Microsoft Unveils New Proactive Incident Response Services to Boost Cyber Resilience
Published on: 2026-01-07
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Explore the latest Microsoft Incident Response proactive services for enhanced resilience
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
Microsoft’s introduction of new proactive incident response services aims to enhance organizational resilience against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. This initiative is likely to improve preparedness and reduce the impact of cyber incidents for organizations utilizing these services. The most likely hypothesis is that these services will lead to a measurable decrease in successful cyberattacks on participating organizations. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Microsoft’s proactive services will significantly enhance organizational resilience, leading to a reduction in successful cyberattacks. This is supported by the company’s extensive experience in handling complex cyber incidents and the comprehensive nature of the services offered. However, the effectiveness may vary based on the organization’s existing cybersecurity posture and resource allocation.
- Hypothesis B: The impact of Microsoft’s proactive services will be limited, with minimal reduction in successful cyberattacks. This could be due to potential over-reliance on external services, insufficient integration with existing systems, or the evolving nature of cyber threats that outpace these measures. Contradicting evidence includes Microsoft’s track record and the detailed, hands-on approach of the services.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to Microsoft’s established expertise and the structured approach of the services. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include reports of significant breaches in organizations using these services or feedback indicating integration challenges.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Organizations will effectively implement Microsoft’s recommendations; cyber threats will not evolve beyond the capabilities of these services; Microsoft will maintain its current level of expertise and service quality.
- Information Gaps: Specific metrics on the success rate of these services in preventing incidents; detailed feedback from organizations currently using these services.
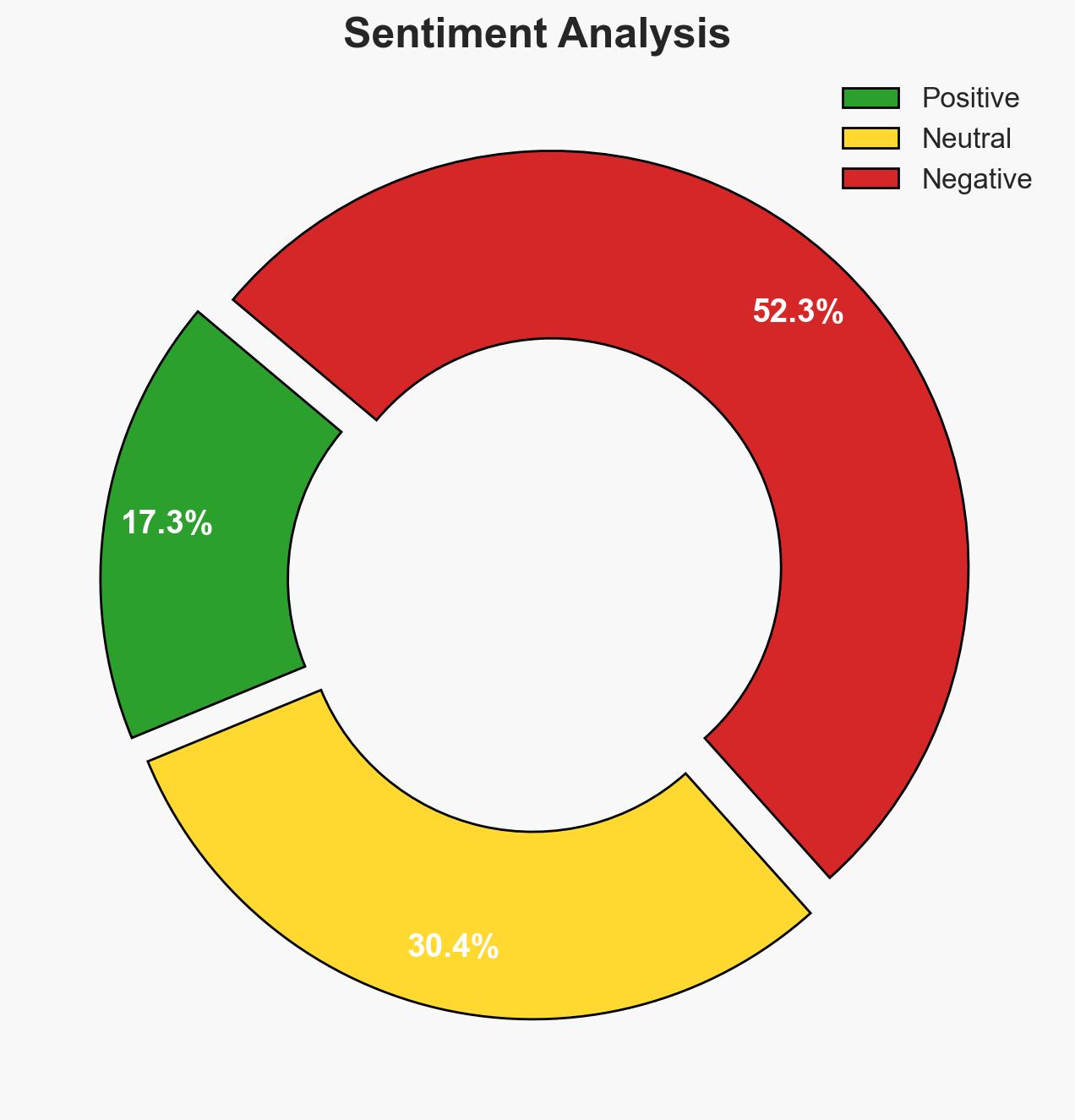
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in Microsoft’s self-reported success metrics; lack of independent verification of service effectiveness; marketing language may obscure limitations.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The introduction of these services could lead to a shift in how organizations approach cybersecurity, prioritizing resilience and proactive measures. This development may influence industry standards and expectations for cybersecurity preparedness.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased resilience in critical sectors could reduce the impact of state-sponsored cyberattacks, potentially altering geopolitical cyber strategies.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced incident response capabilities may deter cyber-terrorism by increasing the cost and complexity of executing successful attacks.
- Cyber / Information Space: The services may set a new benchmark for cybersecurity practices, influencing other providers to adopt similar proactive measures.
- Economic / Social: Improved cybersecurity resilience could bolster economic stability by reducing the frequency and severity of disruptions caused by cyber incidents.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor feedback and case studies from early adopters of Microsoft’s services; assess integration compatibility with existing systems.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with Microsoft for tailored incident response planning; invest in training for security teams to maximize service benefits.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Significant reduction in successful cyberattacks, leading to widespread adoption and improved industry standards.
- Worst: Limited impact due to integration challenges or evolving threats, resulting in continued vulnerability.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in resilience with varying success across different sectors, contingent on implementation quality.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
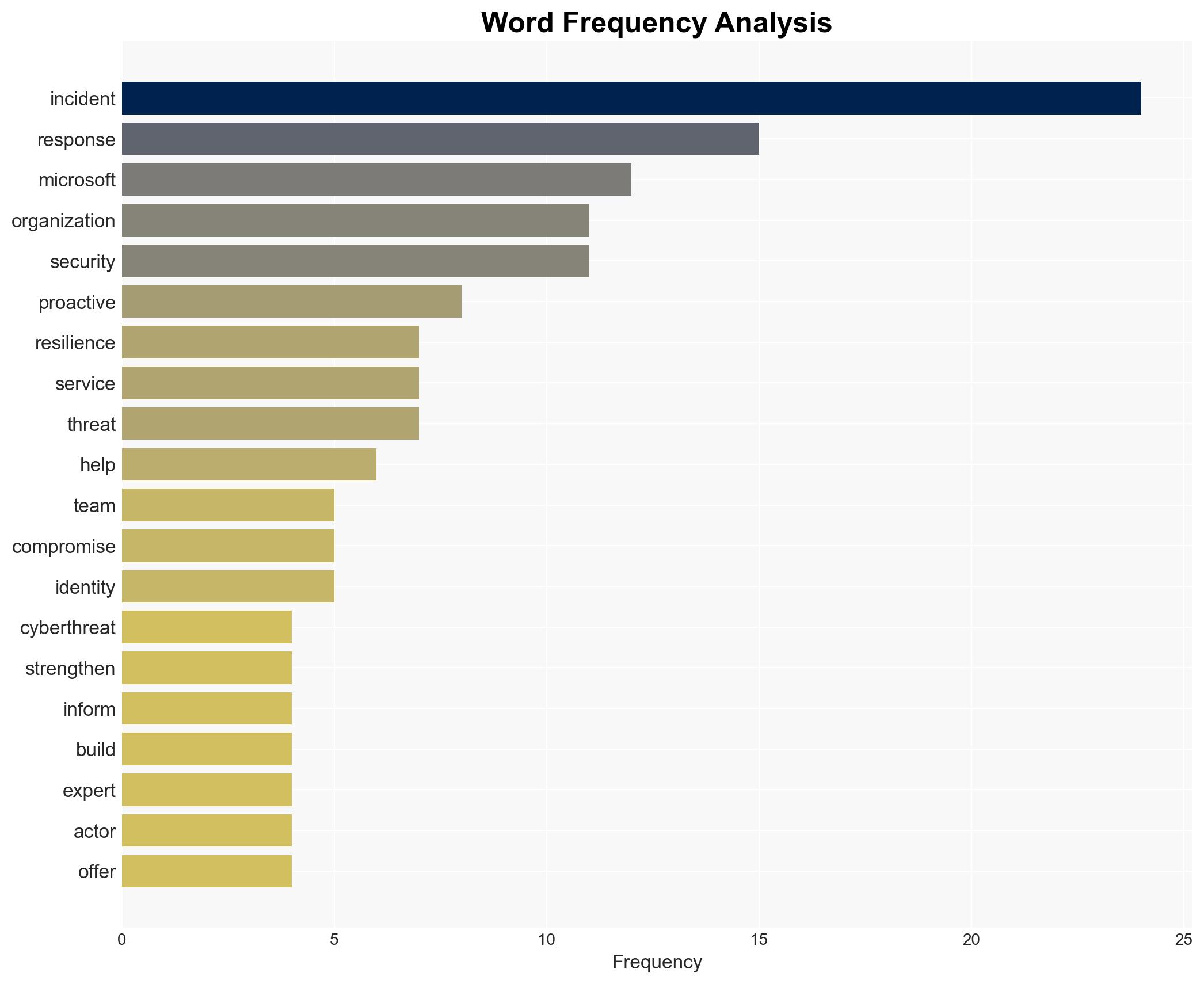
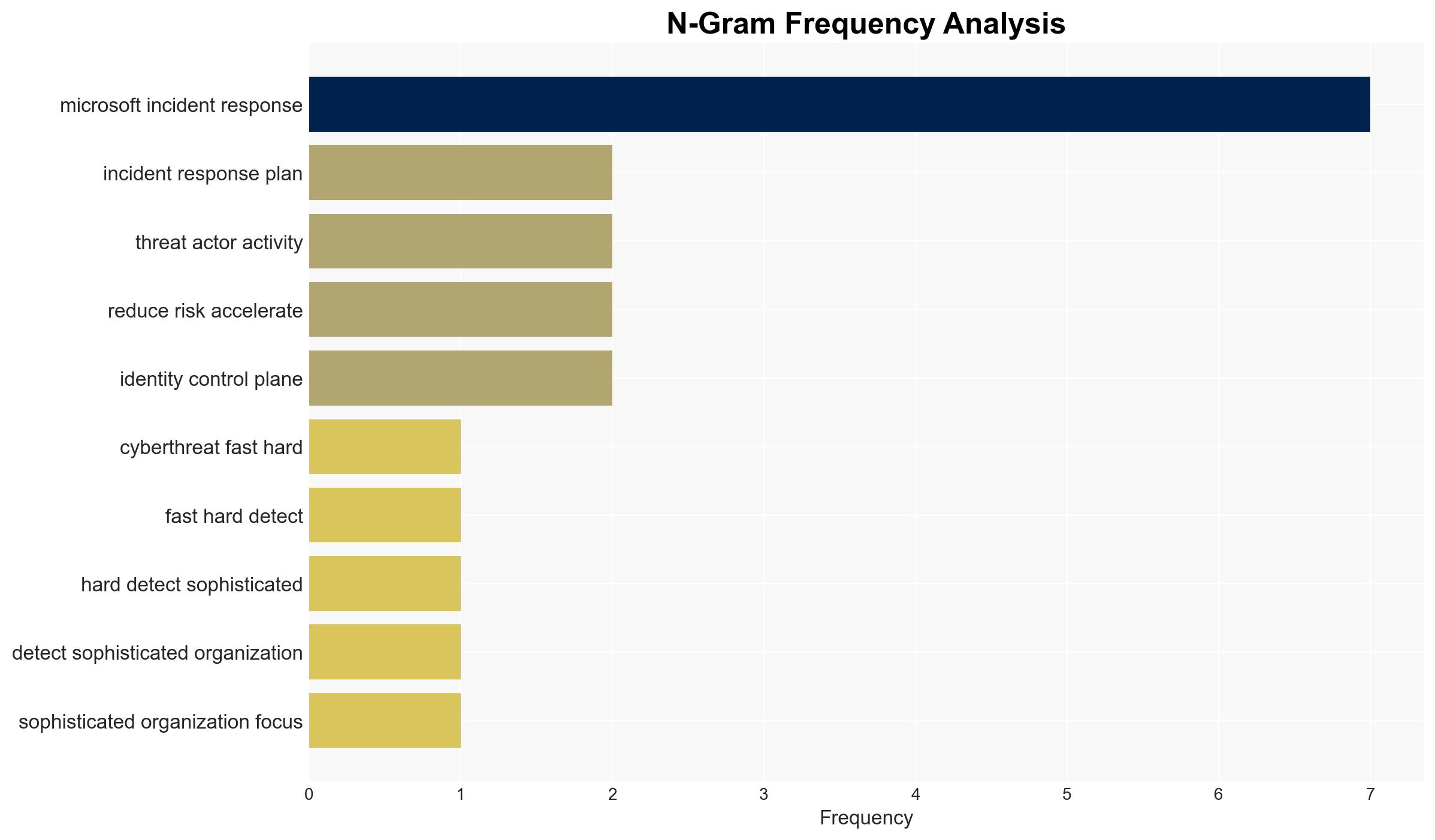
cybersecurity, incident response, resilience, Microsoft, proactive services, cyber threats, organizational preparedness
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us