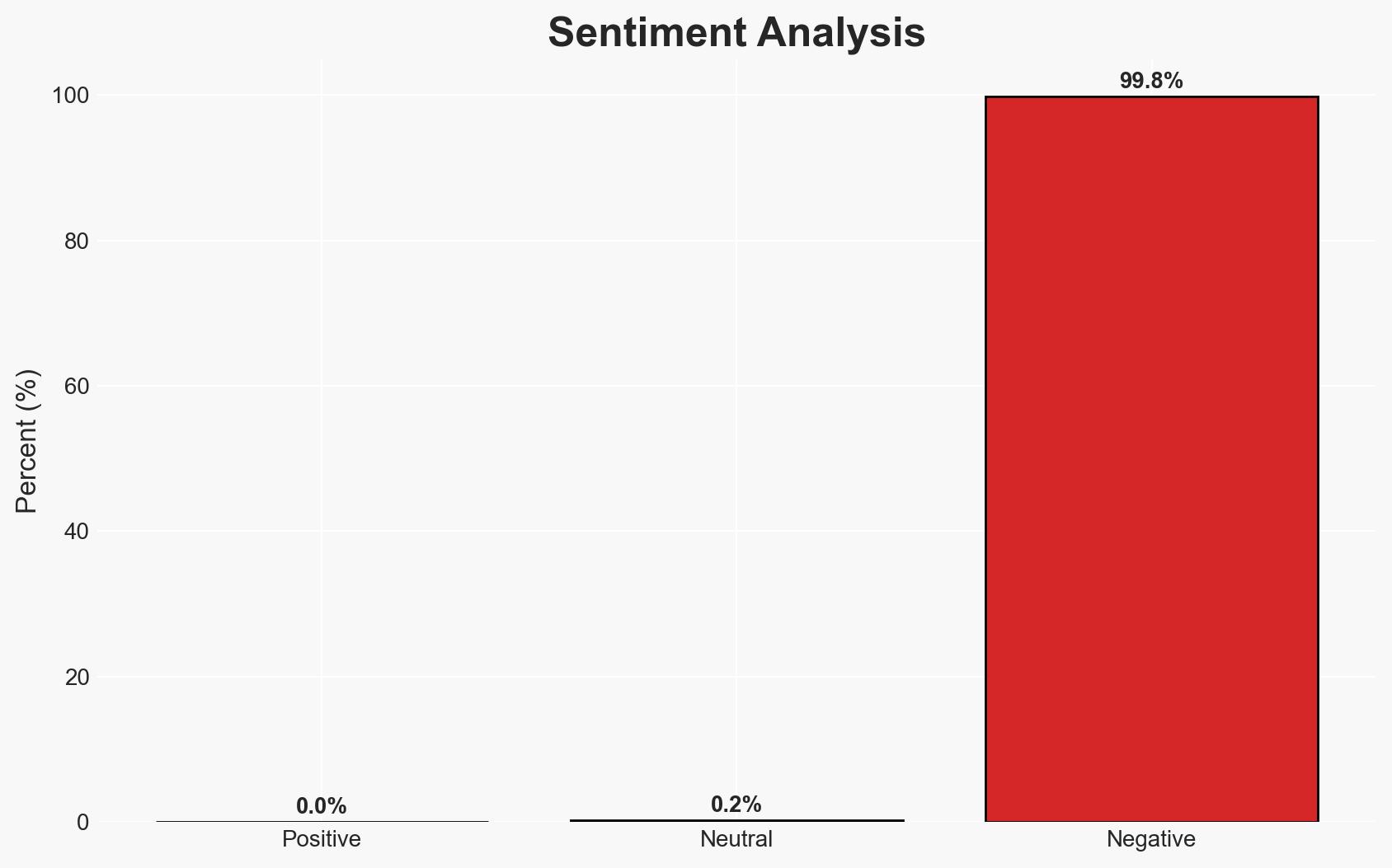
Militant Organizations Increasingly Utilize AI, Heightening Security Threats and Recruitment Potential
Published on: 2025-12-15
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Militant groups are experimenting with AI and the risks are expected to grow
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
Militant groups are increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance recruitment, propaganda, and cyber capabilities, posing a growing threat to national security. The most likely hypothesis is that these groups will continue to exploit AI for influence operations and cyberattacks, impacting global security and stability. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to existing information gaps and the evolving nature of AI technology.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Militant groups will primarily use AI to enhance recruitment and propaganda efforts. This is supported by evidence of AI-generated deepfakes and propaganda videos used to recruit and polarize audiences. However, the exact scale and effectiveness of these efforts remain uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: Militant groups will use AI to significantly advance their cyberattack capabilities. While AI could theoretically enhance cyber operations, there is limited direct evidence of successful AI-driven cyberattacks by these groups, making this hypothesis less supported.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to documented instances of AI-generated content being used for recruitment and propaganda. Indicators such as increased sophistication in AI-generated media or reports of AI-driven cyberattacks could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Militant groups have access to AI tools; AI technology will remain accessible and continue to advance; extremist groups prioritize recruitment and propaganda; current AI capabilities are sufficient for impactful influence operations.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on the extent of AI usage in cyber operations by militant groups; effectiveness and reach of AI-generated propaganda; internal decision-making processes within these groups regarding AI adoption.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential overestimation of AI capabilities by intelligence sources; confirmation bias towards AI as a primary threat vector; possible manipulation of open-source information by adversaries to exaggerate capabilities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The integration of AI by militant groups could significantly alter the threat landscape, influencing global security dynamics and necessitating adaptive countermeasures.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased AI-driven propaganda could exacerbate regional tensions and influence political narratives, potentially destabilizing fragile states.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced recruitment and propaganda capabilities could lead to a resurgence in militant activities and complicate counter-terrorism efforts.
- Cyber / Information Space: AI could enable more sophisticated disinformation campaigns and cyber operations, challenging existing cyber defenses and information integrity.
- Economic / Social: Polarization and misinformation could undermine social cohesion and economic stability, particularly in vulnerable regions.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of AI-related activities in extremist forums; increase collaboration with tech companies to identify and mitigate AI-generated threats.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures against AI-driven propaganda; strengthen partnerships with international allies to share intelligence and best practices.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Effective countermeasures limit AI’s impact, reducing recruitment and propaganda success.
- Worst: AI-driven operations significantly enhance militant capabilities, leading to increased attacks and instability.
- Most-Likely: Gradual increase in AI usage for propaganda and recruitment, with limited but growing cyber capabilities.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, AI, propaganda, cyber operations, recruitment, disinformation, national security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us