More than 160 people killed in Pakistan in heavy rains flash floods – Al Jazeera English
Published on: 2025-08-15
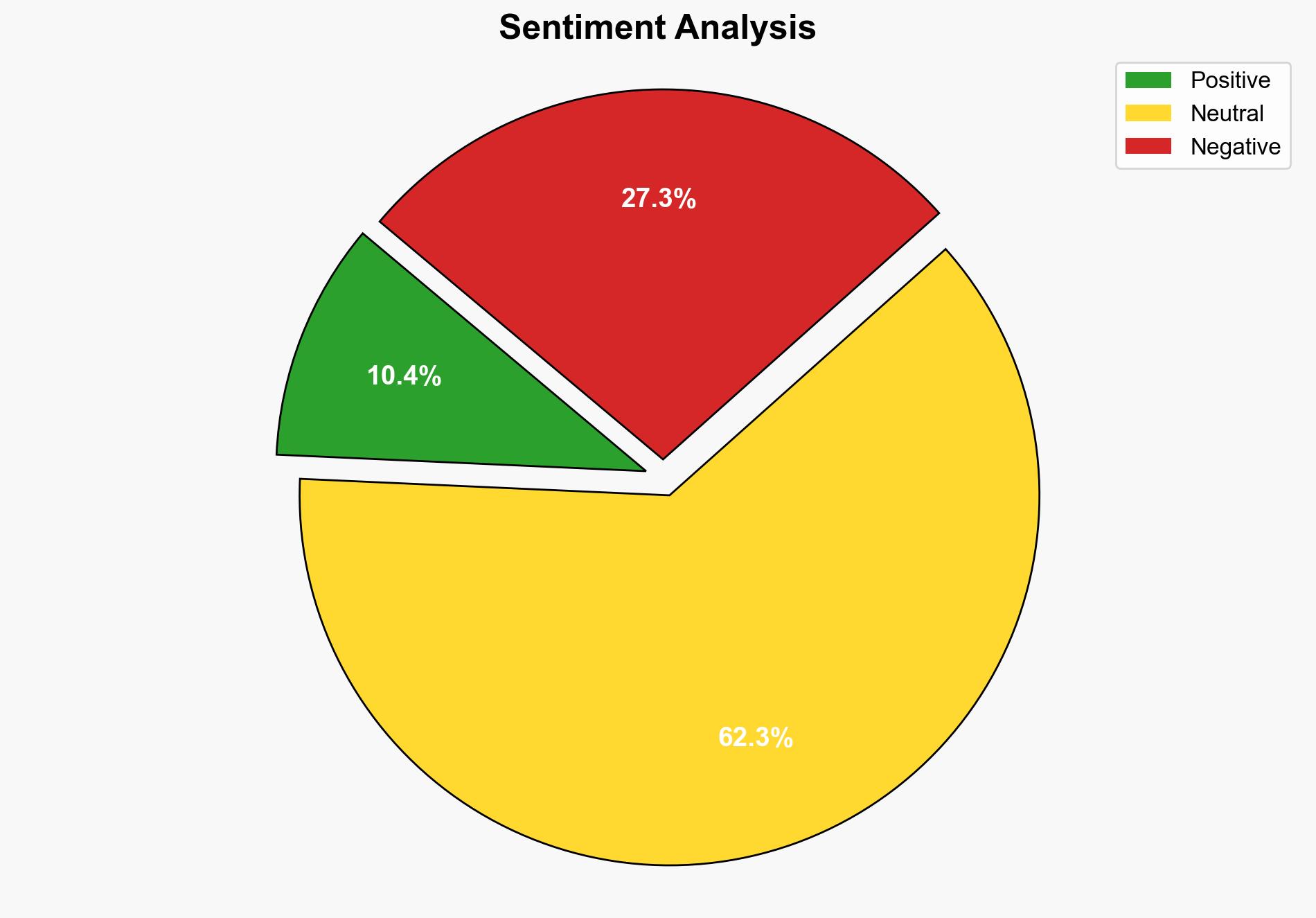
Intelligence Report: More than 160 people killed in Pakistan in heavy rains flash floods – Al Jazeera English
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The most supported hypothesis is that the heavy rains and flash floods in Pakistan are primarily a result of natural climatic patterns exacerbated by climate change. Confidence level is moderate due to the complexity of climate dynamics and potential underreporting. Recommended action includes enhancing early warning systems and infrastructure resilience to mitigate future impacts.
2. Competing Hypotheses
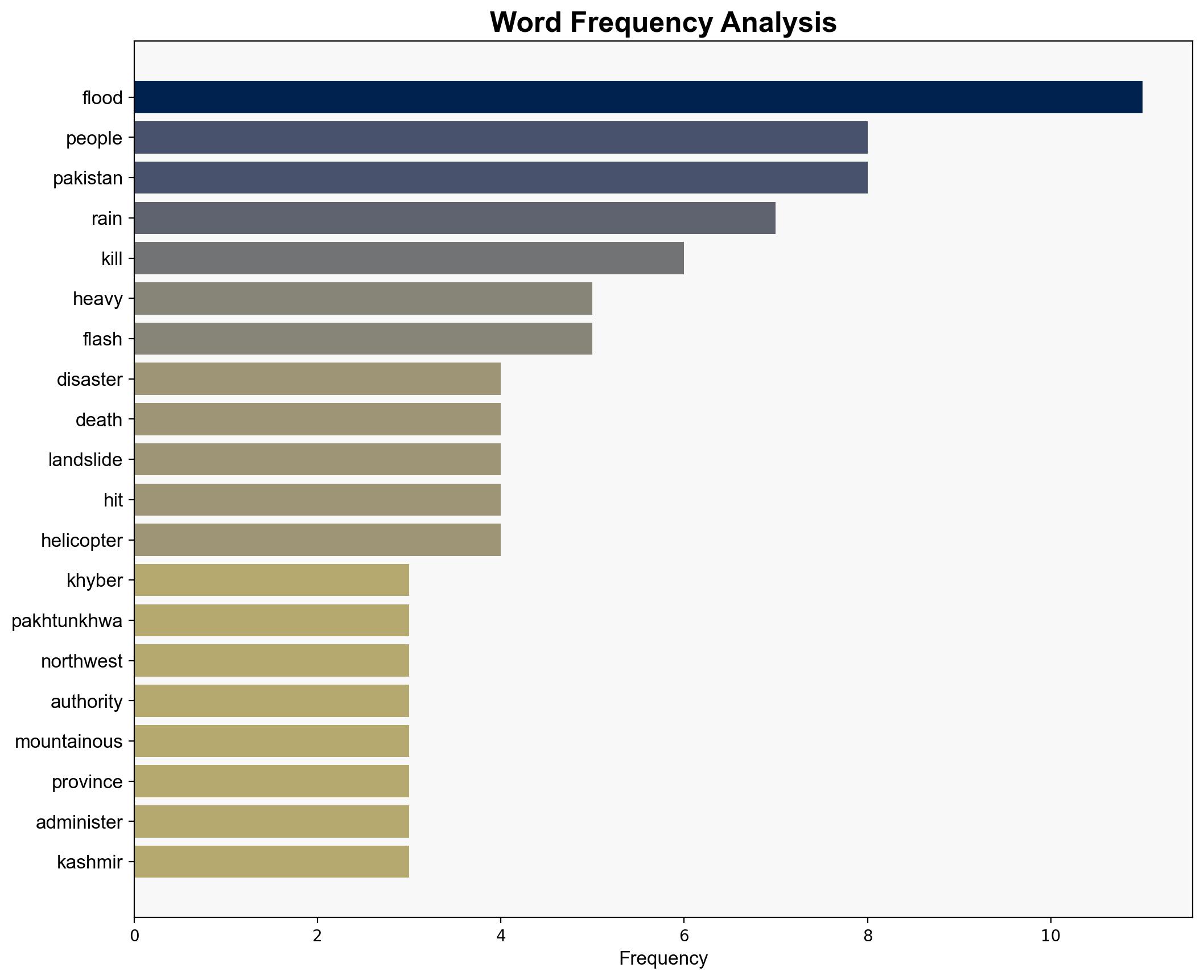
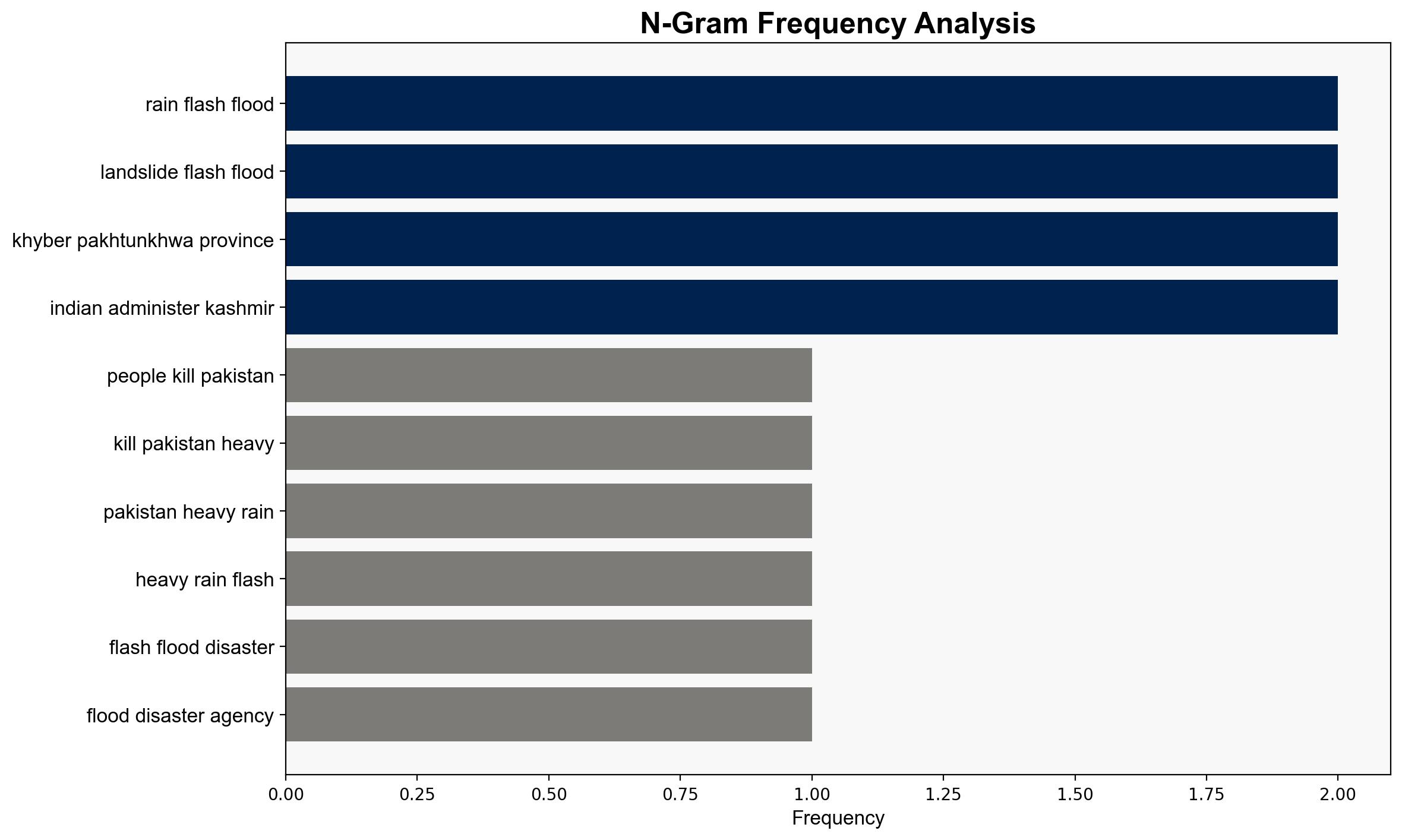
1. **Natural Climatic Patterns Exacerbated by Climate Change**: The heavy rains and flash floods are primarily due to the annual monsoon season, with increased intensity and frequency driven by climate change.
2. **Inadequate Infrastructure and Emergency Response**: The high death toll and destruction are largely due to insufficient infrastructure and emergency response capabilities, rather than solely natural causes.
Using ACH 2.0, the first hypothesis is better supported by the consistent pattern of increased rainfall and flooding in the region, as well as scientific consensus on climate change impacts. The second hypothesis is plausible but less supported by the available data, which focuses more on the natural disaster aspects.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: It is assumed that climate change is a significant factor in the increased intensity of the monsoon. It is also assumed that local infrastructure is inadequate to handle such disasters.
– **Red Flags**: Potential underreporting of casualties and damage due to remote and inaccessible areas. Lack of detailed data on infrastructure resilience and emergency response effectiveness.
– **Cognitive Bias**: Confirmation bias towards attributing all impacts to climate change without considering local governance and infrastructure issues.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The increased frequency and intensity of such natural disasters pose significant risks to regional stability, economic development, and food security. There is a potential for cascading effects, including displacement of populations, increased poverty, and strain on government resources. Geopolitical tensions may rise if cross-border impacts occur, particularly with India-administered Kashmir.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Enhance early warning systems and invest in climate-resilient infrastructure.
- Strengthen regional cooperation on disaster management and climate adaptation.
- Best-case scenario: Improved infrastructure and response systems reduce future casualties and damage.
- Worst-case scenario: Continued inadequate response leads to higher casualties and regional instability.
- Most likely scenario: Incremental improvements in response and infrastructure, with ongoing challenges from climate change impacts.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Kamal Hyder (Al Jazeera reporter)
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, climate change, disaster management, regional focus