NATO’s Unity at Risk: Greenland’s Status Sparks Tensions Among Member States
Published on: 2026-01-10
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Greenland claims How close have NATO members come to fighting each other
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
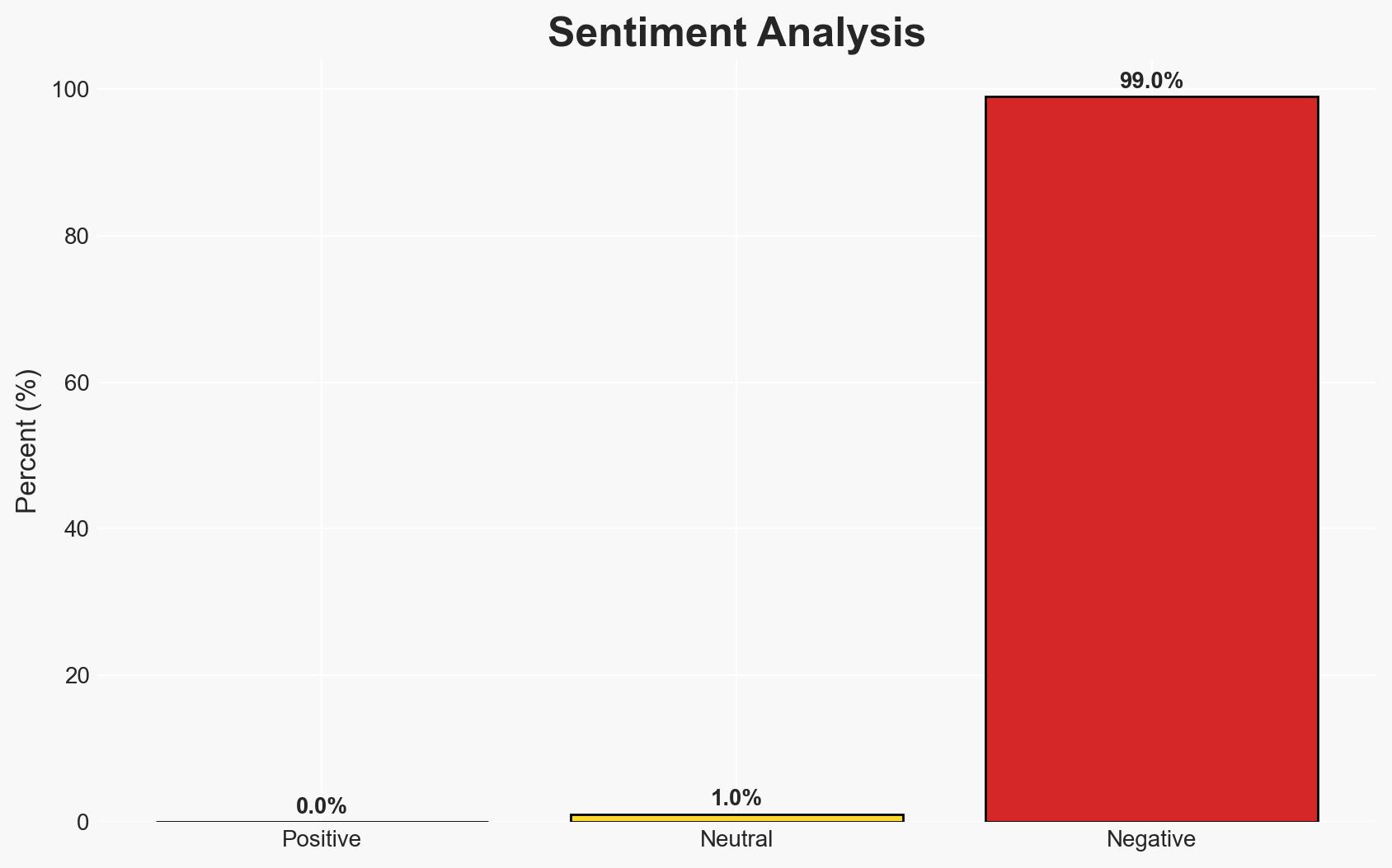
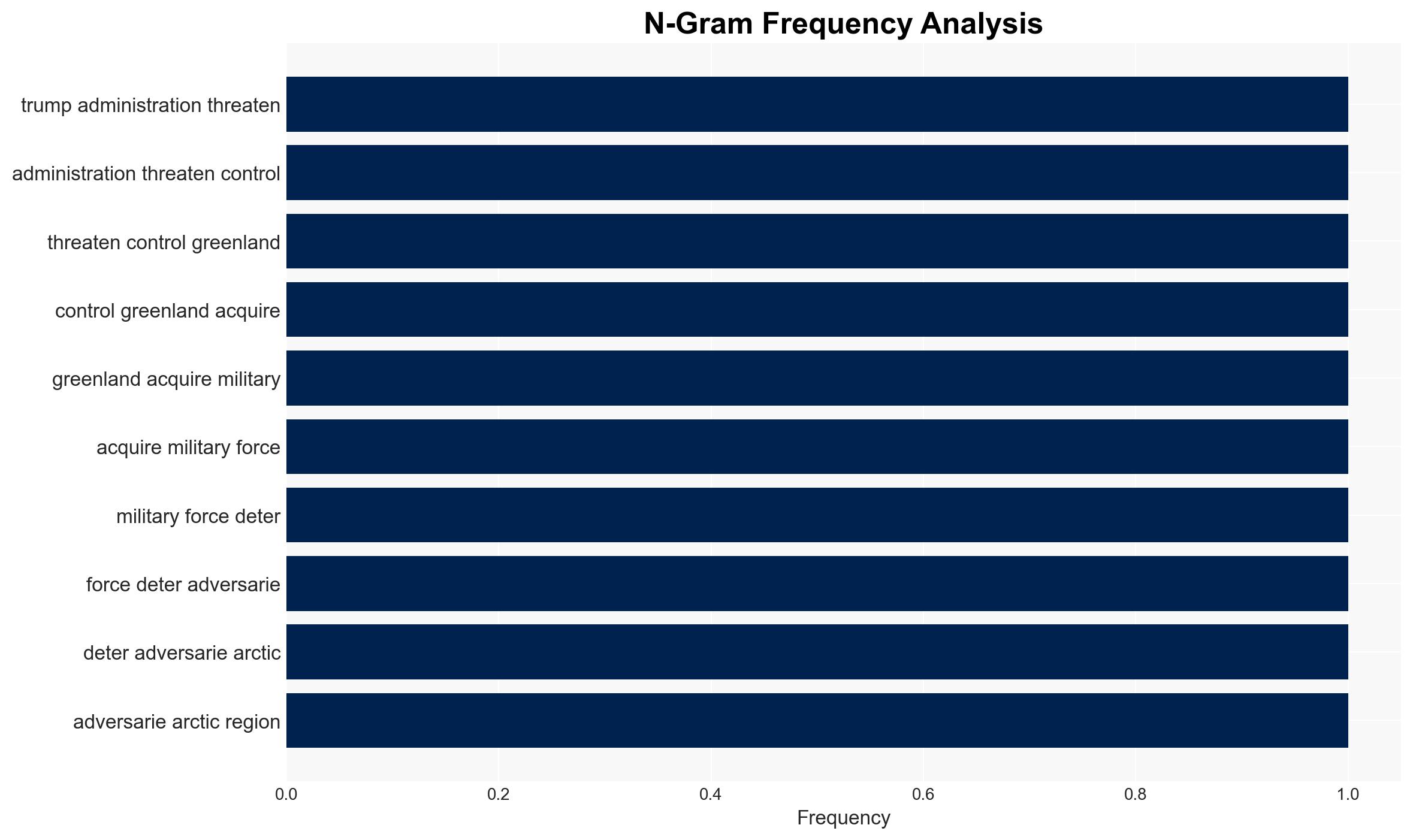
The Trump administration’s threats to acquire Greenland pose a significant risk to NATO cohesion, potentially challenging the alliance’s foundational principles. The situation could lead to unprecedented intra-NATO conflict, testing the limits of Article 5. This assessment is made with moderate confidence, considering historical precedents and current geopolitical dynamics.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The US is serious about acquiring Greenland, potentially through military means, to counter adversaries in the Arctic. Supporting evidence includes repeated threats from the Trump administration. Contradicting evidence includes the lack of historical precedent and potential diplomatic fallout.
- Hypothesis B: The US threats are primarily rhetorical, aimed at strategic posturing rather than actual acquisition. This is supported by the complexity and risks involved in such a move, as well as NATO’s historical ability to manage internal conflicts without escalation.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the high diplomatic costs and historical NATO resilience in managing internal disputes. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include increased military activity in the region or formal policy shifts from the US administration.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The US values NATO cohesion; Denmark will resist US acquisition attempts; NATO members prioritize alliance stability over individual disputes.
- Information Gaps: Specific US military plans regarding Greenland; Denmark’s contingency plans; NATO’s internal discussions on the issue.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential US domestic political motivations influencing foreign policy; media sensationalism affecting perception; lack of transparency from involved parties.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could strain NATO’s internal dynamics and test its conflict resolution mechanisms. It may also influence Arctic geopolitics and US-European relations.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential diplomatic rift within NATO; increased tension in Arctic geopolitics.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Possible reallocation of NATO resources to manage internal disputes; distraction from external threats.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased cyber operations targeting NATO communications; disinformation campaigns to exploit alliance tensions.
- Economic / Social: Economic implications for Greenland and Denmark; potential social unrest in Greenland due to uncertainty.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor US military movements in the Arctic; engage in diplomatic dialogue with Denmark and Greenland; assess NATO’s internal cohesion.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen NATO conflict resolution mechanisms; enhance Arctic security cooperation; develop contingency plans for potential escalation.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Diplomatic resolution reinforcing NATO unity.
- Worst: Military confrontation leading to NATO fragmentation.
- Most-Likely: Continued diplomatic tensions with no military escalation, maintaining NATO’s current structure.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Trump Administration
- Government of Denmark
- NATO Leadership
- Greenland Authorities
7. Thematic Tags
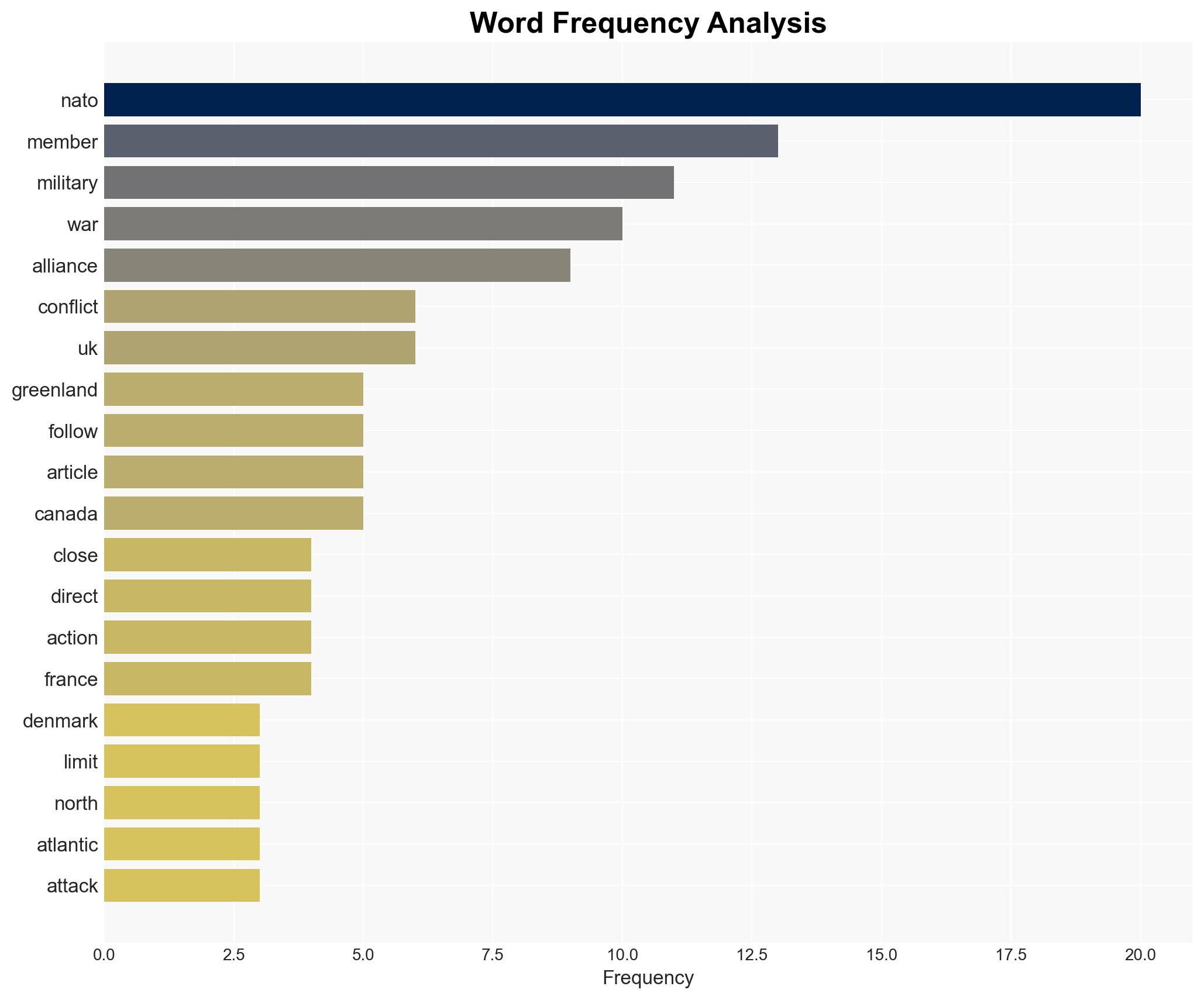
regional conflicts, NATO cohesion, Arctic strategy, US foreign policy, Denmark-Greenland relations, military posturing, alliance dynamics, geopolitical tensions
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us