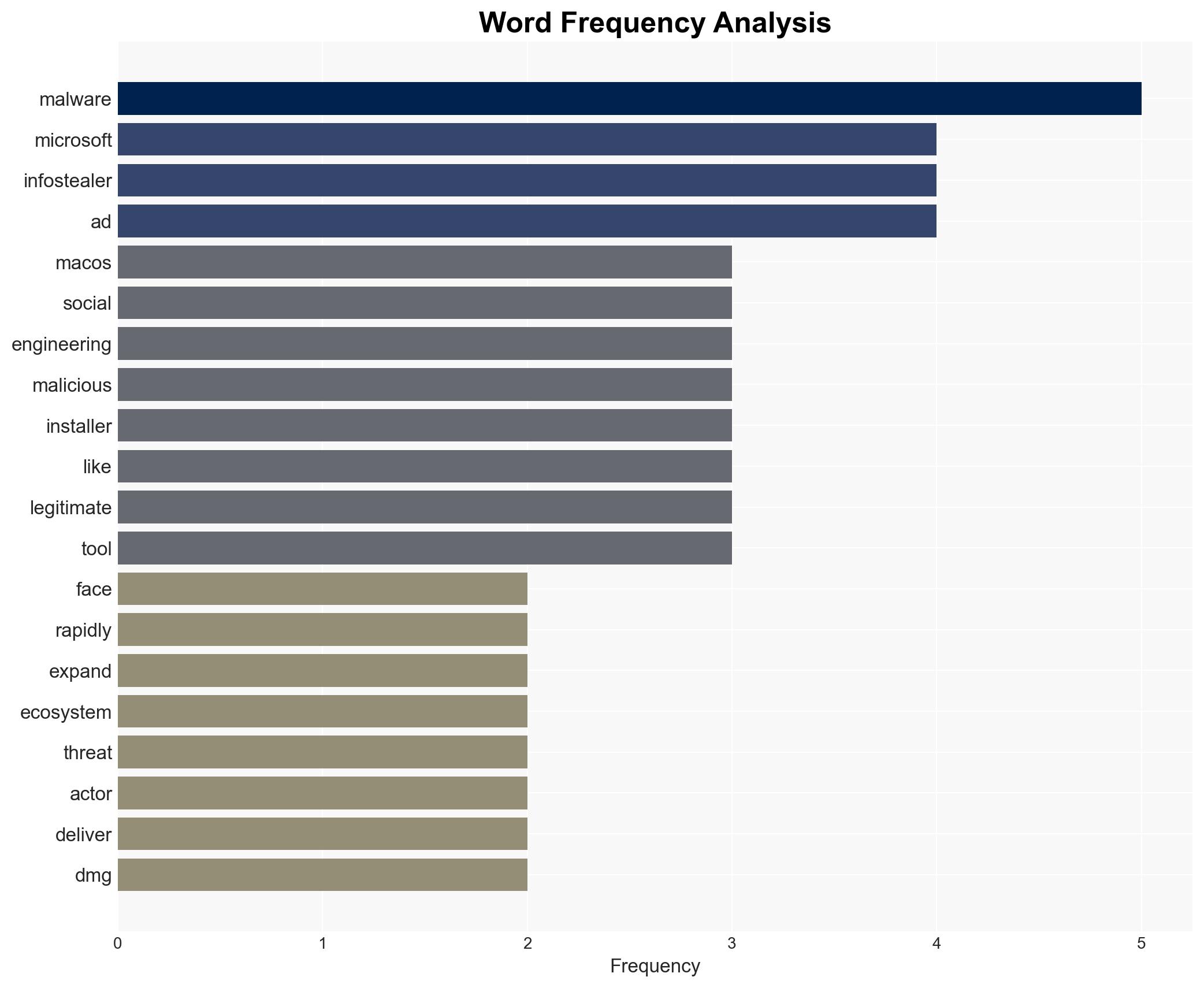
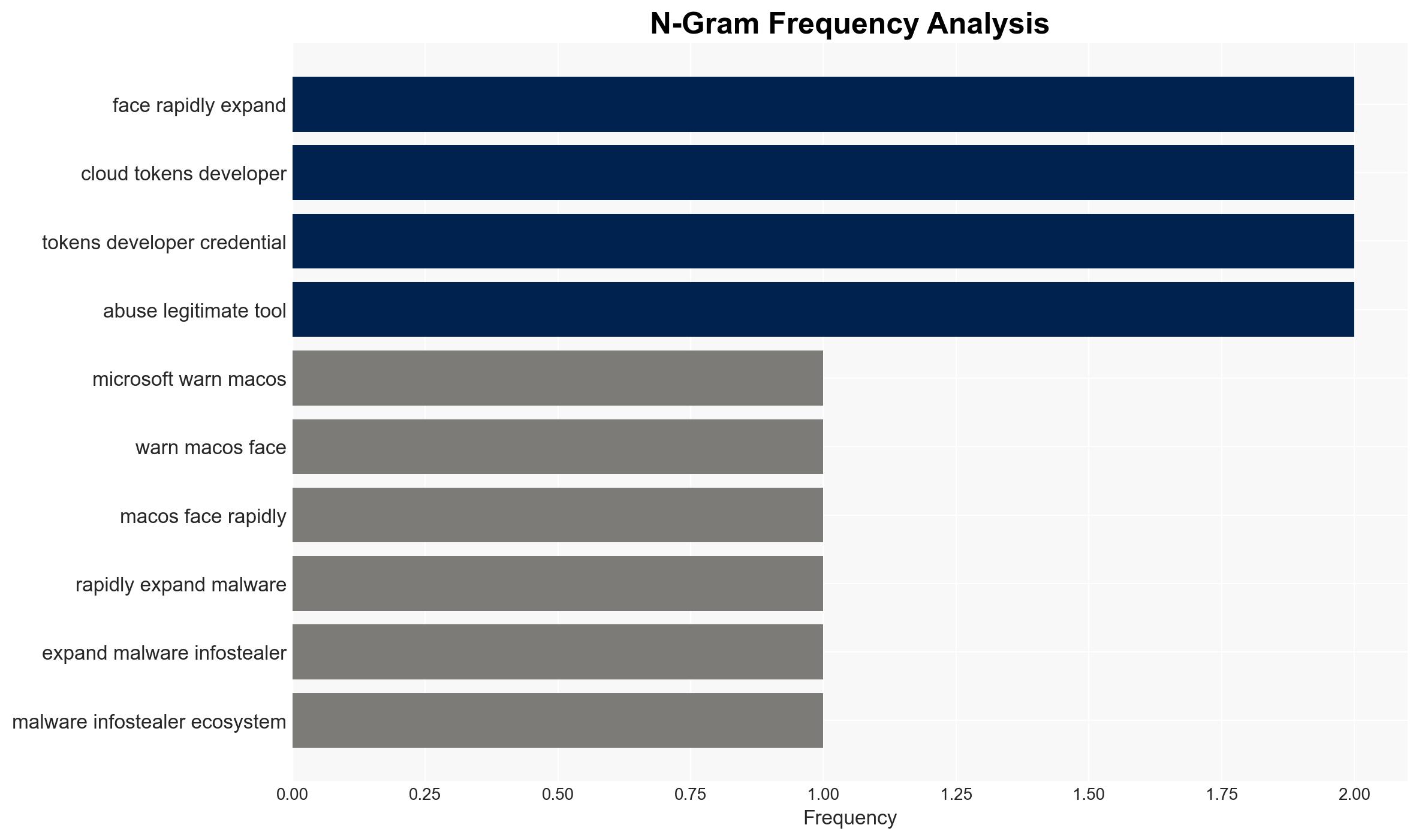
The threat landscape for macOS users is evolving, with a rapidly expanding ecosystem of malware, particularly infostealers, now targeting Mac devices. This shift is facilitated by social engineering tactics and the abuse of legitimate tools. The most likely hypothesis is that threat actors are diversifying their targets to exploit less defended systems. This assessment is made with moderate confidence due to the reliance on reported observations from a single source.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Threat actors are expanding their focus to macOS due to increased market share and perceived vulnerabilities. Supporting evidence includes the use of social engineering and cross-platform malware. Contradicting evidence is limited, but the extent of macOS vulnerabilities remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The observed increase in macOS-targeted malware is a temporary trend driven by opportunistic actors rather than a strategic shift. This is supported by the historical focus on Windows systems and the potential for over-reporting by security vendors. However, the sustained use of advanced tactics suggests a more deliberate approach.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the documented use of sophisticated techniques and the strategic targeting of sensitive data. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include increased reporting of similar campaigns or a significant rise in macOS market share.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: macOS market share is increasing; threat actors are motivated by financial gain; cross-platform malware development is feasible and effective.
- Information Gaps: Detailed statistics on macOS market penetration; comprehensive data on the success rate of these attacks; independent verification of reported tactics.
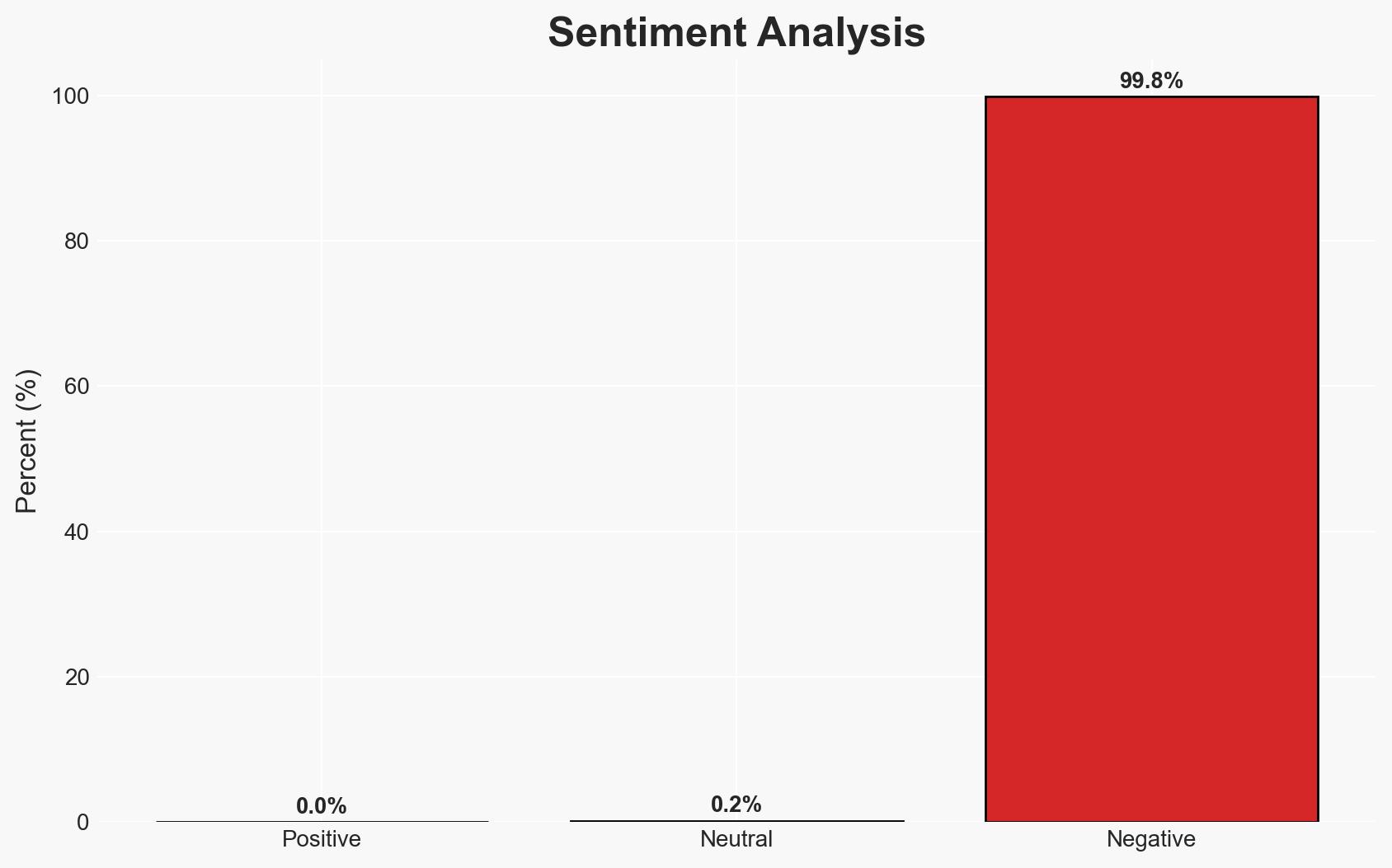
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from Microsoft as a security vendor; risk of overemphasizing macOS threats due to recent high-profile incidents.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The expansion of malware targeting macOS could lead to broader security challenges, impacting both individual users and enterprises. This development may influence threat actor strategies and the cybersecurity landscape.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased cyber threats could strain international relations if state actors are implicated.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced threat environment necessitating improved defenses and intelligence sharing.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber espionage and data breaches, affecting information integrity.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact from data breaches and increased cybersecurity costs; erosion of trust in digital platforms.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of macOS systems, implement recommended mitigations, and conduct awareness campaigns on social engineering tactics.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop cross-platform cybersecurity capabilities, foster public-private partnerships, and invest in threat intelligence sharing.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Rapid adaptation of defenses mitigates threats; Worst: Significant data breaches occur, impacting critical infrastructure; Most-Likely: Continued diversification of malware targets with moderate impact.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, macOS, infostealer malware, social engineering, cross-platform threats, data breaches, cyber defense
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us