New UEFI vulnerability exposes Gigabyte, MSI, ASUS, and ASRock motherboards to DMA attack risks; firmware upd…
Published on: 2025-12-22
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
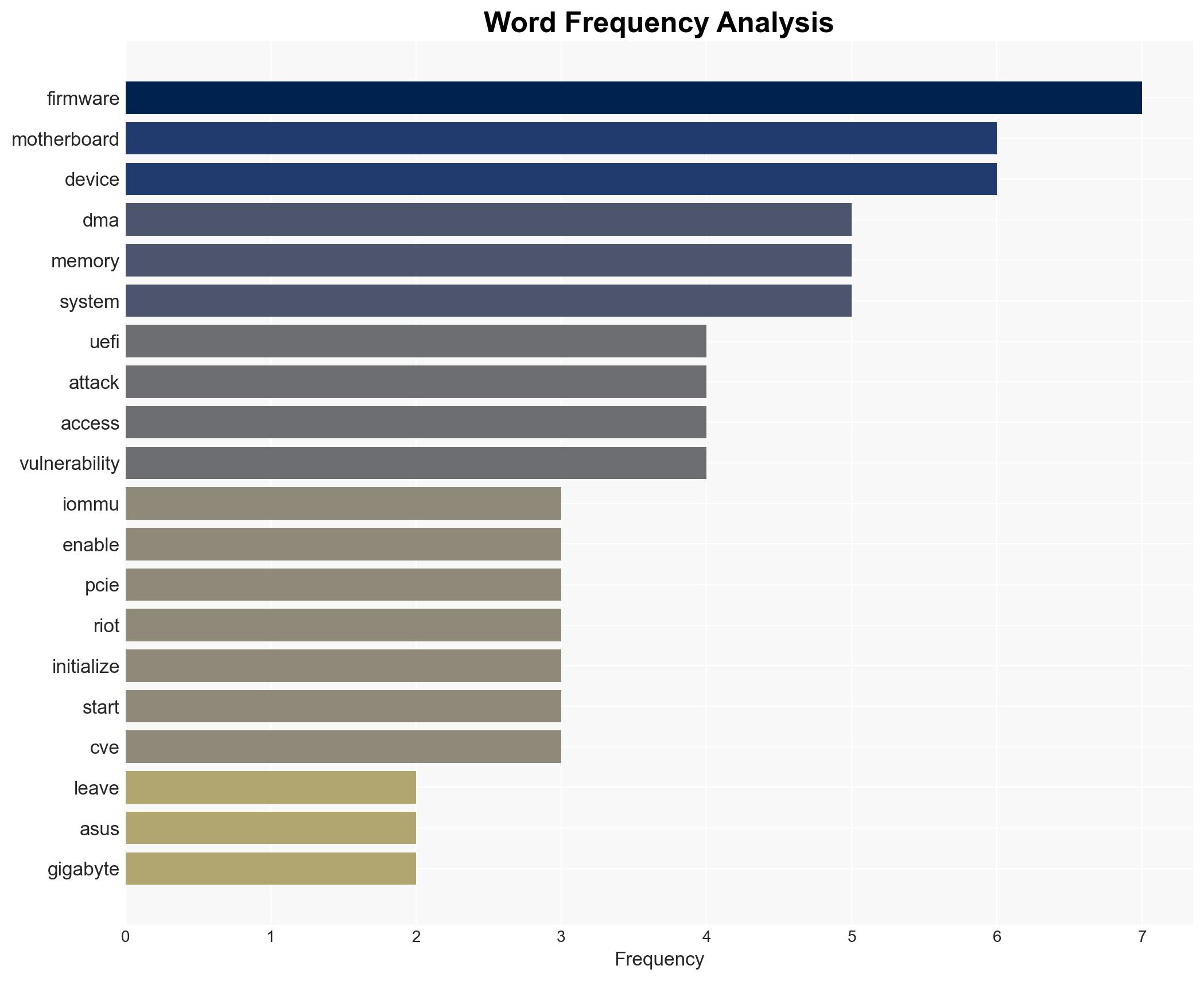
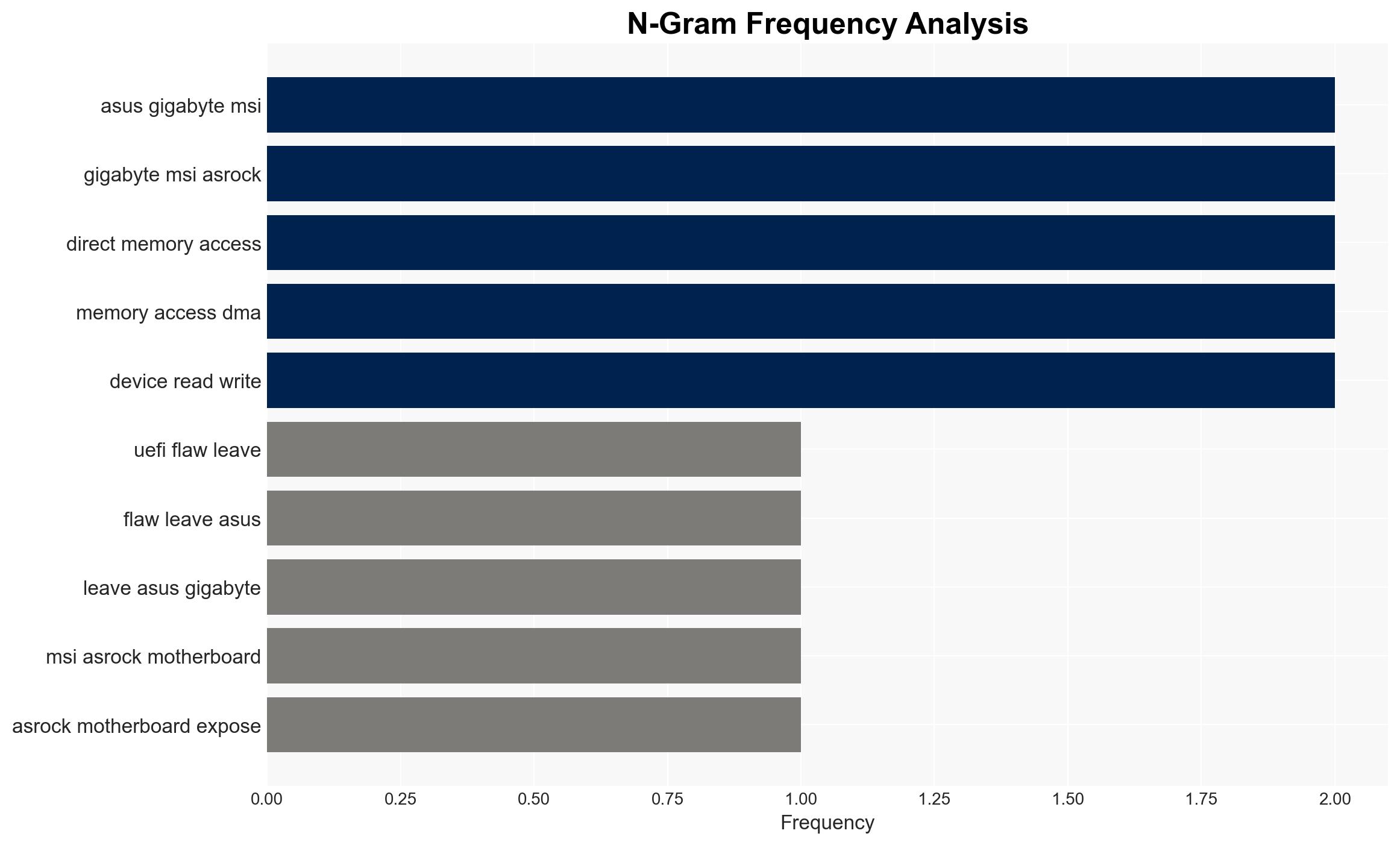
Intelligence Report: Motherboards from Gigabyte MSI ASUS ASRock at risk from new UEFI flaw attack – here’s what we know
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
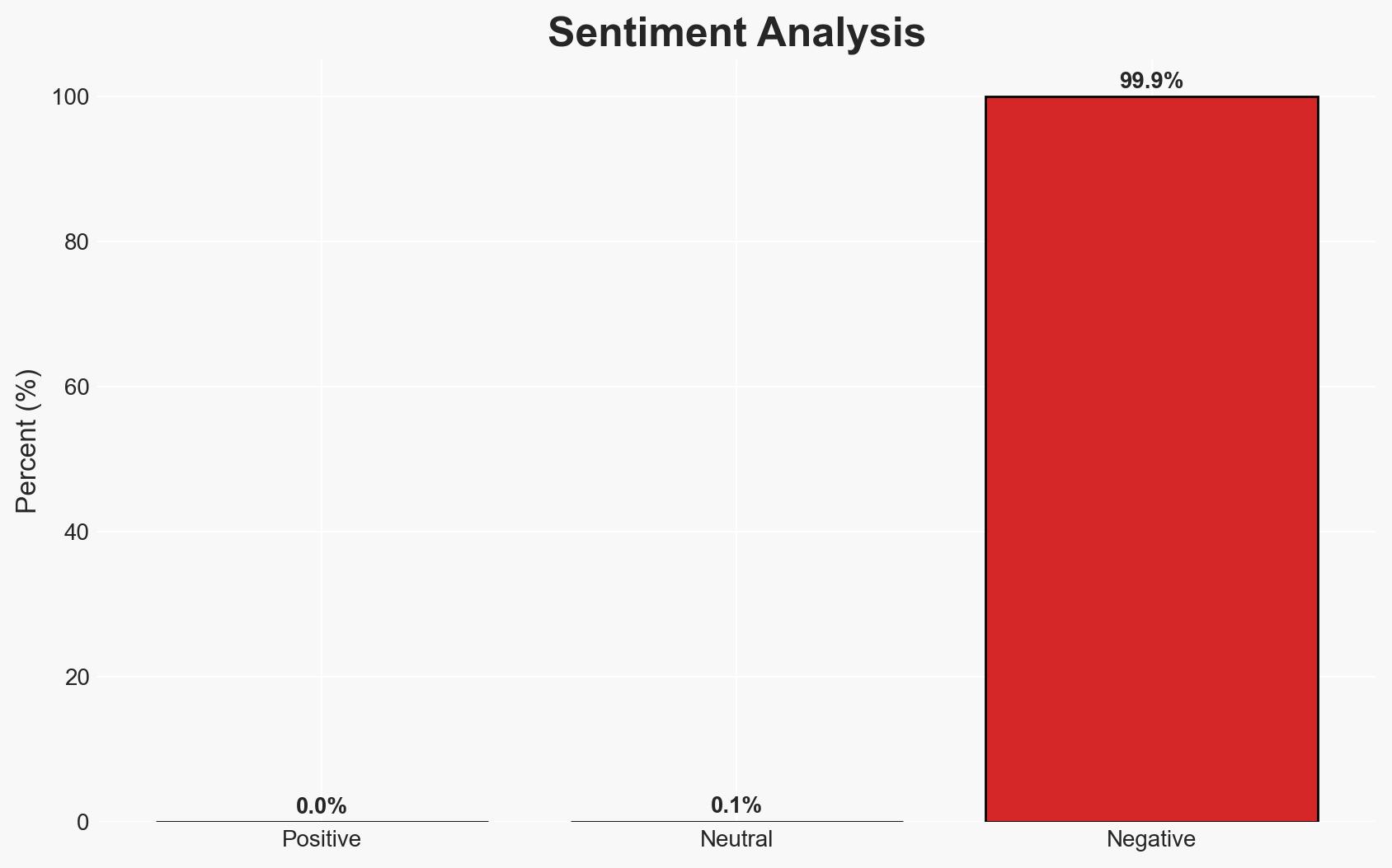
A vulnerability in UEFI firmware affecting ASUS, Gigabyte, MSI, and ASRock motherboards exposes systems to direct memory access (DMA) attacks. This flaw could lead to unauthorized access to sensitive data. The most likely hypothesis is that this vulnerability is primarily a technical oversight rather than a deliberate act, with moderate confidence due to limited information on the origin of the flaw.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The UEFI vulnerability is a result of a technical oversight during firmware development. Evidence includes the complexity of UEFI implementations and the variability in vendor firmware, which supports accidental misconfiguration. However, the lack of detailed technical documentation on the flaw introduces uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: The vulnerability is an intentional backdoor introduced for malicious purposes. This is contradicted by the lack of direct evidence of malicious intent and the discovery by a third-party (Riot Games) rather than through adversarial exploitation.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the absence of direct evidence of malicious intent and the complexity of UEFI firmware, which makes accidental misconfigurations plausible. Indicators such as discovery of similar flaws in other contexts could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The vulnerability is not yet widely exploited; firmware updates will effectively mitigate the risk; the flaw is not a result of coordinated malicious activity.
- Information Gaps: Detailed technical analysis of the vulnerability’s origin; comprehensive data on the extent of affected systems; evidence of any exploitation in the wild.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in vendor reporting due to reputational concerns; risk of underreporting exploitation to avoid panic.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This vulnerability could lead to increased cyber threats if exploited, affecting both individual users and organizations. The situation may evolve as more technical details emerge and as adversaries potentially exploit the flaw.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if state actors are suspected of exploiting the flaw.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of cyber espionage and data breaches, particularly targeting sensitive sectors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on firmware security and potential for widespread patching efforts.
- Economic / Social: Possible economic impact on affected vendors and loss of consumer trust if not addressed promptly.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor for exploitation attempts; encourage users to apply firmware updates; engage with vendors for technical briefings.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for enhanced threat detection; invest in research for firmware security improvements.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Vulnerability is patched with no significant exploitation, leading to improved firmware security practices.
- Worst: Widespread exploitation leads to significant data breaches and loss of trust in affected vendors.
- Most-Likely: Limited exploitation occurs, prompting increased security measures and awareness.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- ASUS
- Gigabyte
- MSI
- ASRock
- Riot Games
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, firmware vulnerability, UEFI, DMA attacks, motherboard security, vendor response, cyber threat mitigation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us