NCSC Chief Warns SMEs Underestimate Cyber-Attack Risks and Must Strengthen Defenses
Published on: 2026-02-16
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: SMEs Wrong to Assume They Wont Be Hit by Cyber-Attacks NCSC Boss Warns
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
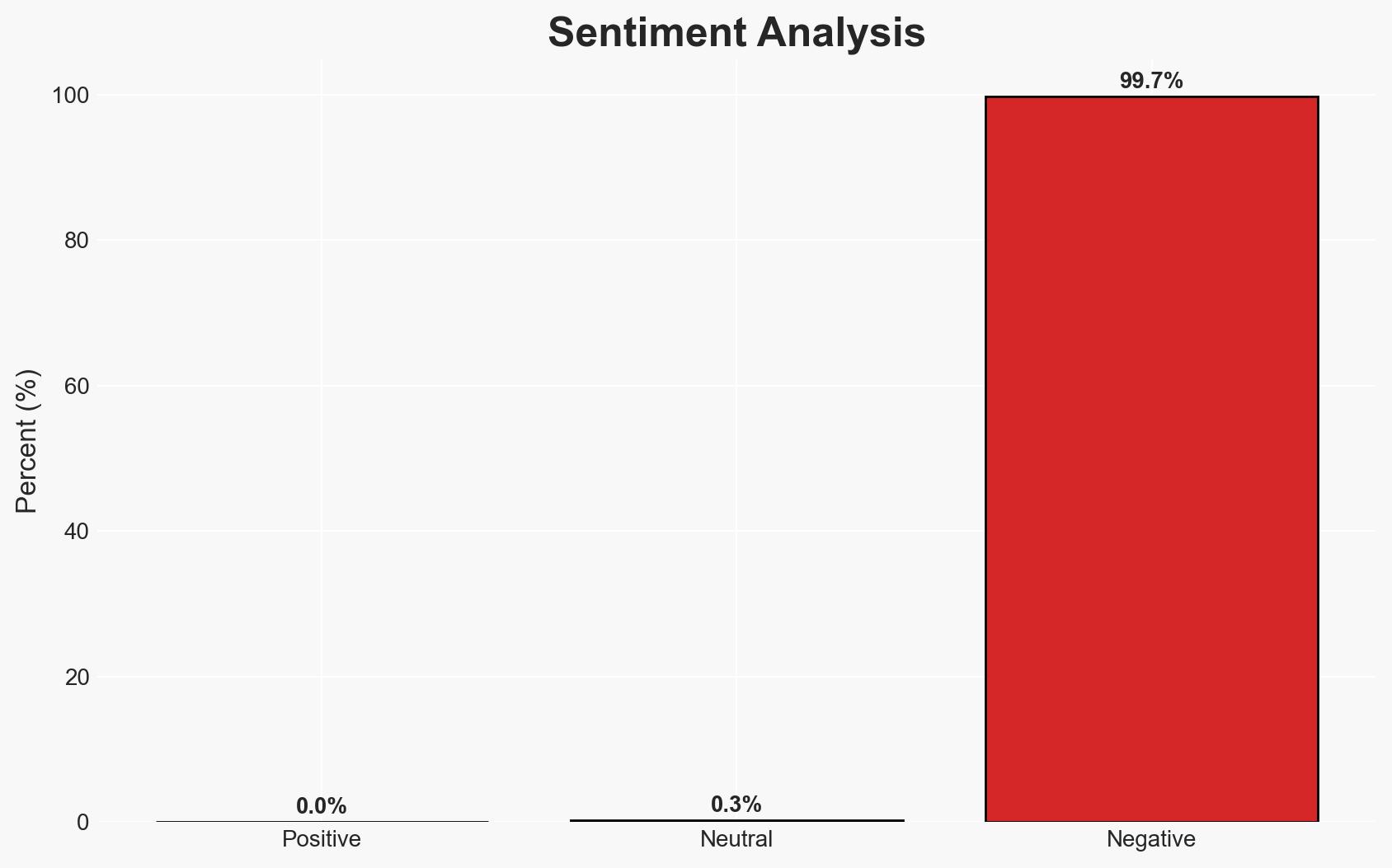
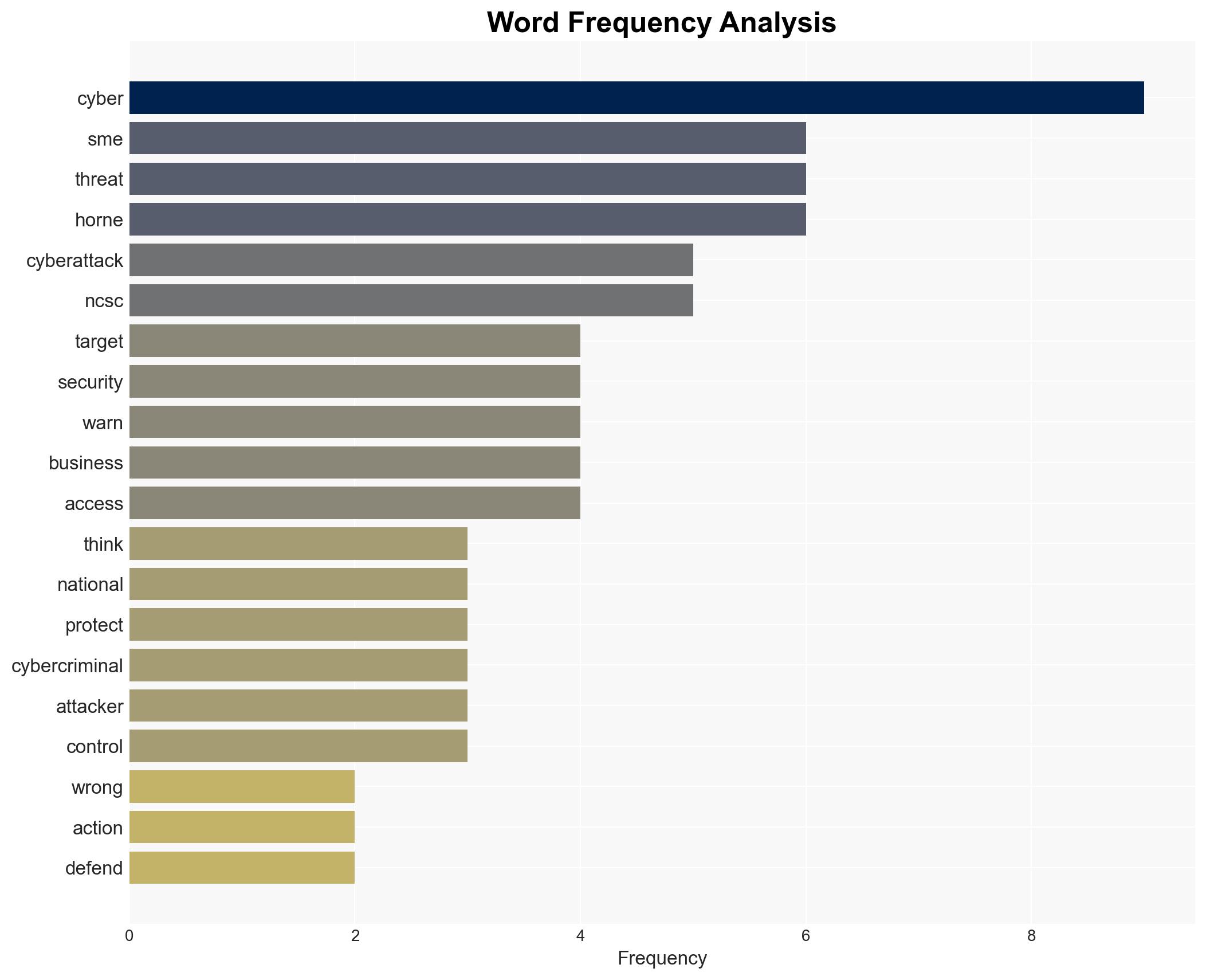
The National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) warns that small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are vulnerable to cyber-attacks due to inadequate cybersecurity measures. Despite misconceptions, SMEs are attractive targets for cybercriminals. The NCSC recommends adopting Cyber Essentials certification to mitigate risks. Confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the lack of specific data on SME cyber-attack incidences.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: SMEs are not primary targets for cybercriminals due to their smaller size and lower profile. This is contradicted by the NCSC’s assertion that attackers seek vulnerabilities rather than high-profile targets. Key uncertainties include the actual frequency of attacks on SMEs.
- Hypothesis B: SMEs are increasingly targeted by cybercriminals due to their perceived lack of robust cybersecurity defenses. Supported by NCSC’s emphasis on vulnerabilities and the call for improved security measures. Contradictory evidence is limited but includes the traditional focus of attackers on larger entities.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the NCSC’s authoritative stance and the logical appeal of targeting less-defended entities. Indicators such as increased reporting of SME breaches could further substantiate this hypothesis.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: SMEs have less robust cybersecurity than larger organizations; cybercriminals prioritize ease of access over target size; Cyber Essentials certification effectively mitigates common threats.
- Information Gaps: Specific data on the frequency and impact of cyber-attacks on SMEs; detailed threat actor profiles targeting SMEs.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in NCSC’s promotion of Cyber Essentials; lack of independent verification of SME threat levels could skew perception.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The trend of increasing cyber threats to SMEs could lead to significant economic and operational disruptions if not addressed. This development may influence broader cybersecurity policies and business practices.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased pressure on governments to support SME cybersecurity initiatives; potential for international collaboration on cyber defense.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: SMEs may become entry points for broader cyber campaigns affecting national infrastructure.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential rise in cyber insurance demand; increased focus on cybersecurity training and awareness for SMEs.
- Economic / Social: Economic instability for SMEs due to cyber-attack losses; potential job losses and reduced market confidence.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Encourage SMEs to conduct cybersecurity audits and adopt Cyber Essentials; increase awareness campaigns targeting SME vulnerabilities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop public-private partnerships to enhance SME cybersecurity; incentivize cybersecurity investments through tax breaks or grants.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Widespread adoption of cybersecurity measures by SMEs reduces attack success rates.
- Worst: Continued neglect leads to significant economic damage and exploitation of SMEs as vectors for larger attacks.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in SME cybersecurity posture with ongoing challenges due to resource constraints.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Richard Horne, CEO of the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC)
- National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, SMEs, cyber-attacks, national security, Cyber Essentials, NCSC, risk management
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us