New Attack Method Lets Hackers Exploit Microsoft Copilot with Just One Click, Compromising User Data Security
Published on: 2026-01-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: How a simple link allowed hackers to bypass Copilot’s security guardrails – and what Microsoft did about it
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
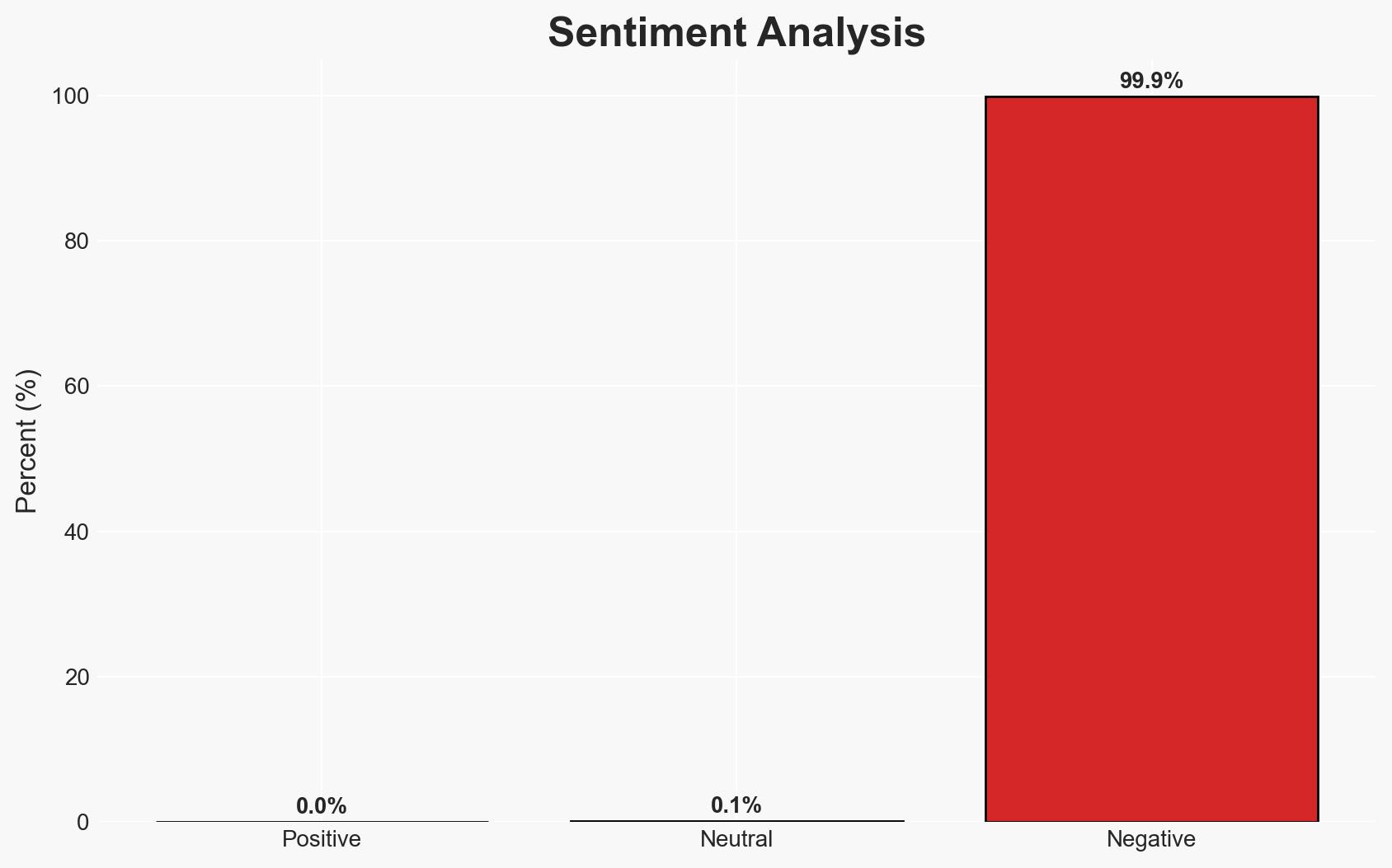
The Reprompt attack method exploited vulnerabilities in Microsoft’s Copilot AI, allowing data exfiltration with a single click. The attack bypassed security controls by chaining multiple techniques, posing a significant risk to user data. Microsoft has since patched the vulnerability. The most likely hypothesis is that this was a targeted attack exploiting emerging AI technologies. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The Reprompt attack was a targeted effort by sophisticated threat actors aiming to exploit specific vulnerabilities in emerging AI technologies. Supporting evidence includes the complexity of the attack chain and the focus on bypassing security controls. Key uncertainties involve the identity and motivations of the attackers.
- Hypothesis B: The attack was an opportunistic attempt by less sophisticated actors leveraging publicly available information on AI vulnerabilities. This is supported by the relatively simple execution method (a single click) and the lack of direct user interaction required. However, the sophisticated chaining of techniques contradicts this hypothesis.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the complexity and specificity of the attack techniques used, indicating a higher level of planning and capability. Indicators that could shift this judgment include new information on the attackers’ identity or additional similar attacks using less sophisticated methods.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The attack required significant planning and technical expertise; Microsoft’s patch effectively mitigates the vulnerability; similar vulnerabilities exist in other AI systems.
- Information Gaps: The identity and motivations of the threat actors; the extent of data compromised before the patch; potential for similar vulnerabilities in other AI platforms.
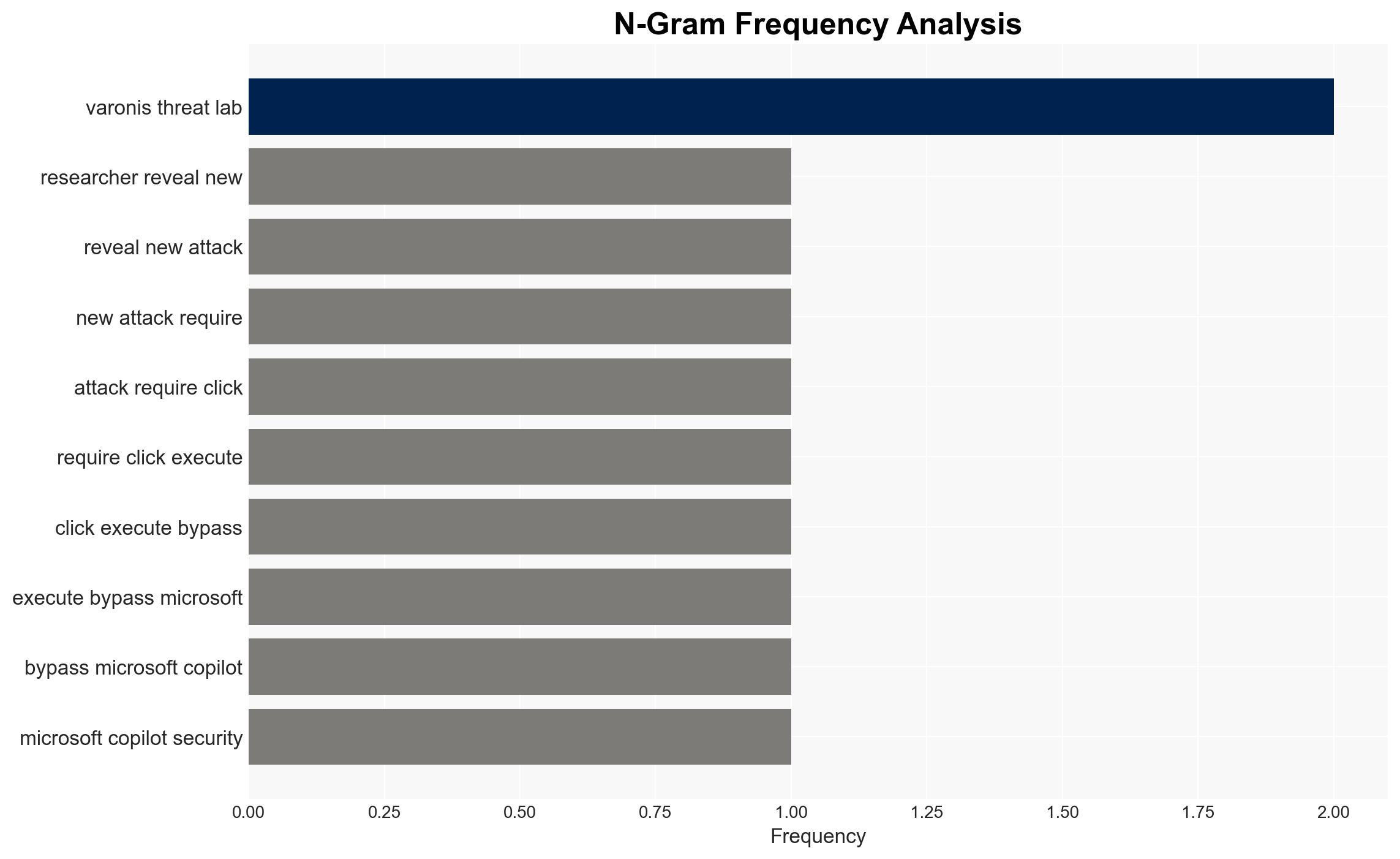
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in assuming high sophistication of attackers; reliance on Varonis Threat Labs as a single source; possibility of attackers using deception to obscure their methods.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development highlights the evolving threat landscape associated with AI technologies and the need for robust security measures. Over time, similar attacks could become more frequent and sophisticated, impacting various sectors.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased scrutiny on AI security could lead to regulatory changes and international cooperation on cybersecurity standards.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Potential for AI vulnerabilities to be exploited by state or non-state actors for espionage or disruptive operations.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened awareness of AI-related vulnerabilities may drive innovation in cybersecurity solutions and threat detection capabilities.
- Economic / Social: Breaches of AI systems could undermine trust in AI technologies, affecting adoption rates and economic growth in tech sectors.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive review of AI security protocols; enhance monitoring for similar attack patterns; engage with cybersecurity experts to assess potential vulnerabilities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with AI developers for collaborative security efforts; invest in AI-specific cybersecurity training and resources; establish a framework for rapid response to AI-related threats.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Enhanced security measures prevent further exploitation, and AI adoption continues to grow securely.
- Worst Case: Widespread exploitation of AI vulnerabilities leads to significant data breaches and loss of trust in AI technologies.
- Most Likely: Incremental improvements in AI security reduce but do not eliminate vulnerabilities, with periodic incidents prompting ongoing vigilance.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Microsoft
- Varonis Threat Labs
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
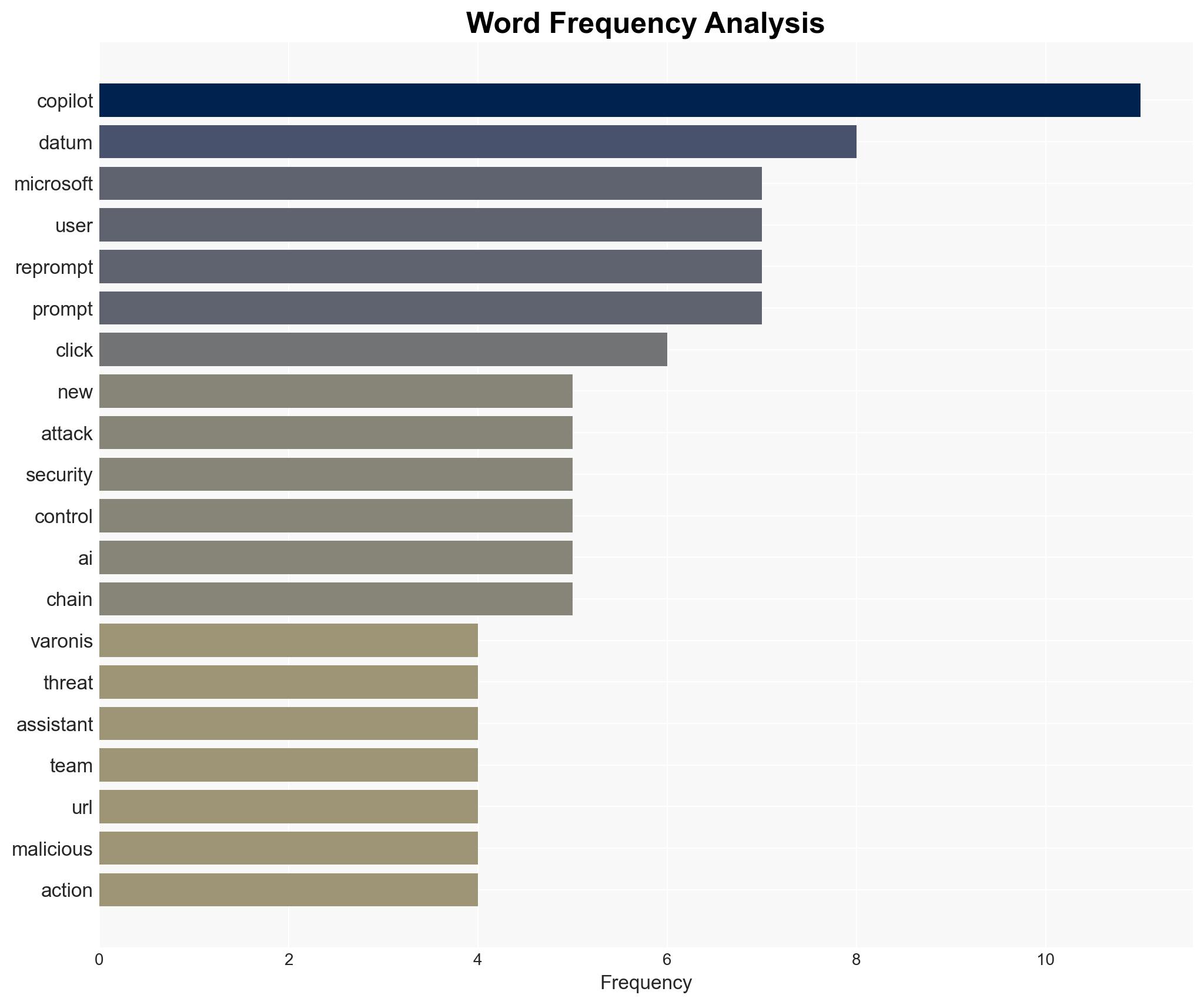
cybersecurity, AI vulnerabilities, data exfiltration, Microsoft, threat actors, information security, emerging technologies
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us