New South Wales enacts stringent gun ownership laws in response to Bondi Beach tragedy
Published on: 2025-12-24
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: New South Wales tightens gun laws after Bondi Hanukkah massacre
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
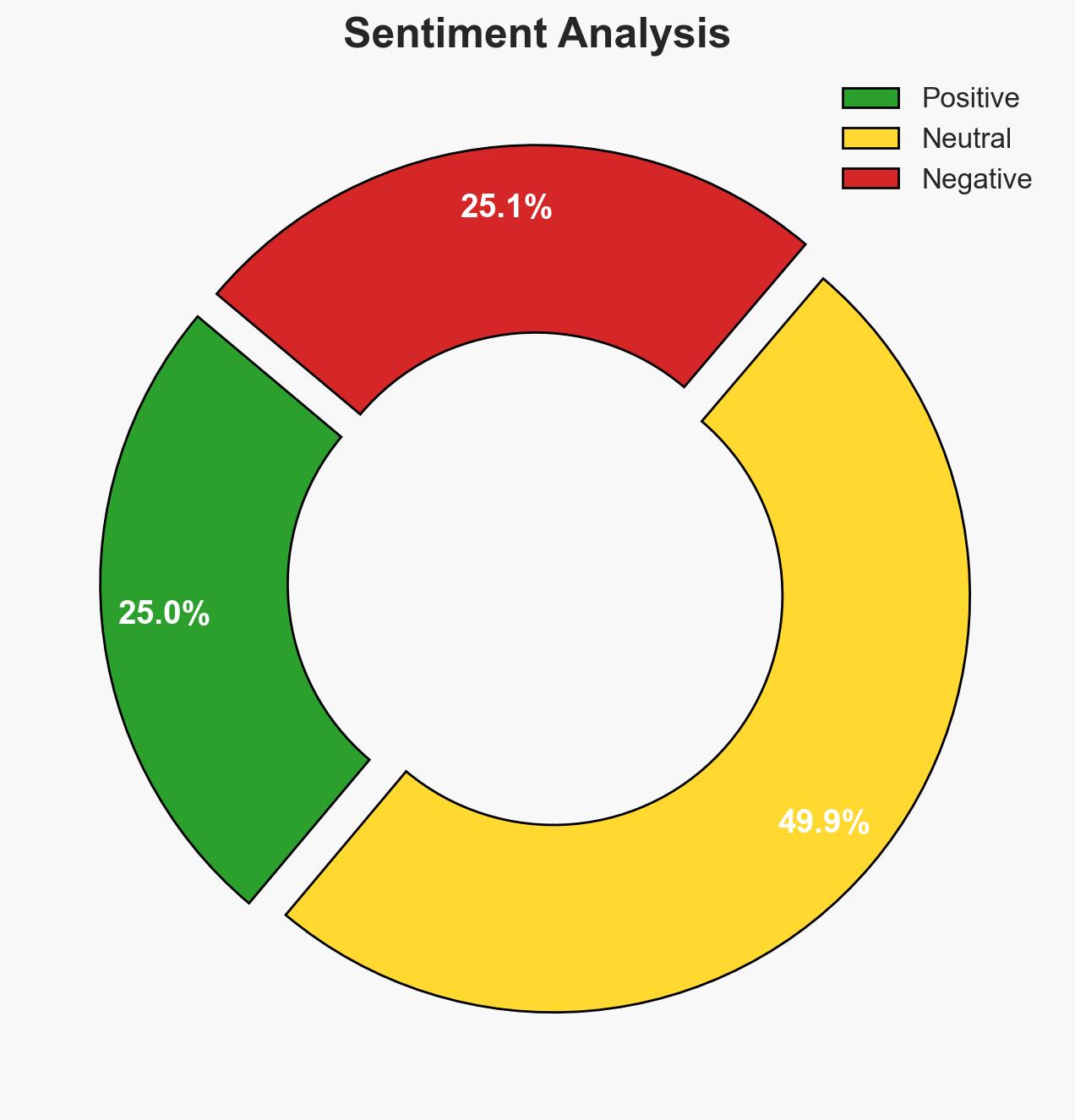
The New South Wales government has enacted stringent gun control measures and protest restrictions following a terrorist attack in Bondi. This legislative response aims to enhance public safety and mitigate future threats. The measures are likely to face scrutiny regarding their effectiveness and potential civil liberties implications. Overall, there is moderate confidence in the assessment that these actions will temporarily reduce the immediate threat level but may provoke political and social contention.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The new laws will effectively reduce the risk of future terrorist attacks by limiting access to firearms and controlling public gatherings. Supporting evidence includes the immediate legislative response to a high-profile attack and historical precedents of gun control reducing violence. Key uncertainties include the adaptability of terrorist tactics and the enforceability of protest bans.
- Hypothesis B: The legislative measures will have limited impact on reducing terrorism risk and may exacerbate social tensions. This is supported by potential civil liberties challenges and the possibility of radicalization through perceived government overreach. Contradicting evidence includes public support for safety measures and the potential deterrent effect of stricter laws.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the immediate need for a security response and historical success of gun control in Australia. However, indicators such as increased social unrest or legal challenges could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The new laws will be effectively enforced; public support for safety measures will remain stable; terrorist groups will not rapidly adapt tactics.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the operational capabilities of terrorist groups in Australia; public sentiment analysis post-legislation; effectiveness metrics of previous gun buyback programs.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential government bias towards overestimating the effectiveness of legislative measures; media portrayal may not accurately reflect public sentiment; risk of terrorist groups using misinformation to exploit social divisions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to a temporary reduction in the likelihood of similar attacks but may also trigger political and social backlash. Over time, the effectiveness of these measures will depend on enforcement and public perception.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased political polarization and challenges to civil liberties; international scrutiny of Australia’s counter-terrorism strategies.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Short-term decrease in attack risk; potential for terrorist groups to adapt tactics or target less protected areas.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased risk of online radicalization and propaganda; potential for cyber campaigns targeting public opinion.
- Economic / Social: Possible economic impact from protest bans; social cohesion may be strained by perceived overreach or ineffective measures.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance intelligence sharing with federal agencies; monitor public sentiment and legal challenges; assess enforcement capabilities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop community engagement programs to address radicalization; strengthen partnerships with civil society to balance security and civil liberties.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Successful reduction in attack risk with public support. Worst: Increased social unrest and ineffective enforcement. Most-Likely: Temporary reduction in risk with ongoing political debate.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Chris Minns (State Premier of New South Wales)
- New South Wales Parliament
- Federal Government of Australia
- Islamic State (referenced in attack motivation)
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, counter-terrorism, gun control, civil liberties, public safety, legislative response, social cohesion, radicalization
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us