Moving from Risk to Resilience Securing Critical Infrastructure by Tackling Technical Debt – Cisco.com
Published on: 2025-11-20
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report:
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The strategic judgment indicates a high confidence level that addressing End-of-Life (EOL) technology in critical infrastructure is imperative to enhance cybersecurity resilience. The most supported hypothesis is that proactive management and replacement of obsolete technology will significantly reduce vulnerabilities. Recommended actions include implementing lifecycle management strategies and adopting new investment models to ensure continuous technology updates.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The primary cybersecurity threat to critical infrastructure stems from outdated and unsupported technology, which can be mitigated by replacing EOL systems and adopting robust lifecycle management practices.
Hypothesis 2: Emerging technologies such as AI and quantum computing pose a more significant threat than EOL systems, and resources should be primarily allocated to counter these novel threats.
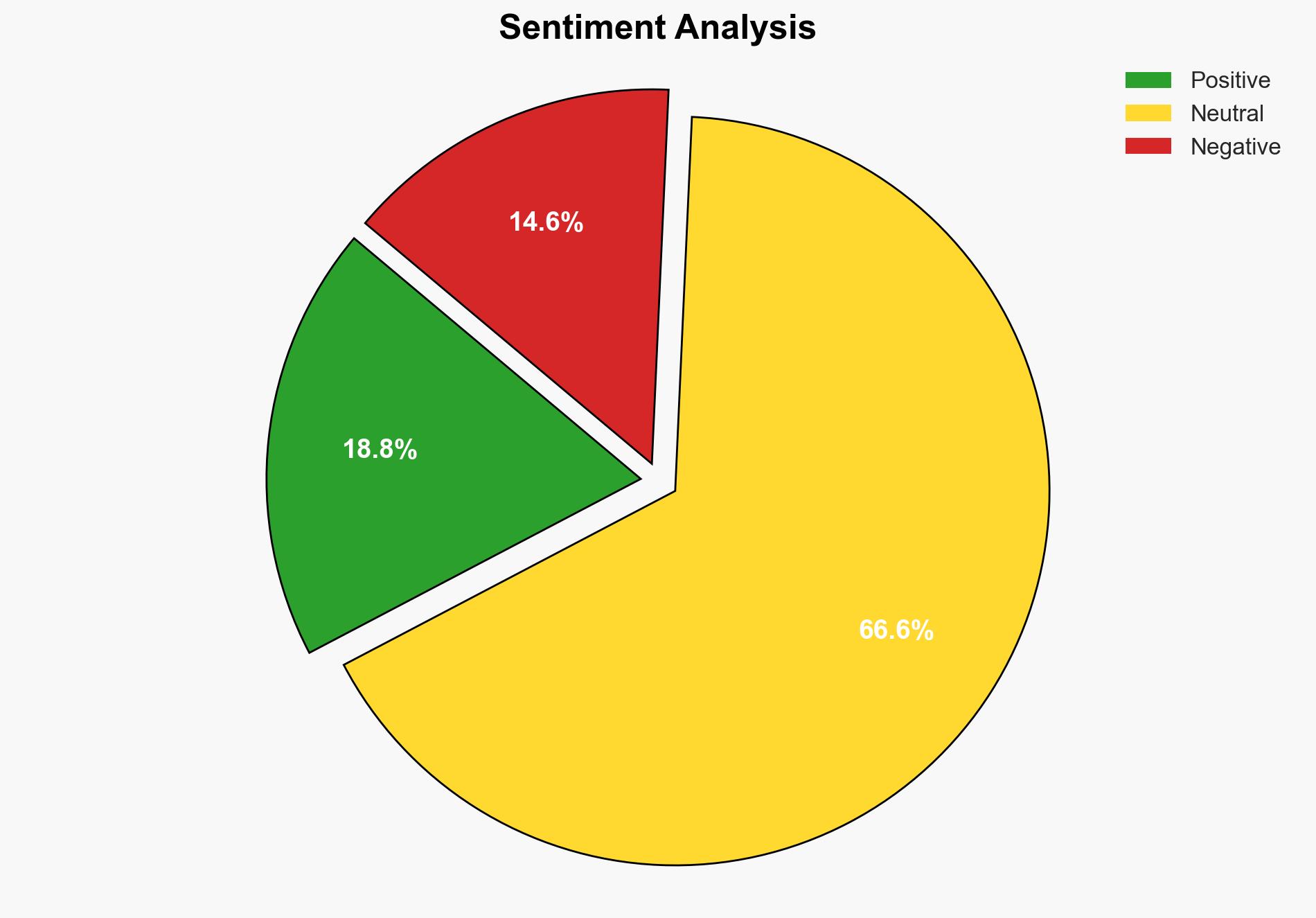
Assessment: Hypothesis 1 is more likely given the current evidence, as the report highlights the immediate risks posed by EOL technology and the lack of basic cyber hygiene. While emerging technologies are a concern, the present vulnerabilities due to outdated systems present a clear and present danger that can be addressed more directly and immediately.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions include the belief that all sectors have equal capacity to manage technology lifecycles and that the cost of replacing EOL systems is universally feasible. Red flags involve potential underestimation of the complexity and cost of replacing legacy systems and overreliance on vendor-provided solutions without independent verification. Deception indicators could include vendor bias in promoting new technologies over maintaining existing ones.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The continued reliance on EOL technology could lead to increased cyber breaches, resulting in economic losses, compromised national security, and public safety risks. Politically, failure to address these vulnerabilities could erode trust in government and private sector capabilities. Economically, the cost of cyber incidents could escalate, impacting national and global markets. Informationally, breaches could lead to data leaks, affecting citizen privacy and national intelligence.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Implement comprehensive asset management systems to track and manage EOL technology.
- Adopt subscription-based models for technology investment to ensure continuous updates and security enhancements.
- Enhance incident reporting mechanisms to improve transparency and accountability.
- Best-case scenario: Successful implementation of lifecycle management reduces cyber incidents significantly.
- Worst-case scenario: Failure to address EOL risks leads to a major cyberattack on critical infrastructure.
- Most-likely scenario: Gradual improvement in resilience as sectors adopt recommended strategies.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
While specific individuals are not named, key entities include national governments, critical infrastructure operators, and technology vendors. Their roles are crucial in policy implementation and technology management.
7. Thematic Tags
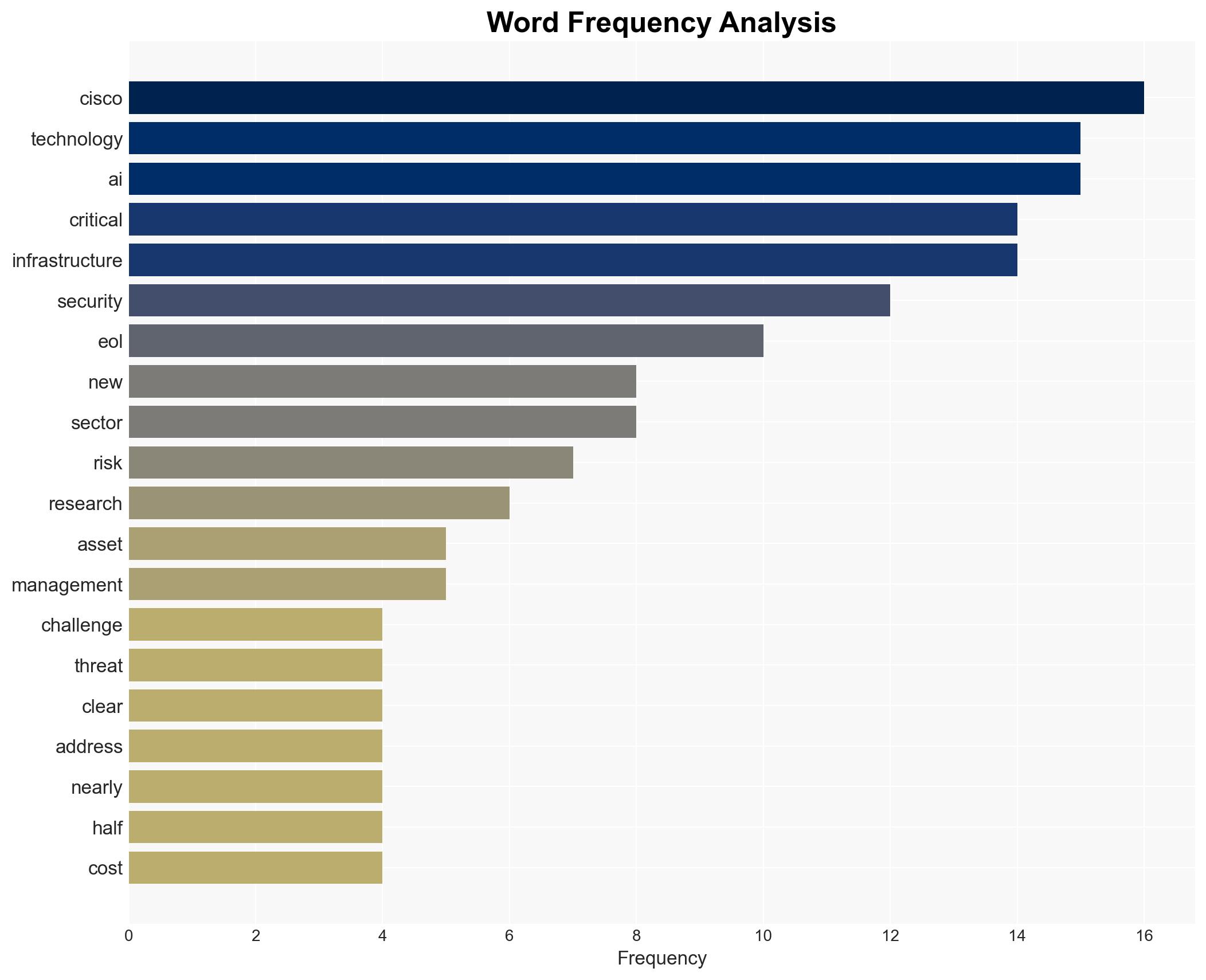
Cybersecurity, Critical Infrastructure, Technology Lifecycle Management, End-of-Life Technology, Risk Mitigation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us