Navigating the Evolving Threat Landscape: Essential Insights for CISOs to Enhance Cyber Defense Strategies
Published on: 2025-12-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Threat actor landscape what every CISO must know to stay ahead
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
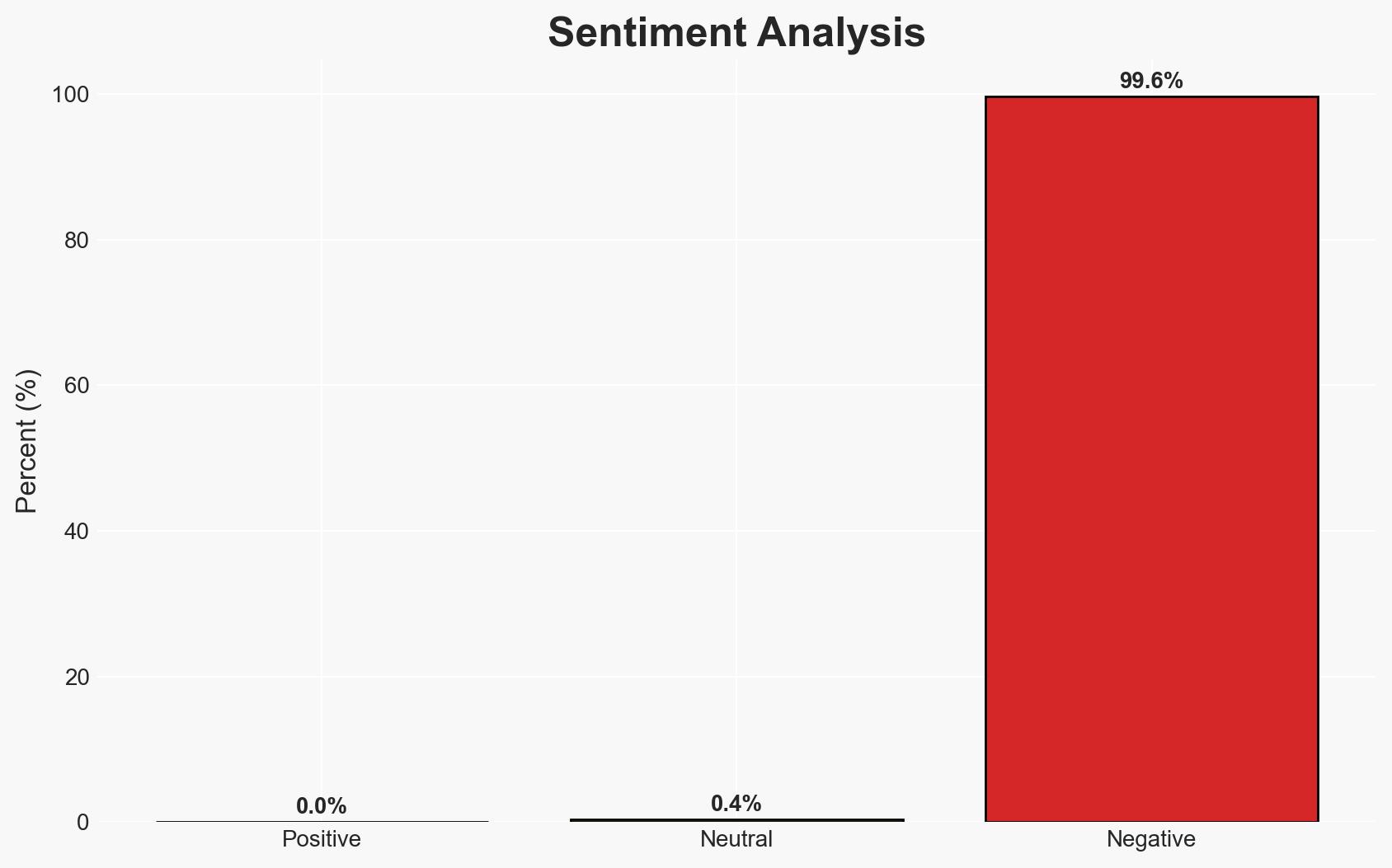
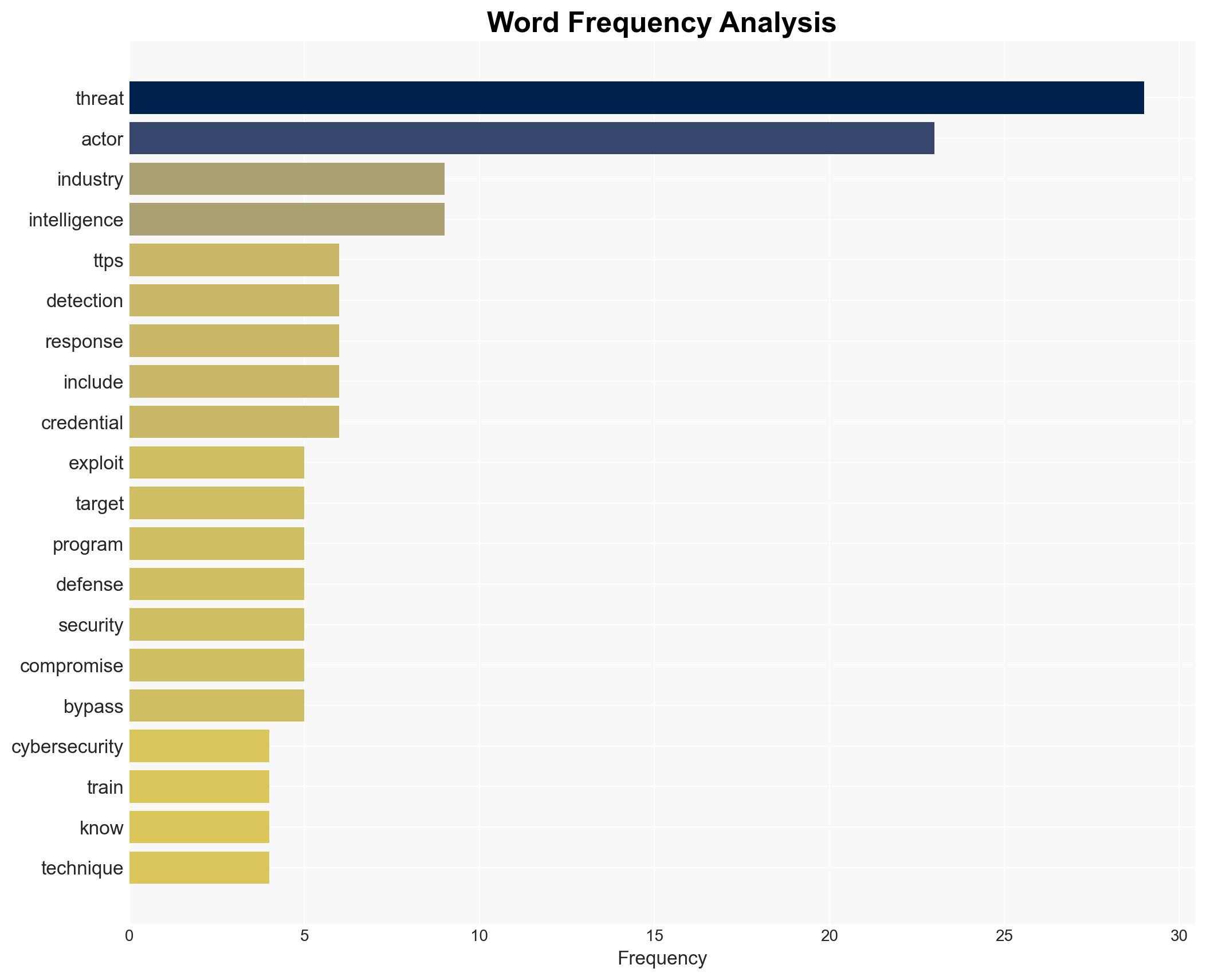
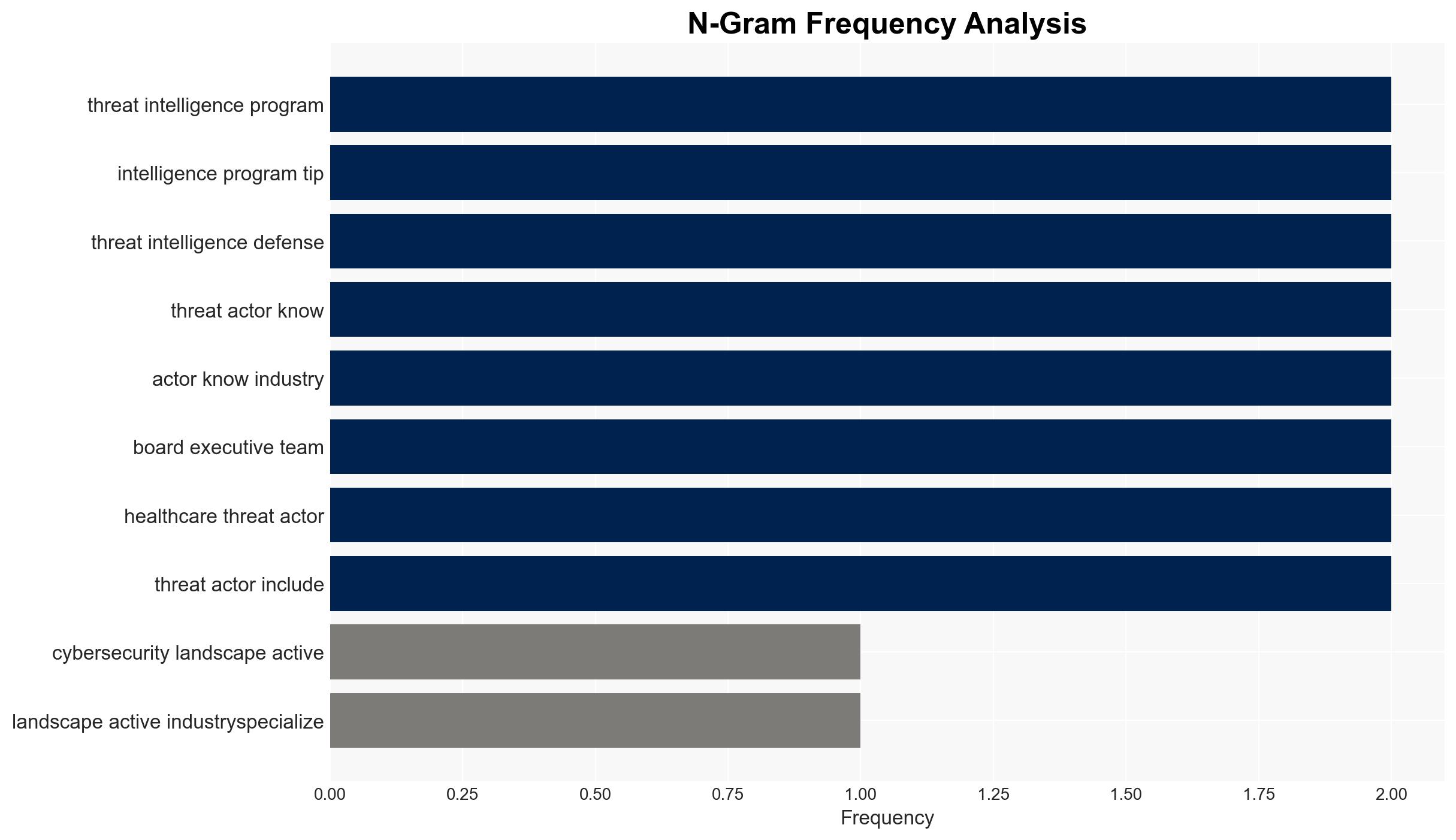
The cybersecurity threat landscape in 2H 2025 is characterized by industry-specific and precision-targeted attacks, requiring CISOs to develop robust threat intelligence programs. Healthcare is notably targeted by advanced threat actors employing sophisticated techniques. This assessment is made with moderate confidence, given the evolving nature of threat actor capabilities and the incomplete data on specific incidents.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Threat actors are increasingly targeting specific industries with tailored tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) due to the high value of sector-specific data and potential financial gain. This is supported by evidence of targeted attacks in healthcare using advanced methods like SIM-swapping and social engineering.
- Hypothesis B: The observed increase in industry-specific attacks is a result of improved detection and reporting capabilities rather than an actual increase in targeted activity. This hypothesis is less supported due to the specificity of the TTPs and the actors identified, which suggest deliberate targeting.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported, as the precision and sophistication of the attacks align with known threat actor capabilities and motivations. Future shifts in this judgment could occur with new data on attack frequency and actor intent.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Threat actors have the capability to conduct industry-specific reconnaissance; CISOs have access to adequate resources for threat intelligence programs; current threat actor motivations are primarily financial.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the frequency and success rate of these targeted attacks; comprehensive threat actor attribution; specific industry response effectiveness.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential confirmation bias in attributing attacks to known actors; source bias from cybersecurity firms with vested interests in promoting threat intelligence solutions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of targeted cyber threats could lead to increased regulatory scrutiny and demand for enhanced cybersecurity measures across industries. The sophistication of attacks may drive innovation in defensive technologies and strategies.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased international tension if state-sponsored actors are implicated.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment necessitating improved coordination between public and private sectors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Accelerated development of threat intelligence platforms and cybersecurity frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK.
- Economic / Social: Increased costs for businesses to implement advanced cybersecurity measures; potential public concern over data privacy and security.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive threat assessment for industry-specific vulnerabilities; enhance monitoring and detection capabilities using frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with industry peers and government agencies for threat intelligence sharing; invest in training programs focused on emerging threats.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Improved threat intelligence leads to a significant reduction in successful attacks.
- Worst: Threat actors adapt faster than defenses, leading to widespread breaches.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in defense capabilities reduce but do not eliminate targeted attacks.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Scattered Spider (UNC3944)
- Black Basta
- RansomHub
- NoEscape
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, threat intelligence, healthcare sector, targeted attacks, threat actors, industry-specific threats, cyber defense
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us