Microsoft’s new AI security tool can spot malware early – and even reverse engineer it to crack the code – TechRadar
Published on: 2025-08-06
Intelligence Report: Microsoft’s new AI security tool can spot malware early – and even reverse engineer it to crack the code – TechRadar
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
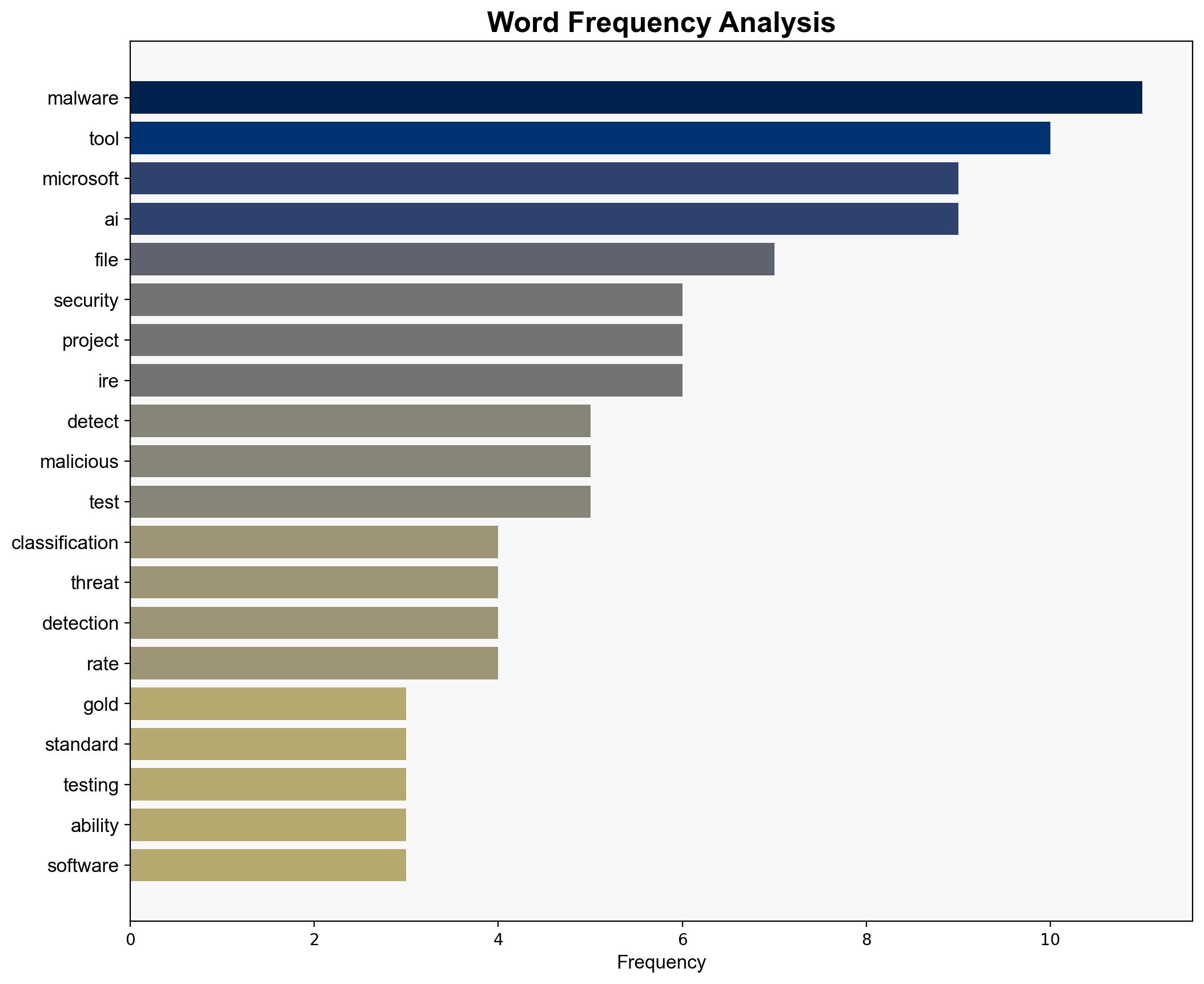
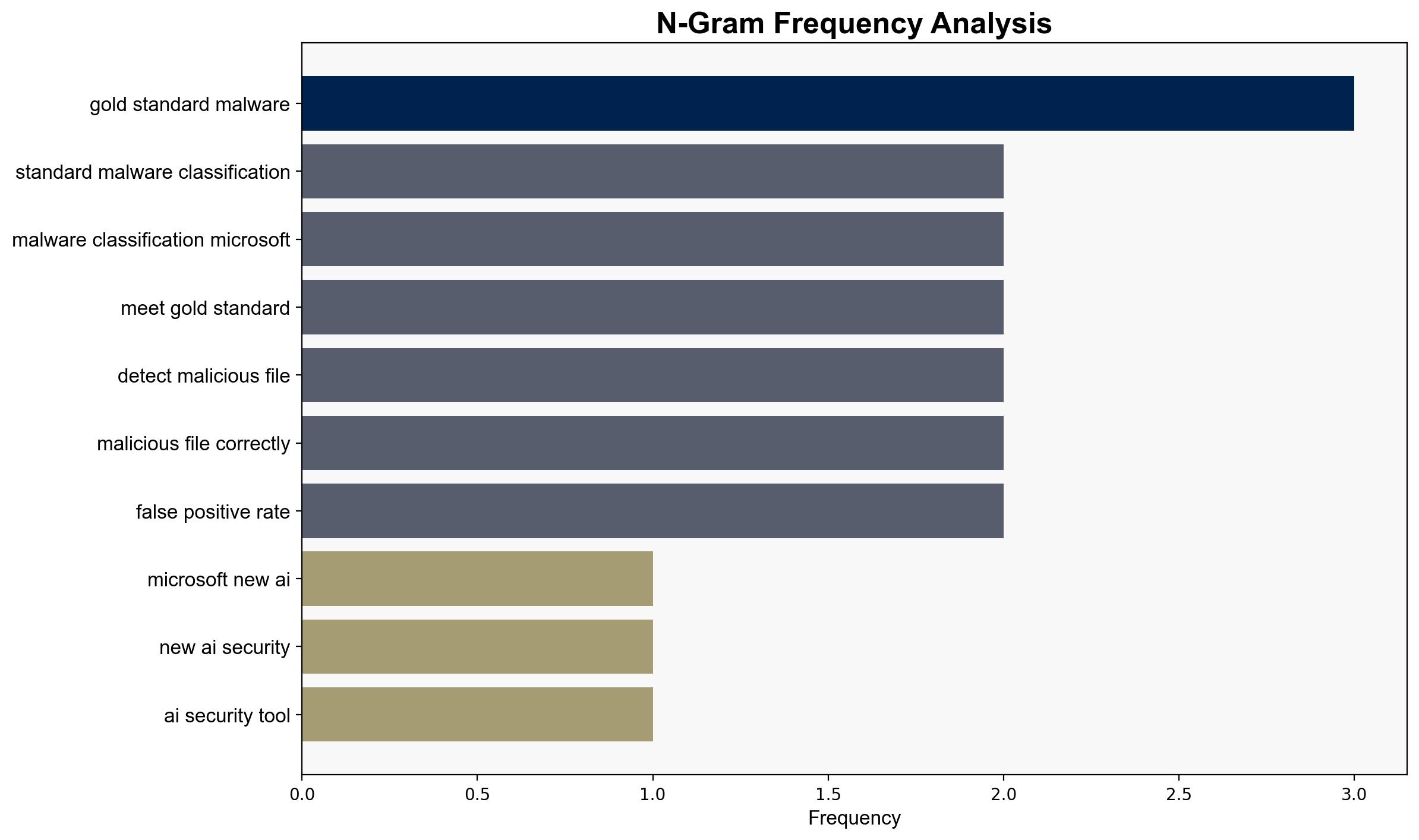
Microsoft’s development of Project IRE, an AI-based malware detection tool, shows potential to significantly enhance cybersecurity capabilities by accurately identifying and reverse engineering malware. The most supported hypothesis is that Project IRE will be successfully integrated into Microsoft’s Defender suite, enhancing its competitive edge in cybersecurity. Confidence level: Moderate. Recommended action: Monitor Project IRE’s development and testing phases closely to assess its real-world efficacy and potential market impact.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis A**: Project IRE will achieve high accuracy and low false positive rates, leading to successful integration into Microsoft’s Defender suite, thereby setting a new standard in AI-driven cybersecurity tools.
2. **Hypothesis B**: Project IRE will face significant challenges in real-world application, such as high false positive rates or inability to adapt to evolving malware, limiting its effectiveness and delaying integration.
Using ACH 2.0, Hypothesis A is better supported due to Microsoft’s track record in AI development and the promising initial test results indicating high precision and low error rates.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: It is assumed that initial test results are indicative of real-world performance. There is an assumption that Microsoft can maintain its development pace and address any emerging challenges.
– **Red Flags**: Lack of detailed data on real-world testing scenarios and potential over-reliance on initial test results. Absence of competitor analysis and potential market reactions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
Successful deployment of Project IRE could redefine cybersecurity standards, pressuring competitors to enhance their offerings. However, if the tool underperforms, it could lead to reputational damage and financial losses for Microsoft. The integration of AI in cybersecurity also raises concerns about adversaries developing countermeasures, leading to an AI arms race in malware development and detection.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Conduct thorough real-world testing to validate Project IRE’s effectiveness and address any identified weaknesses.
- Engage in strategic partnerships with cybersecurity firms to enhance tool capabilities and market reach.
- Scenario-based projections:
- Best Case: Project IRE sets a new industry standard, leading to increased market share and enhanced cybersecurity.
- Worst Case: Tool fails to perform as expected, resulting in financial and reputational damage.
- Most Likely: Gradual integration with iterative improvements, maintaining competitive parity.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Microsoft
– TechRadar (source of the report)
7. Thematic Tags
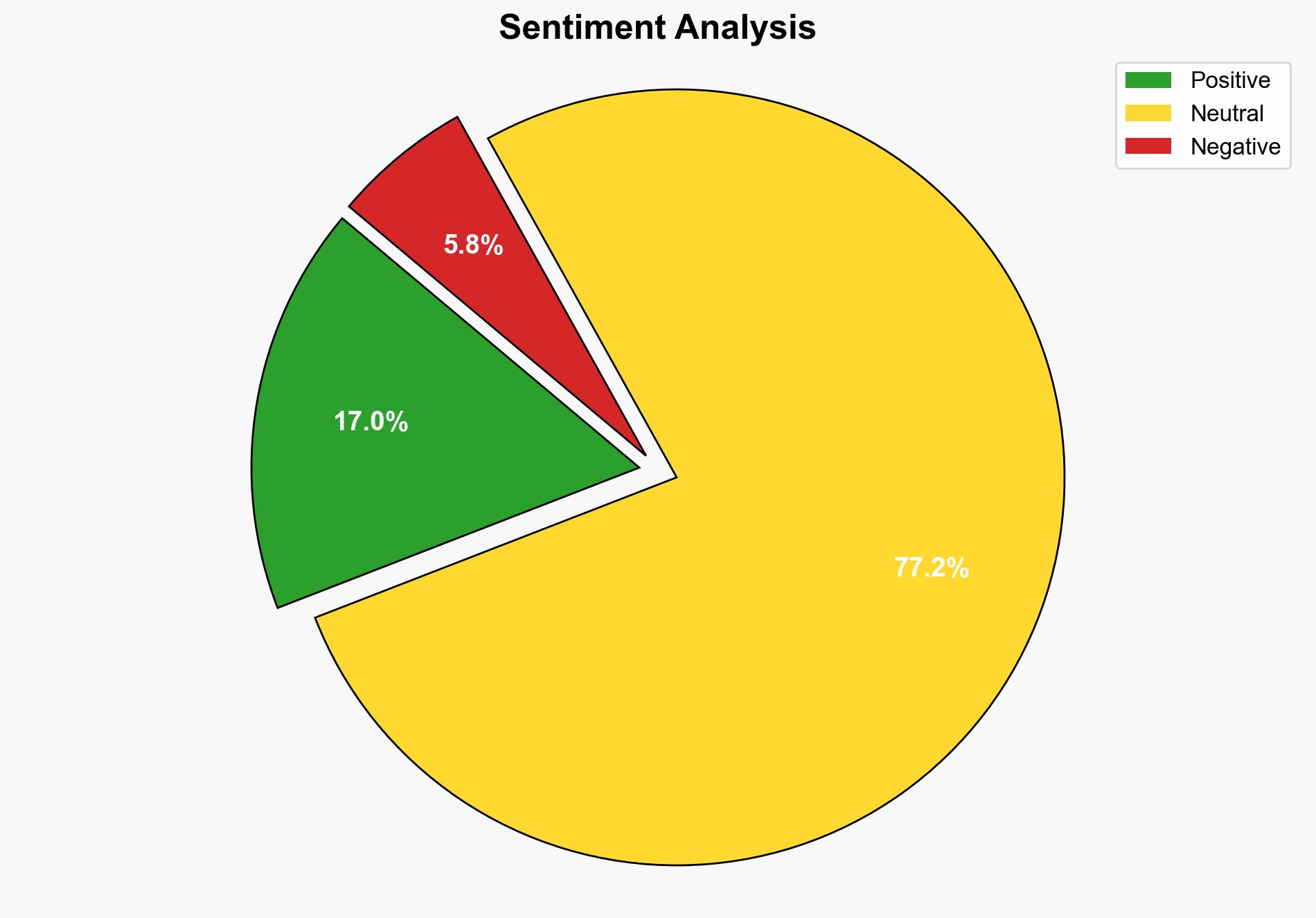
national security threats, cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, regional focus