Myanmar’s military conducts elections in conflict zones, raising concerns over legitimacy amid civil war
Published on: 2026-01-11
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Myanmars military holds second phase of elections amid civil war
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The Myanmar military’s orchestration of elections amid ongoing civil conflict appears aimed at consolidating power and legitimizing its rule. The elections are likely to exacerbate existing tensions and undermine democratic processes. The most likely hypothesis is that the military will continue to manipulate political structures to maintain control, with moderate confidence in this assessment.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The elections are a genuine attempt by the military to restore democratic governance and stabilize the country. Supporting evidence includes the formal conduct of elections and the military’s claim of voter turnout. Contradicting evidence includes the dissolution of opposition parties and reports of election manipulation.
- Hypothesis B: The elections are a strategic maneuver by the military to entrench its power and suppress opposition. Supporting evidence includes the exclusion of major opposition parties and the military’s historical pattern of control. Contradicting evidence is limited but could include any genuine reforms post-election.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the military’s history of power consolidation and the lack of credible opposition in the elections. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include significant political reforms or increased international pressure leading to genuine democratic processes.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The military intends to maintain long-term control; opposition parties lack the capacity to challenge the military effectively; international response will remain limited.
- Information Gaps: Detailed voter turnout data, independent verification of election results, and the military’s long-term political strategy.
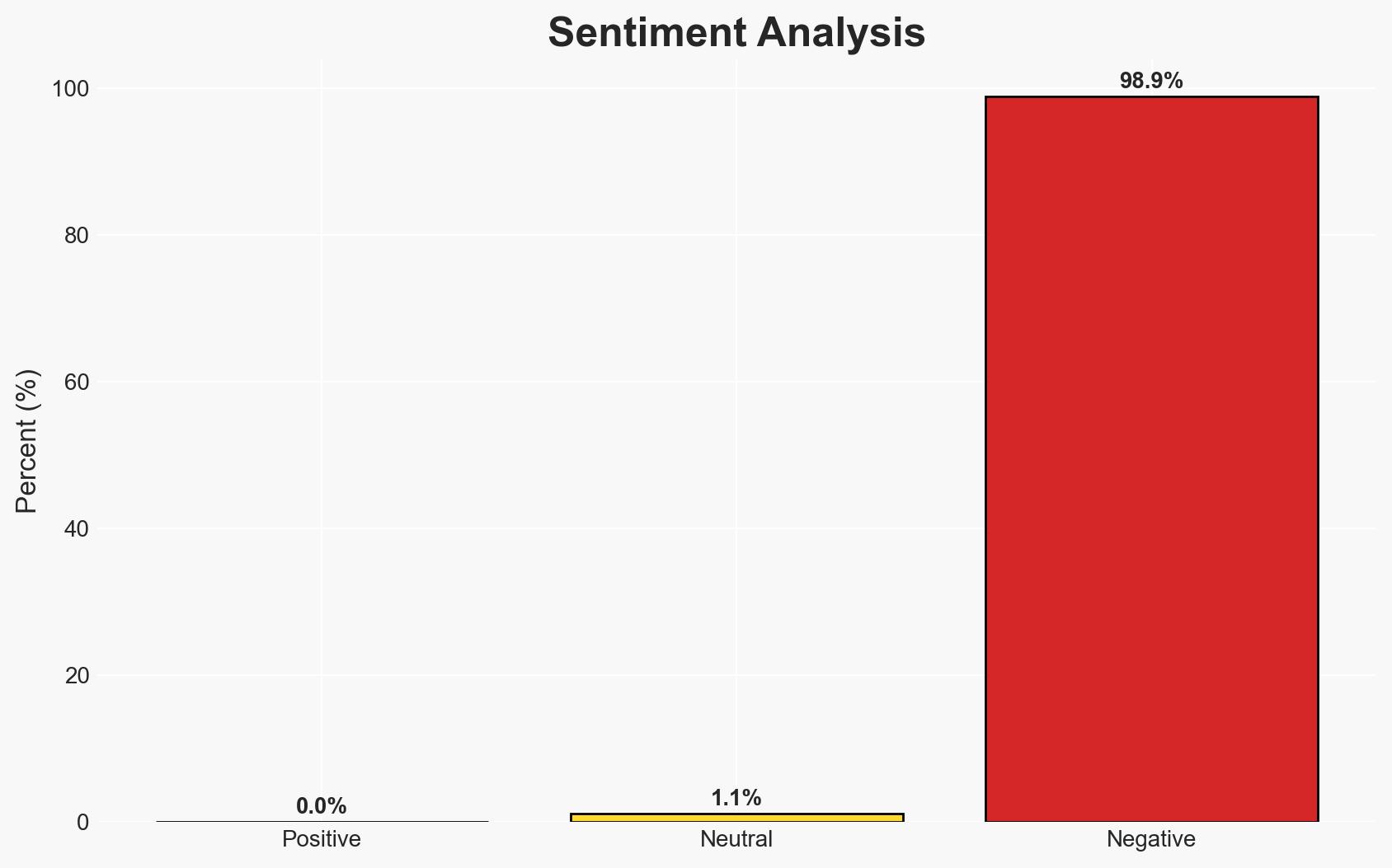
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in military-reported election data; risk of underestimating local resistance movements; possible deception in military’s stated intentions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The continuation of elections under military control is likely to deepen political divisions and may lead to increased violence and instability. The international community’s response could influence the military’s actions.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased international isolation and sanctions; risk of regional instability affecting neighboring countries.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of insurgency and terrorist activities as opposition groups may resort to violence.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased likelihood of cyber operations targeting election processes and information warfare to control narratives.
- Economic / Social: Economic instability due to sanctions and reduced foreign investment; social unrest due to perceived illegitimacy of the government.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor election processes and outcomes closely; engage with regional partners to assess collective response options.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures to counter potential insurgency; strengthen diplomatic channels with ASEAN and other regional actors.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Military initiates genuine reforms, leading to gradual stabilization.
- Worst: Escalation of civil conflict and international isolation.
- Most-Likely: Continued military control with periodic unrest and limited international intervention.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
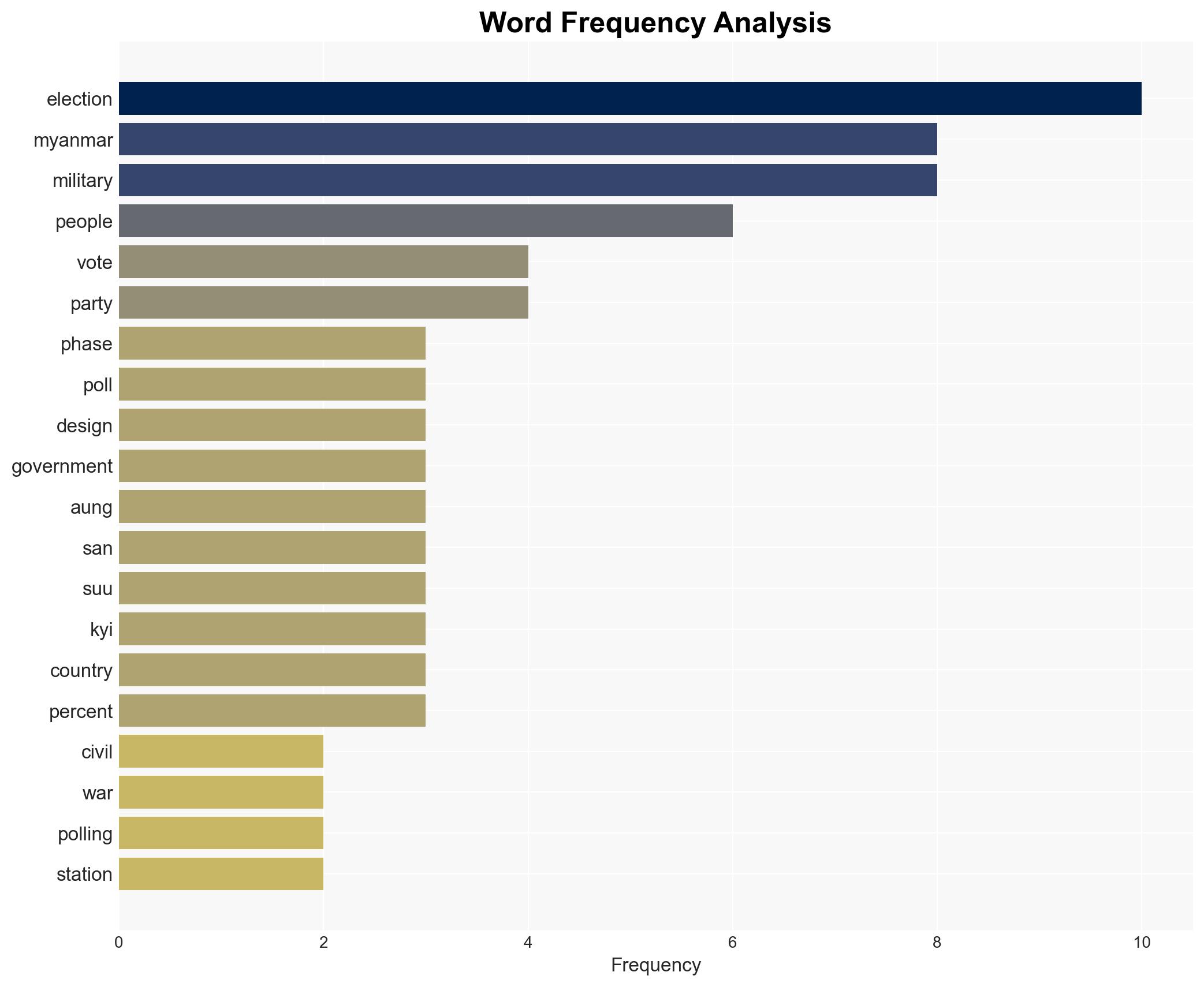
regional conflicts, military control, elections, civil conflict, Myanmar, international response, political instability, opposition suppression
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us