News outlets reject Pentagon’s new press rules – DW (English)
Published on: 2025-10-15
Intelligence Report: News outlets reject Pentagon’s new press rules – DW (English)
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The most supported hypothesis is that the Pentagon’s new press rules are primarily intended to enhance operational security, but they inadvertently threaten press freedoms, leading to widespread media rejection. Confidence level: Moderate. Recommended action: Engage in dialogue with media organizations to address concerns while maintaining necessary security protocols.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis A**: The Pentagon’s new press rules are designed to tighten security and prevent unauthorized disclosures, with no intention to infringe on press freedoms. This hypothesis suggests that the rules are a response to recent security breaches or leaks.
2. **Hypothesis B**: The new rules are a strategic move to control media narratives and limit journalistic scrutiny of military operations, under the guise of security concerns. This hypothesis implies a deliberate attempt to suppress critical reporting.
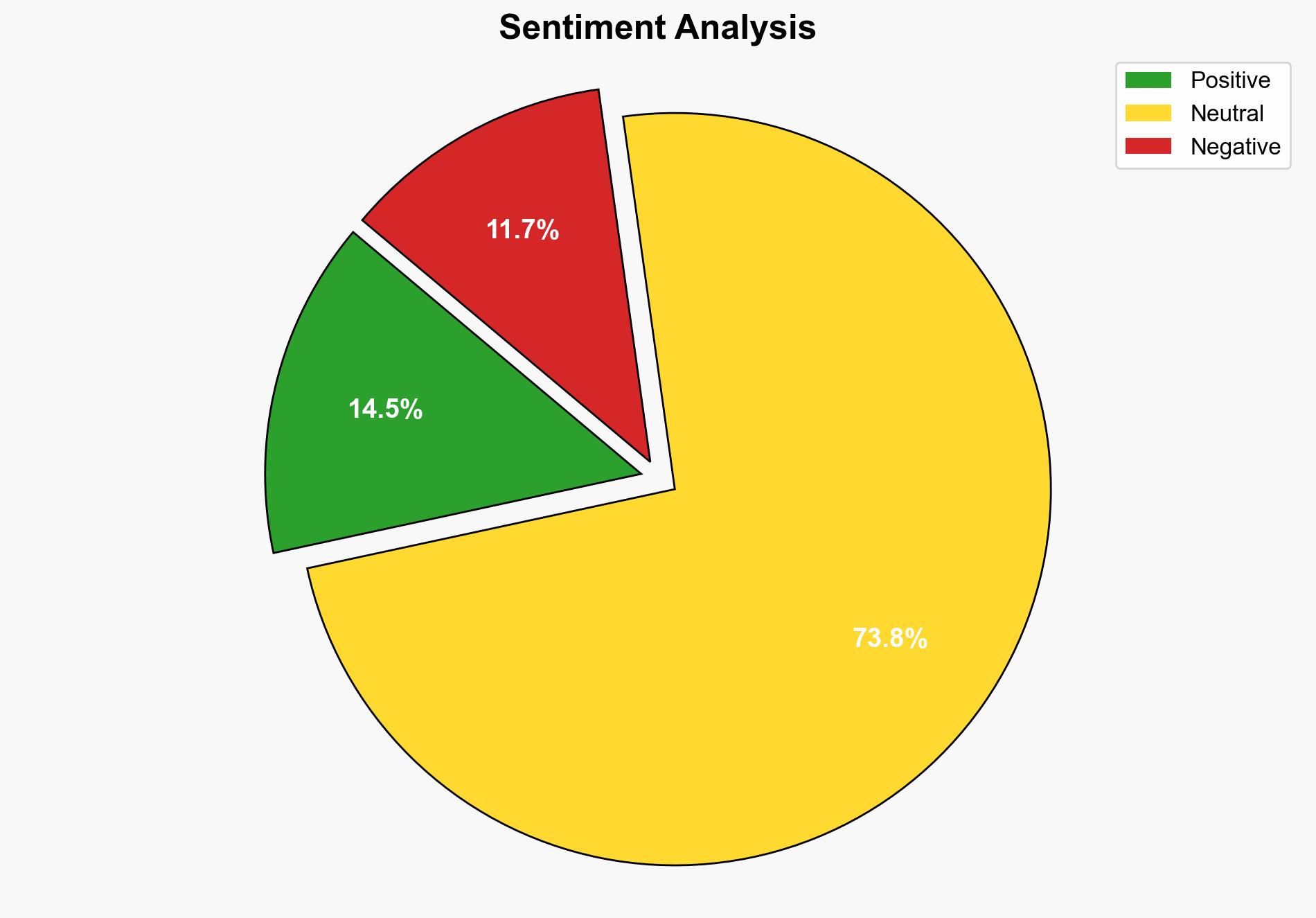
Using ACH 2.0, Hypothesis A is better supported by the Pentagon’s emphasis on national security and the common sense rationale provided by Pete Hegseth. However, the strong opposition from major news outlets and the potential constitutional implications lend some credibility to Hypothesis B.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: Hypothesis A assumes that the Pentagon’s primary motive is security-related and that the media’s concerns are secondary. Hypothesis B assumes a more adversarial relationship between the Pentagon and the press.
– **Red Flags**: The lack of transparency about specific security threats necessitating these rules raises questions. The absence of any news organization signing the new policy suggests widespread dissent and potential overreach by the Pentagon.
– **Blind Spots**: The potential impact on international media relations and the broader implications for press freedom globally are not addressed in the current discourse.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
– **Patterns**: A trend of increasing tension between government entities and the press could lead to a chilling effect on journalistic practices.
– **Cascading Threats**: If unresolved, this conflict could escalate into legal battles or legislative interventions, impacting both national security operations and media freedoms.
– **Geopolitical Dimensions**: International perception of U.S. commitment to free press principles may be adversely affected, influencing diplomatic relations.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Initiate a roundtable discussion between the Pentagon and media representatives to clarify security needs and address press freedom concerns.
- Develop a transparent framework for media access that balances security with journalistic integrity.
- Scenario Projections:
- Best Case: A revised policy that satisfies both security requirements and media freedoms, enhancing mutual trust.
- Worst Case: Legal challenges and international criticism leading to strained relations and operational disruptions.
- Most Likely: Continued negotiations with incremental policy adjustments.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Pete Hegseth
– Sean Parnell
– Zac Crellin
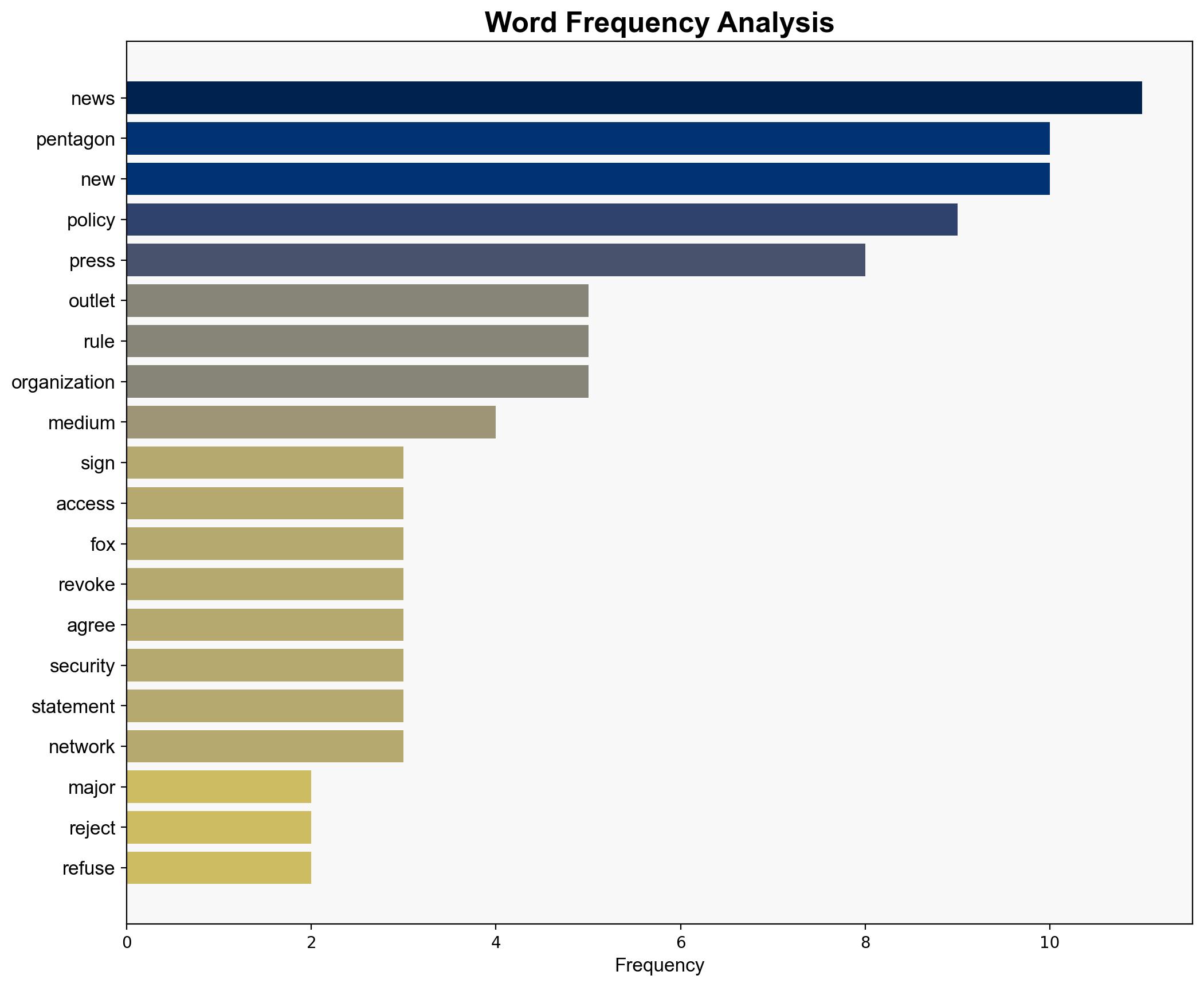
– Major news organizations: New York Times, Associated Press, Reuters, AFP, Fox News
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, media relations, press freedom, U.S. military policy