New Bluetooth vulnerability in earbuds could enable remote eavesdropping; mitigation steps available.
Published on: 2026-01-17
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: A new earbud security flaw may expose you to remote eavesdropping – here’s how to fix it
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
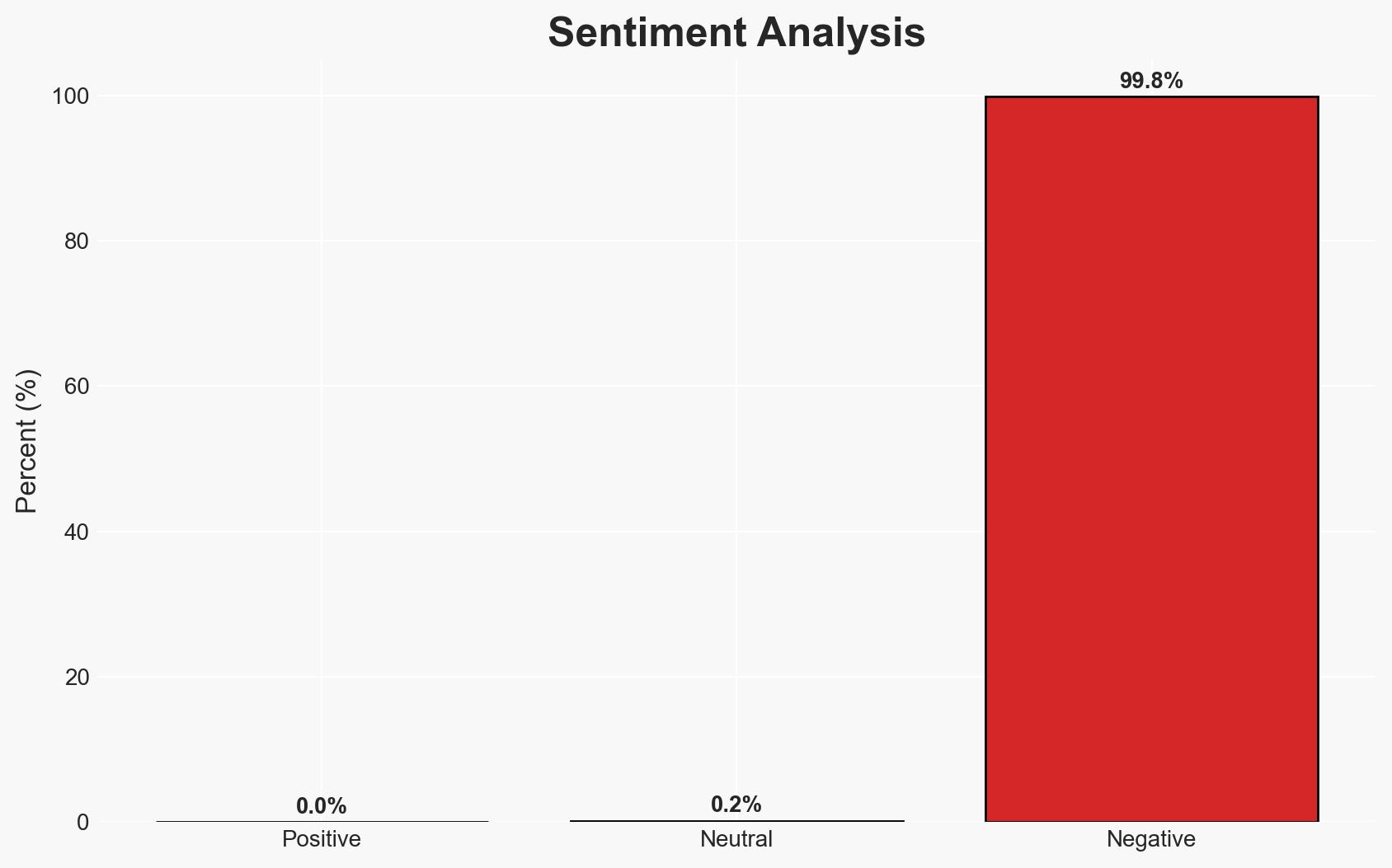
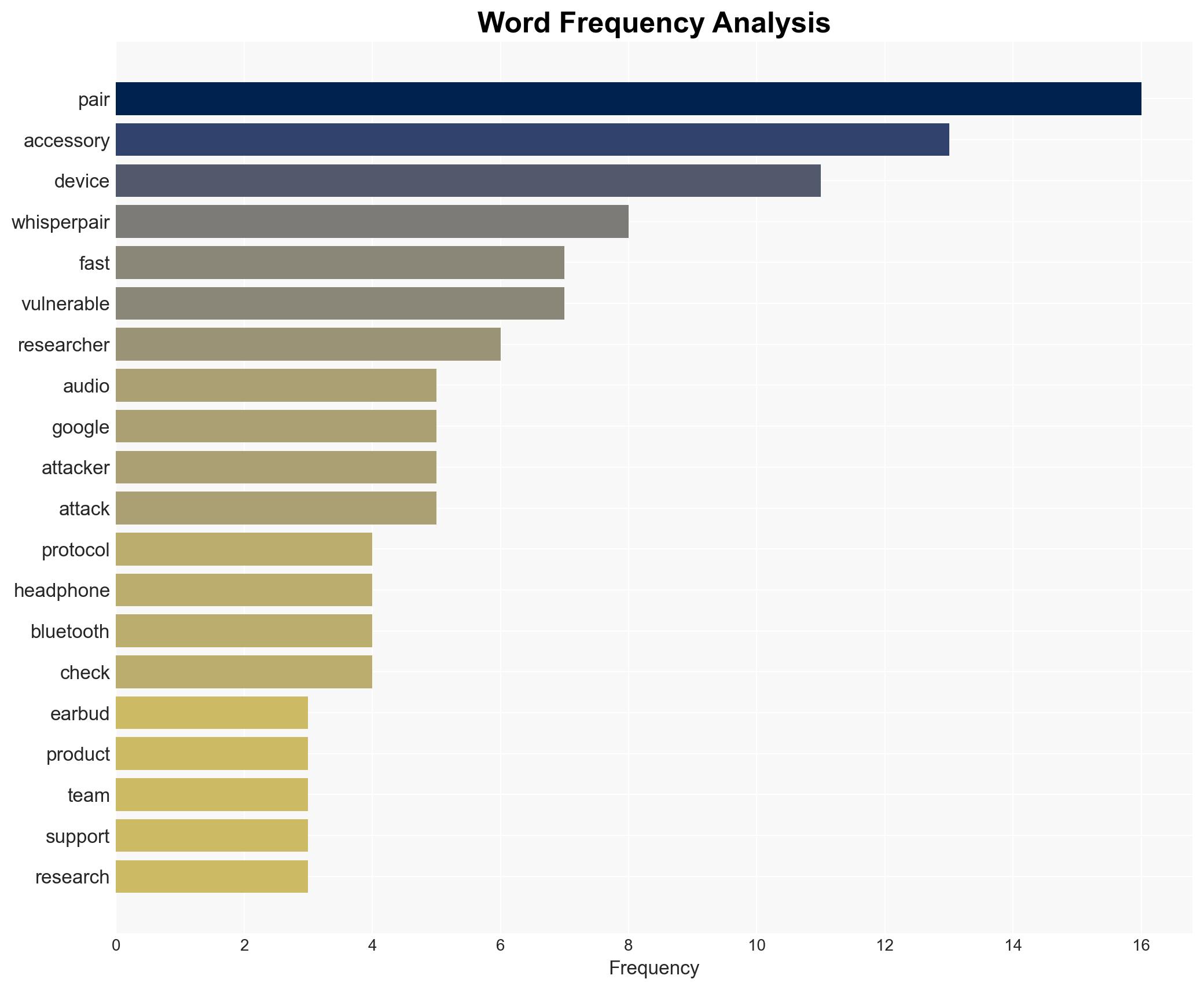
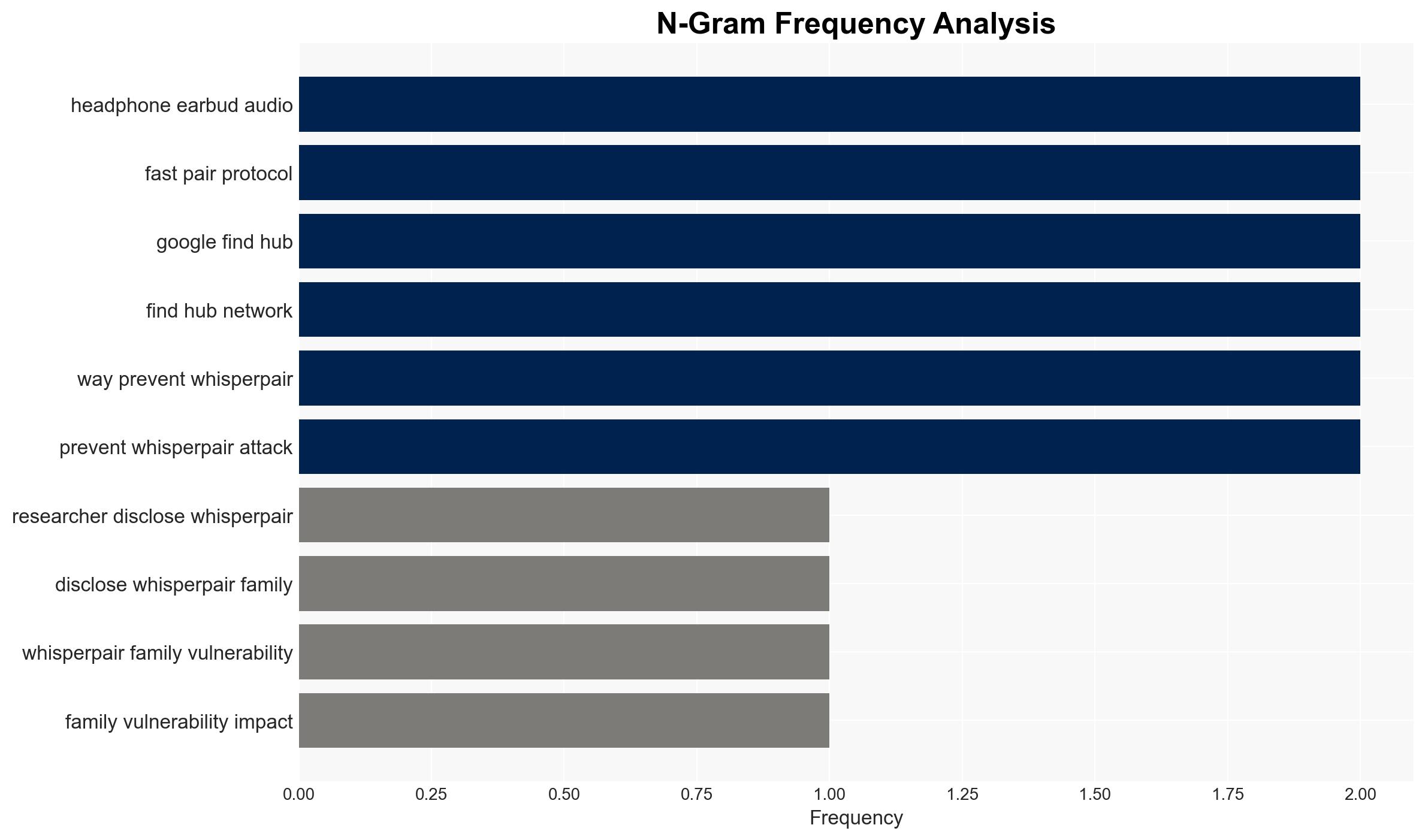
The WhisperPair vulnerability in Bluetooth audio devices poses a significant eavesdropping and tracking risk, affecting both Android and iPhone users. This flaw, primarily due to improper implementation of Google’s Fast Pair protocol, allows unauthorized access and control over audio accessories. The vulnerability is currently assessed with moderate confidence due to the limited scope of testing and potential for broader impact.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: WhisperPair is a widespread vulnerability affecting a large number of Bluetooth audio devices due to systemic implementation flaws in the Fast Pair protocol. This is supported by the identification of multiple affected brands and the critical CVE rating. However, the extent of affected devices remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: WhisperPair is a limited issue, primarily affecting a small subset of devices due to specific implementation errors by certain manufacturers. This hypothesis is less supported due to the broad range of brands identified as vulnerable, but it cannot be ruled out without more comprehensive testing data.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the critical nature of the vulnerability and the involvement of multiple major brands. Further data on the implementation practices of other manufacturers could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The vulnerability is primarily due to improper protocol implementation; the list of affected devices is comprehensive; attackers have the capability to exploit this flaw at scale.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the number of devices affected and the specific conditions under which the vulnerability can be exploited are lacking.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in the reporting due to reliance on a single research team’s findings; no independent verification of the vulnerability’s scope.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The WhisperPair vulnerability could lead to increased eavesdropping and tracking incidents, affecting user privacy and security. If not addressed, it may undermine trust in Bluetooth technology and associated brands.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for international scrutiny on tech companies’ security practices, impacting regulatory environments.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of exploitation by malicious actors for espionage or targeted attacks.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened awareness and potential for increased cyber defense measures among consumers and manufacturers.
- Economic / Social: Possible economic impact on affected brands due to loss of consumer confidence and potential recalls or fixes.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Encourage manufacturers to issue patches, conduct awareness campaigns for users, and monitor for exploitation attempts.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop industry standards for Bluetooth security, enhance collaboration between tech companies and cybersecurity agencies.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Vulnerability is swiftly patched, restoring consumer confidence. Worst: Widespread exploitation leads to significant privacy breaches. Most-Likely: Gradual patching with sporadic exploitation incidents.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Google, Sony, Harman (JBL), Anker, KU Leuven University
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, Bluetooth vulnerabilities, eavesdropping, privacy risks, technology standards, consumer electronics
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us