Microsoft Disrupts RedVDS, a Cybercrime Subscription Service Linked to Millions in Fraud Losses
Published on: 2026-01-14
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Criminal Subscription Service Behind AI-Powered Cyber-Attacks Taken Out By Microsoft
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
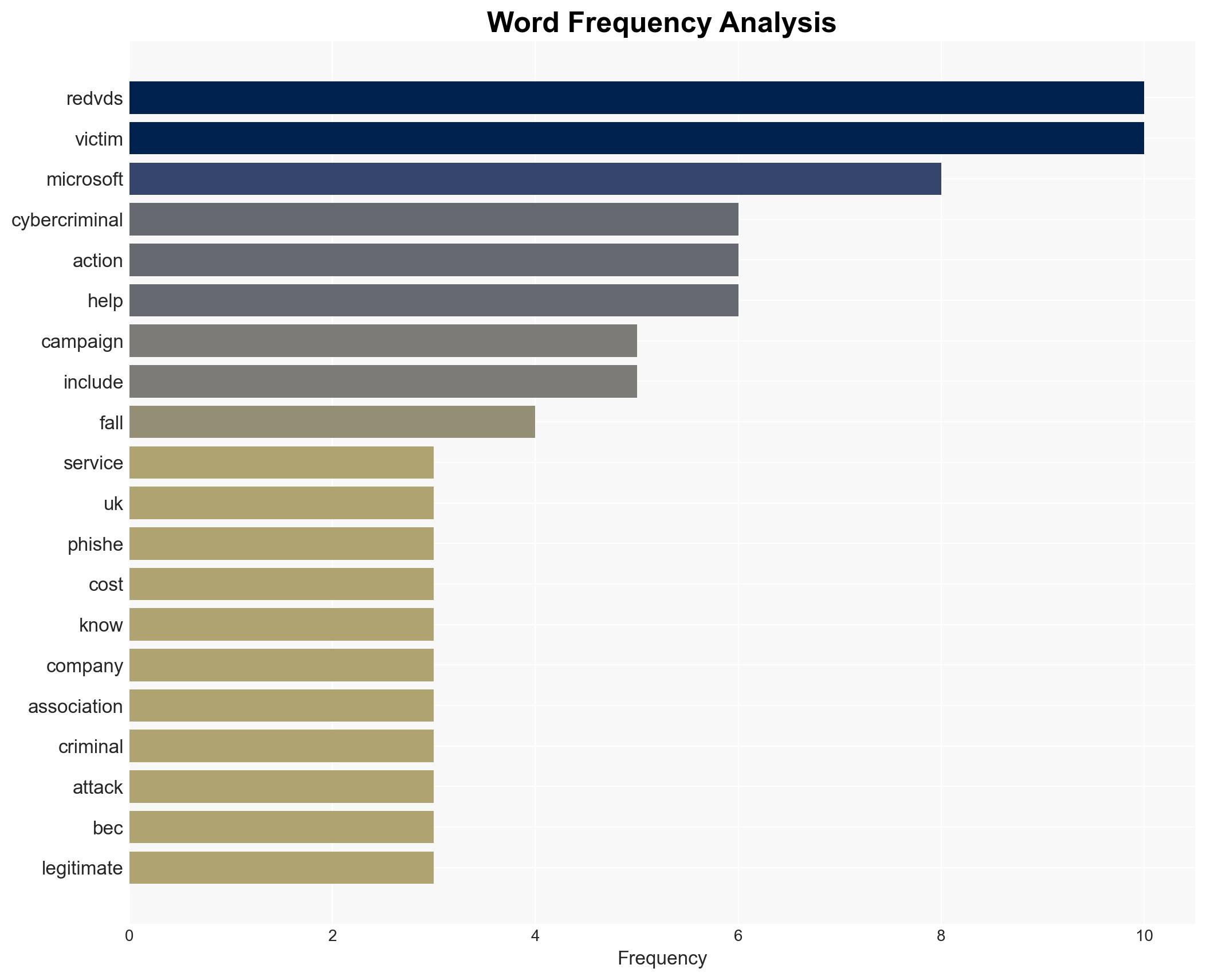
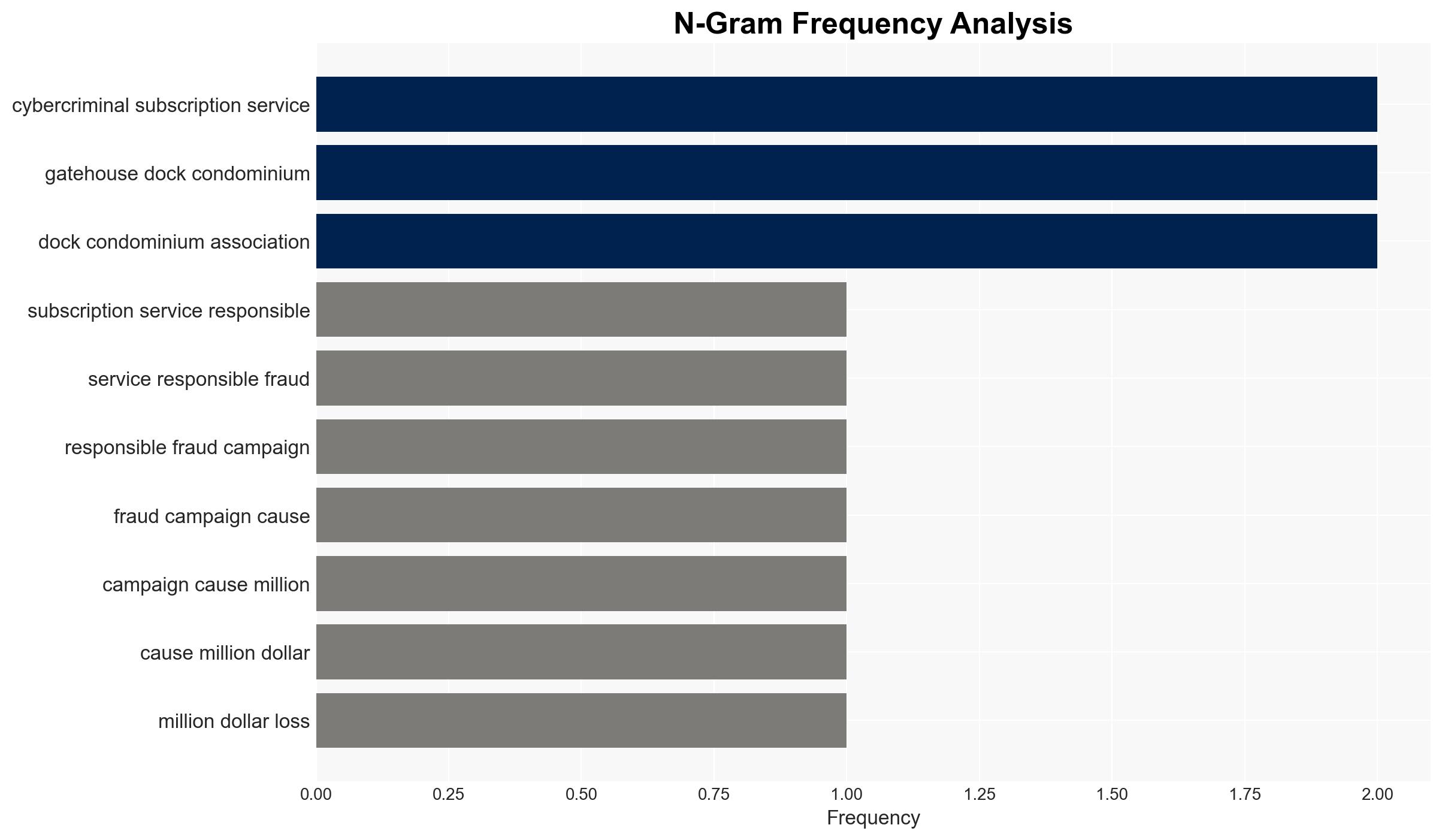
Microsoft, in collaboration with legal partners in the US and UK, has disrupted RedVDS, a cybercriminal subscription service responsible for significant financial losses through AI-powered cyber-attacks. The takedown impacts numerous organizations globally, particularly in the US, Canada, and the UK. The most likely hypothesis is that this disruption will temporarily reduce the operational capacity of similar cybercriminal networks. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The disruption of RedVDS will significantly weaken cybercriminal activities in the short term. Supporting evidence includes the seizure of critical infrastructure and legal actions. However, uncertainties remain about the ability of cybercriminals to quickly adapt and migrate to alternative platforms.
- Hypothesis B: The disruption will have minimal long-term impact as cybercriminals will quickly adapt by using alternative services or creating new platforms. This is supported by the low barriers to entry in cybercrime and the availability of similar services. Contradicting evidence includes the coordinated international legal actions that may deter similar operations.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the immediate impact of the infrastructure seizure and legal actions. Indicators that could shift this judgment include the emergence of new platforms or services replicating RedVDS’s capabilities.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The legal and technical actions taken will prevent RedVDS from quickly resuming operations; cybercriminals will face challenges in finding equivalent platforms; international cooperation will continue to disrupt similar services.
- Information Gaps: Details on the full extent of RedVDS’s network and potential undiscovered infrastructure; the resilience and adaptability of the cybercriminal community; the effectiveness of legal deterrents.
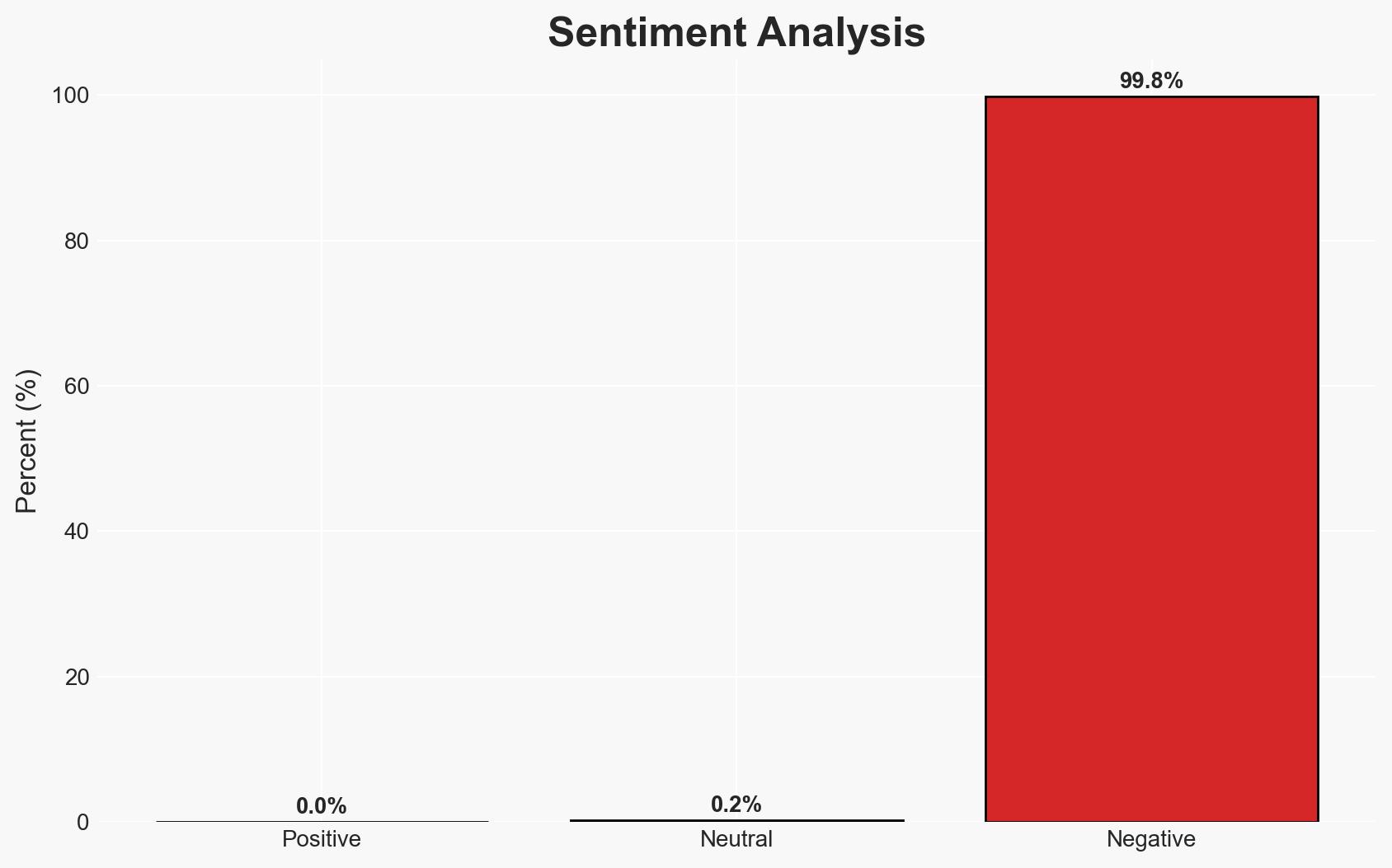
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on Microsoft’s narrative; underestimation of cybercriminal adaptability; possible misinformation from cybercriminals to obscure their operational capabilities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The disruption of RedVDS could lead to shifts in cybercriminal tactics and the emergence of new platforms. The broader dynamics of cybercrime may evolve, influencing international cybersecurity policies and cooperation.
- Political / Geopolitical: Strengthened international cooperation against cybercrime could lead to enhanced diplomatic relations and joint cybersecurity initiatives.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Temporary reduction in cybercriminal activity may allow security agencies to focus on other threats, but could also lead to increased sophistication in future attacks.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased innovation in cybercriminal tactics and technologies, including the use of AI and deepfakes.
- Economic / Social: Reduced immediate financial losses for targeted organizations, but potential long-term economic impacts if cybercriminals adapt effectively.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of cybercriminal forums for signs of adaptation; strengthen cybersecurity measures in vulnerable sectors; continue international legal and technical cooperation.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for organizations; invest in AI-driven cybersecurity tools; foster public-private partnerships to share threat intelligence.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Sustained disruption leads to a significant decline in cybercrime activities.
- Worst: Cybercriminals quickly adapt, leading to more sophisticated and damaging attacks.
- Most-Likely: Temporary reduction in activity with gradual adaptation by cybercriminals.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Microsoft
- RedVDS
- H2-Pharma
- Gatehouse Dock Condominium Association
- Europol
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, cybercrime, AI-powered attacks, international cooperation, phishing, business email compromise, legal action
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us