Myanmar’s Ongoing Crisis: Volunteer Medics Face Harrowing Conditions Amid Military Strikes
Published on: 2026-02-13
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Revolution Without Headlines Myanmars Forgotten Struggle
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
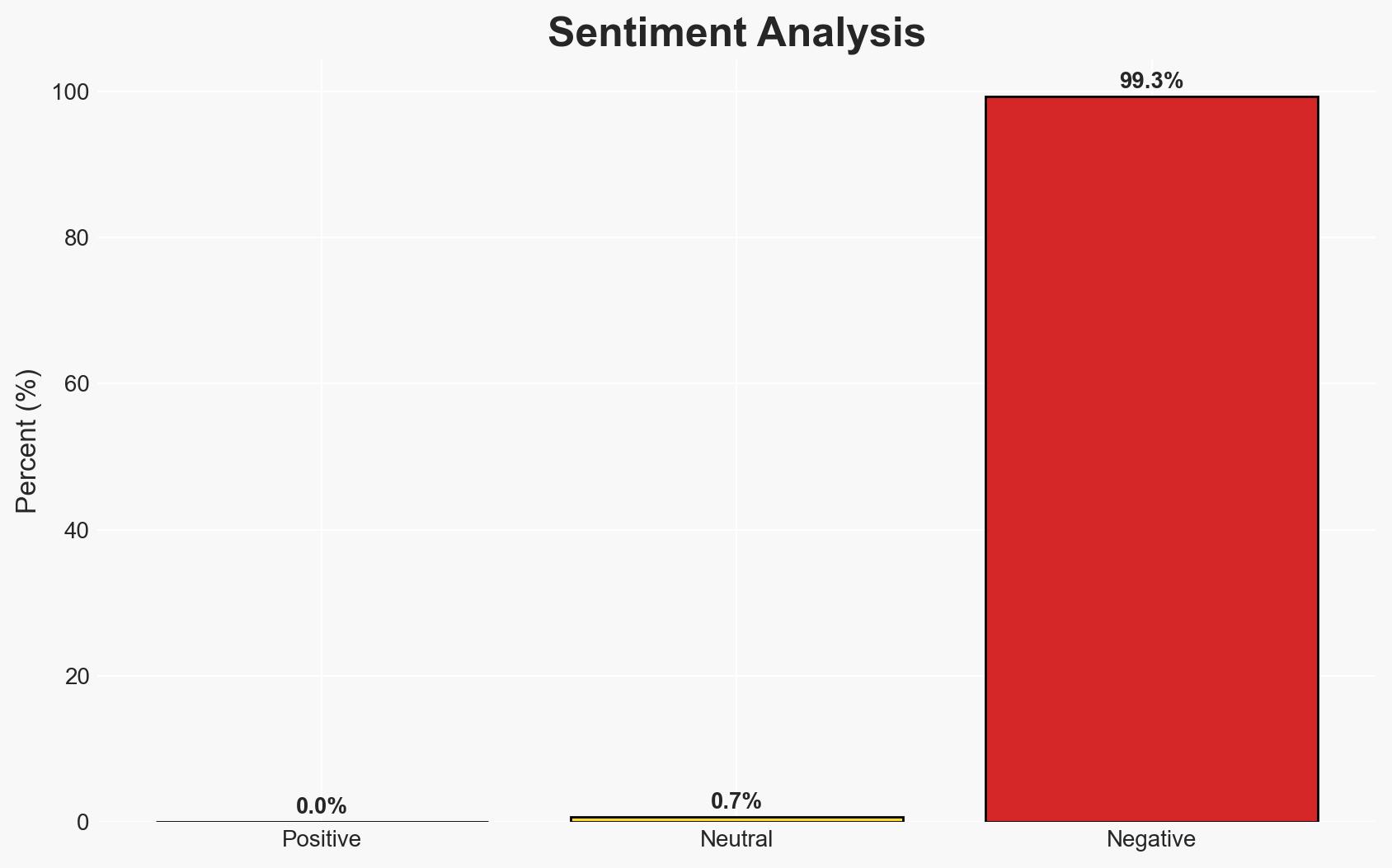
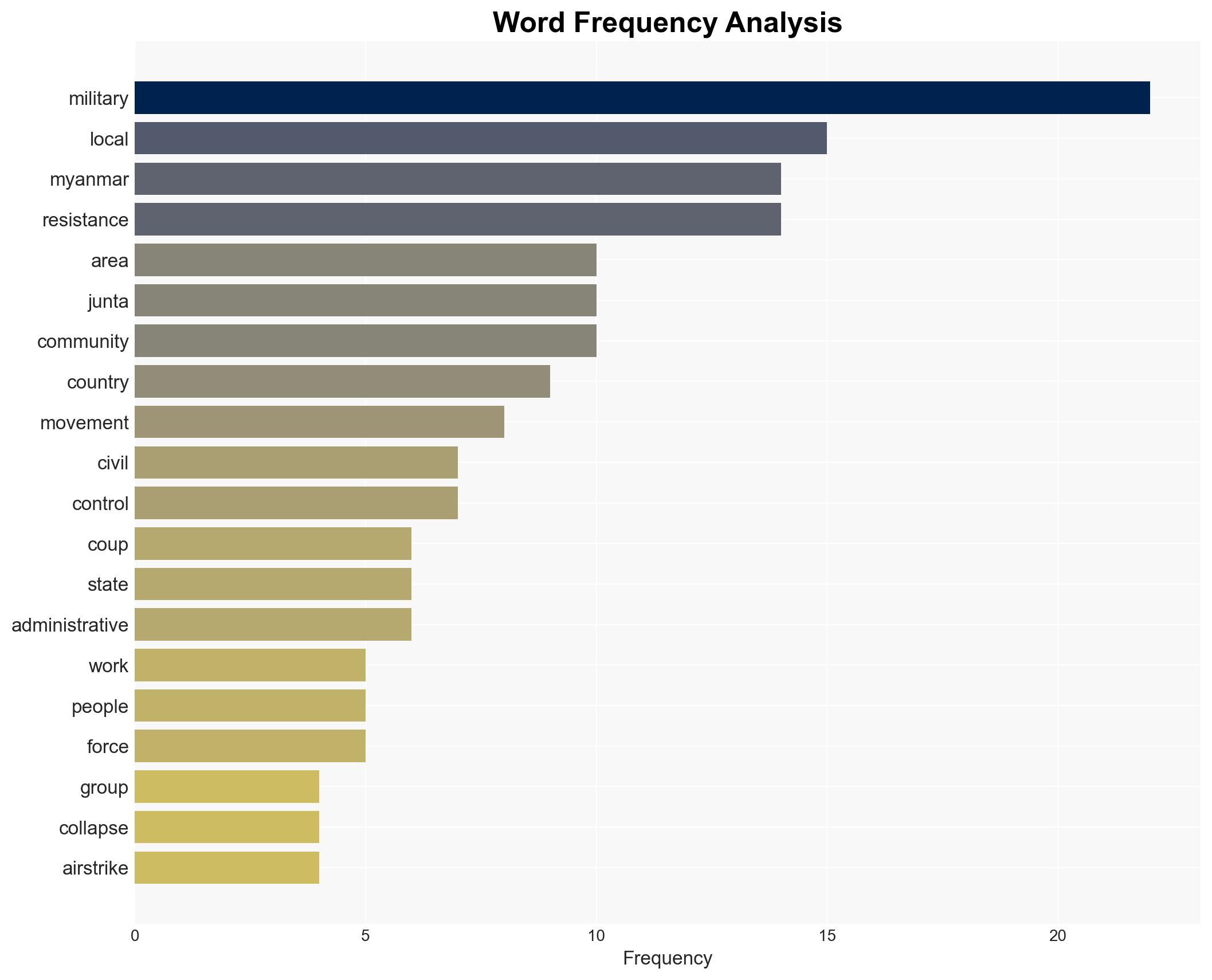
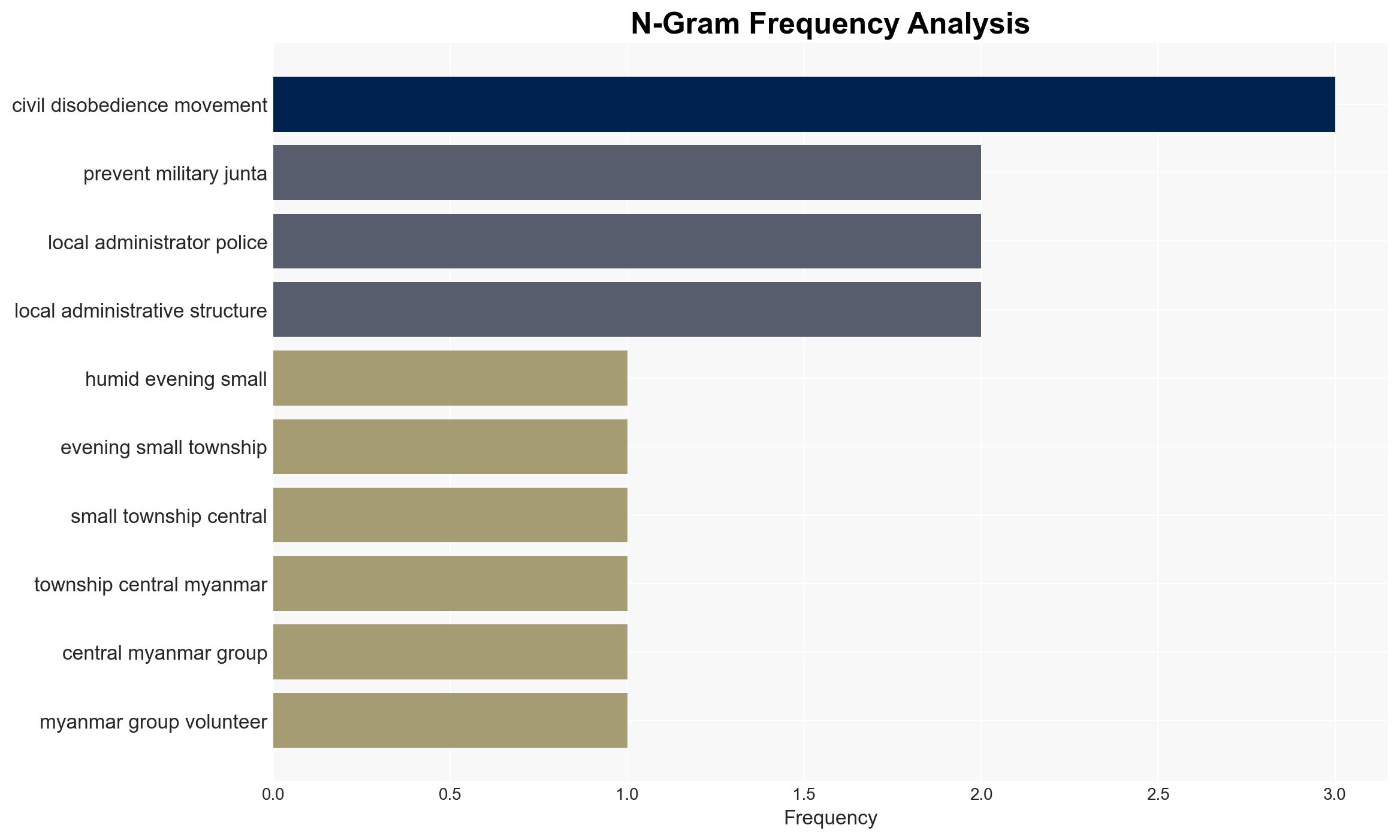
The ongoing resistance in Myanmar against the military junta is characterized by decentralized, grassroots efforts involving various local groups and civil society networks. The situation remains largely underreported internationally, which may affect global response strategies. The most likely hypothesis is that this resistance will persist in a fragmented manner, posing a sustained challenge to the junta. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to significant information gaps and potential biases in available sources.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The resistance in Myanmar will remain fragmented and localized, lacking a unified command structure, which will limit its effectiveness against the military junta. This is supported by the diverse nature of the groups involved and the absence of a central leadership. However, the resilience and adaptability of these groups could contradict this view.
- Hypothesis B: The resistance could coalesce into a more organized and unified movement, potentially increasing its effectiveness. This could be supported by shared goals and increasing international support, but is contradicted by historical ethnic divisions and the current lack of cohesive leadership.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported given the current evidence of a patchwork resistance and lack of central coordination. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of emerging leadership or increased international support leading to greater unity.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The military junta will continue to employ violent repression; international attention will remain limited; local resistance groups will persist in their efforts despite resource constraints.
- Information Gaps: Detailed information on the internal dynamics of resistance groups and their interactions with international actors is lacking.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential biases include over-reliance on anecdotal evidence from resistance sources and underestimation of the junta’s capabilities. There is also a risk of manipulation in reports from both sides.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ongoing resistance in Myanmar could lead to prolonged instability, affecting regional security and international diplomatic efforts. The fragmented nature of the resistance may hinder effective governance and reconstruction efforts post-conflict.
- Political / Geopolitical: Prolonged conflict may strain regional relations and complicate international diplomatic interventions.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Continued violence could lead to increased militarization and potential for extremist exploitation.
- Cyber / Information Space: Limited data on cyber operations, but potential for misinformation campaigns by both the junta and resistance groups.
- Economic / Social: Ongoing conflict may exacerbate economic decline and social fragmentation, leading to humanitarian crises.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of resistance activities and junta responses; engage with regional partners to assess humanitarian needs.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for affected communities; explore diplomatic channels for conflict resolution support.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Resistance coalesces into a unified front leading to negotiations (trigger: emergence of central leadership).
- Worst: Escalation into full-scale civil war with regional spillover (trigger: increased military offensives).
- Most-Likely: Continued fragmented resistance with sporadic violence (trigger: sustained local resistance efforts).
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
regional conflicts, civil resistance, military junta, Myanmar conflict, grassroots movements, international attention, humanitarian crisis, regional stability
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us