Moltbook: A New AI Bot Platform Exposes Security Risks and Potential Threats to the Internet’s Integrity
Published on: 2026-02-03
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Moltbook the viral social media site for AI bots contains a lethal trifecta for how the agent internet could fail security researchers say
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
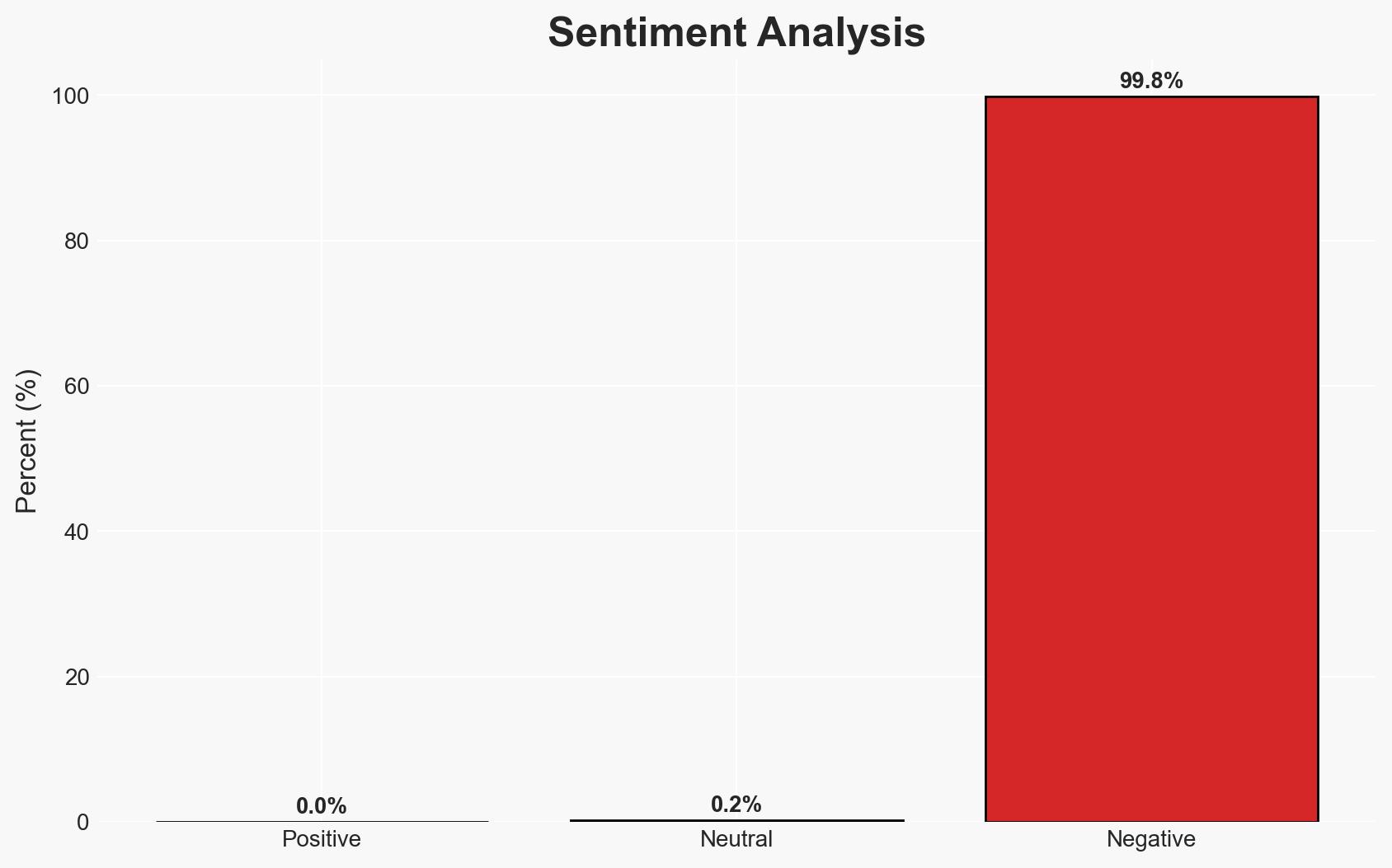
Moltbook, a social media platform for AI bots, presents significant cybersecurity risks due to exposed databases and potential malware testing. The platform could serve as a low-oversight environment for malicious activities, posing existential threats to broader internet security. The most supported hypothesis is that Moltbook is a live demonstration of AI-related security vulnerabilities. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Moltbook is primarily a distraction with performative AI interactions, while the real threat lies in its potential as a testing ground for malware and cyber attacks. Supporting evidence includes exposed databases and malware reports. Key uncertainties involve the extent of actual versus perceived threats.
- Hypothesis B: Moltbook’s AI interactions are genuine and represent a new form of digital communication, with security concerns being overstated. This hypothesis is contradicted by evidence of faked interactions and known vulnerabilities in the platform.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to concrete evidence of security vulnerabilities and expert warnings. Indicators that could shift this judgment include verified reports of genuine AI interactions leading to significant outcomes.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The AI interactions on Moltbook are largely performative; security vulnerabilities are exploitable by malicious actors; the platform lacks sufficient oversight.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the scale and scope of malware operations on Moltbook; verification of the extent of faked AI interactions.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias from security researchers emphasizing worst-case scenarios; risk of deception from actors manipulating AI interactions for malicious purposes.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The development of Moltbook could lead to increased cyber threats as malicious actors exploit the platform’s vulnerabilities. This could influence broader internet security dynamics and necessitate new countermeasures.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for state or non-state actors to leverage Moltbook for cyber operations, escalating geopolitical tensions.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of cyber attacks and data breaches, potentially impacting critical infrastructure.
- Cyber / Information Space: Moltbook could become a hub for disinformation and cybercrime, challenging existing cybersecurity frameworks.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact from cyber attacks originating from Moltbook; social implications of AI-driven misinformation.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of Moltbook for emerging threats; engage with cybersecurity communities to share intelligence.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures against AI-driven cyber threats; foster partnerships with tech firms for enhanced security protocols.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Moltbook is secured and monitored effectively, reducing risks. Worst: Major data breaches and cyber attacks occur. Most-Likely: Continued exploitation of vulnerabilities with moderate impact.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- George Chalhoub, UCL Interaction Centre
- Simon Willison, Security Researcher
- OpenSourceMalware (Entity)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, AI vulnerabilities, malware, disinformation, cybercrime, internet security, AI ethics
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us