Microsoft fixed 100 security flaws in Windows and Office this month – PCWorld
Published on: 2025-08-13
Intelligence Report: Microsoft fixed 100 security flaws in Windows and Office this month – PCWorld
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
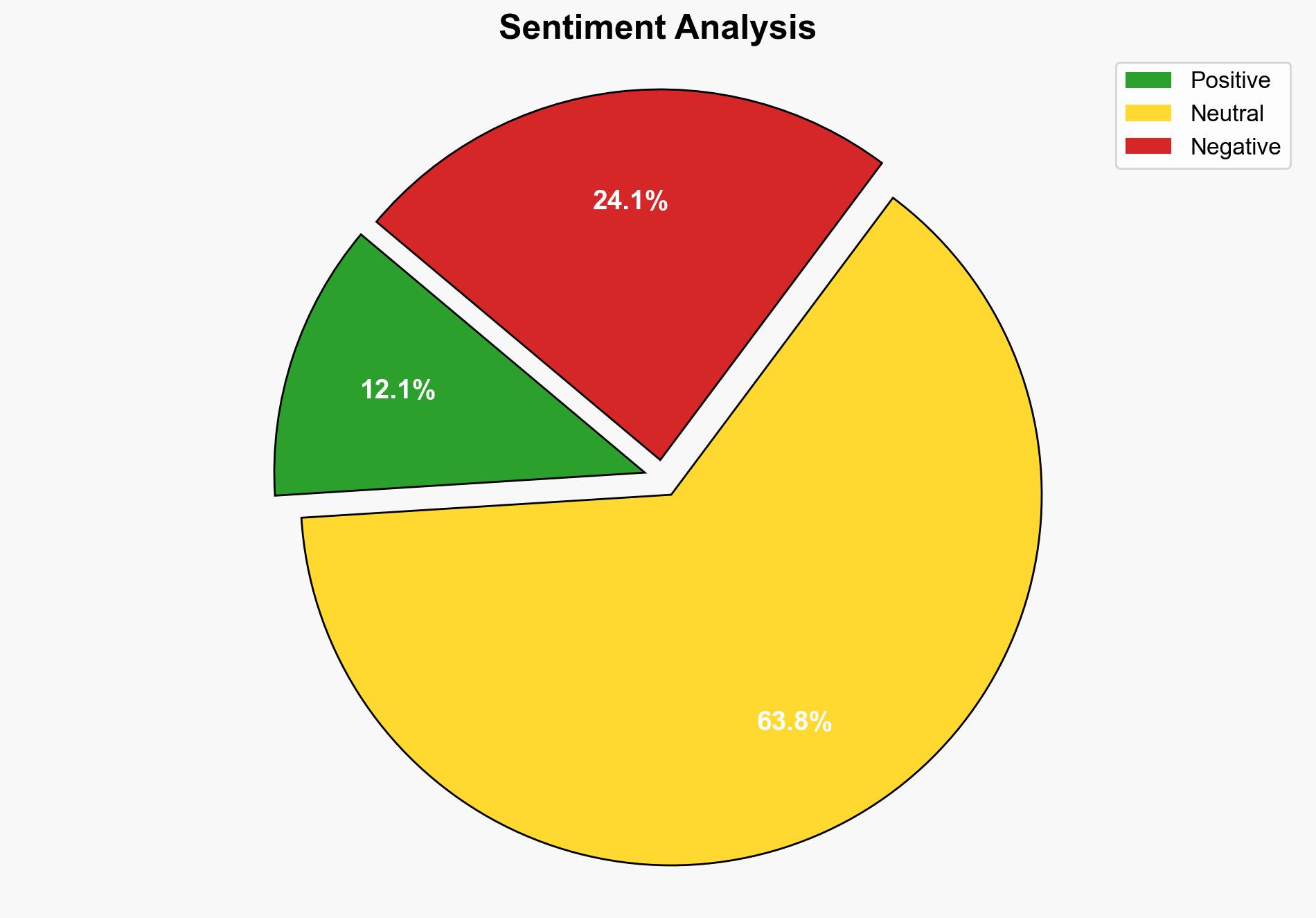
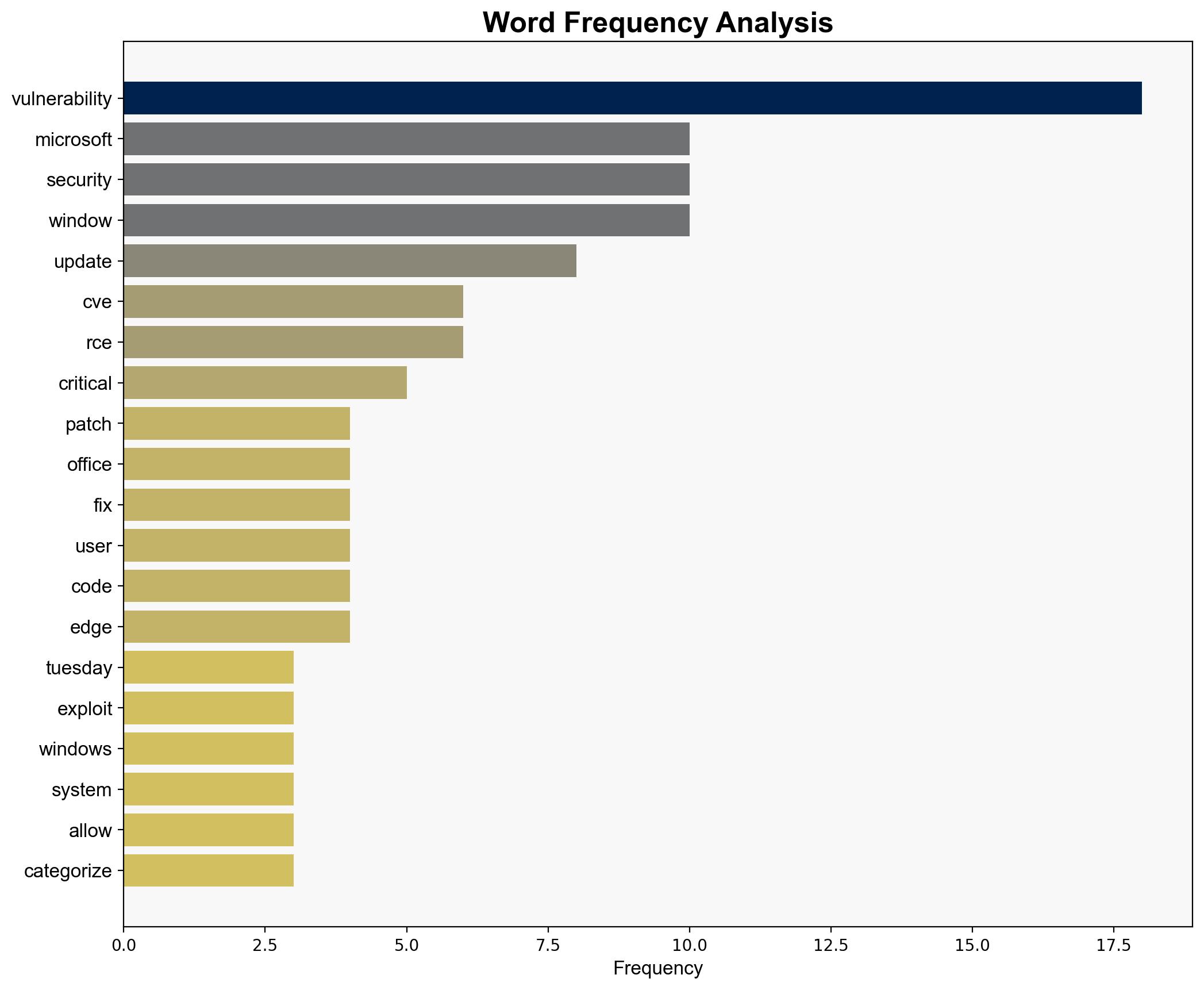
Microsoft’s recent patching of 100 security vulnerabilities in Windows and Office highlights significant cybersecurity risks. The most supported hypothesis is that Microsoft is proactively addressing vulnerabilities to prevent potential exploitation, with a moderate confidence level. It is recommended that organizations prioritize updating their systems to mitigate risks associated with these vulnerabilities.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Proactive Security Enhancement Hypothesis**: Microsoft is actively identifying and patching vulnerabilities to enhance security and protect users from potential cyber threats.
2. **Reactive Damage Control Hypothesis**: The patching is a response to known exploits or breaches, indicating that some vulnerabilities may have already been exploited, necessitating urgent fixes.
Using ACH 2.0, the proactive hypothesis is better supported due to the structured and regular nature of Microsoft’s Patch Tuesday updates, suggesting a systematic approach to vulnerability management rather than a reaction to specific incidents.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: It is assumed that Microsoft has identified all critical vulnerabilities and that the patches are effective in mitigating risks.
– **Red Flags**: The report does not specify if any vulnerabilities were exploited before patching, which could indicate potential underreporting or lack of transparency.
– **Blind Spots**: There is limited information on the effectiveness of the patches and whether they have been universally adopted by users.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The large number of vulnerabilities patched suggests a persistent risk environment for Windows and Office users. Failure to update systems could lead to increased cyber threats, including data breaches and system compromises. The economic impact of potential exploits could be significant, affecting both individual users and enterprises. Geopolitically, vulnerabilities in widely-used software could be leveraged by state actors for cyber espionage.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Organizations should immediately apply the latest patches to all systems to mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Conduct regular cybersecurity audits to ensure all systems are up-to-date and secure.
- Scenario Projections:
- Best Case: All users apply patches promptly, significantly reducing the risk of exploitation.
- Worst Case: Delays in patch application lead to widespread exploitation and data breaches.
- Most Likely: A majority of users update systems, but some vulnerabilities remain unpatched, posing ongoing risks.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Microsoft Corporation
– Users of Windows and Office products
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, software vulnerabilities, proactive security measures