Ninety seconds could have saved lives on Baltimore bridge US agency – CNA
Published on: 2025-11-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report:
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
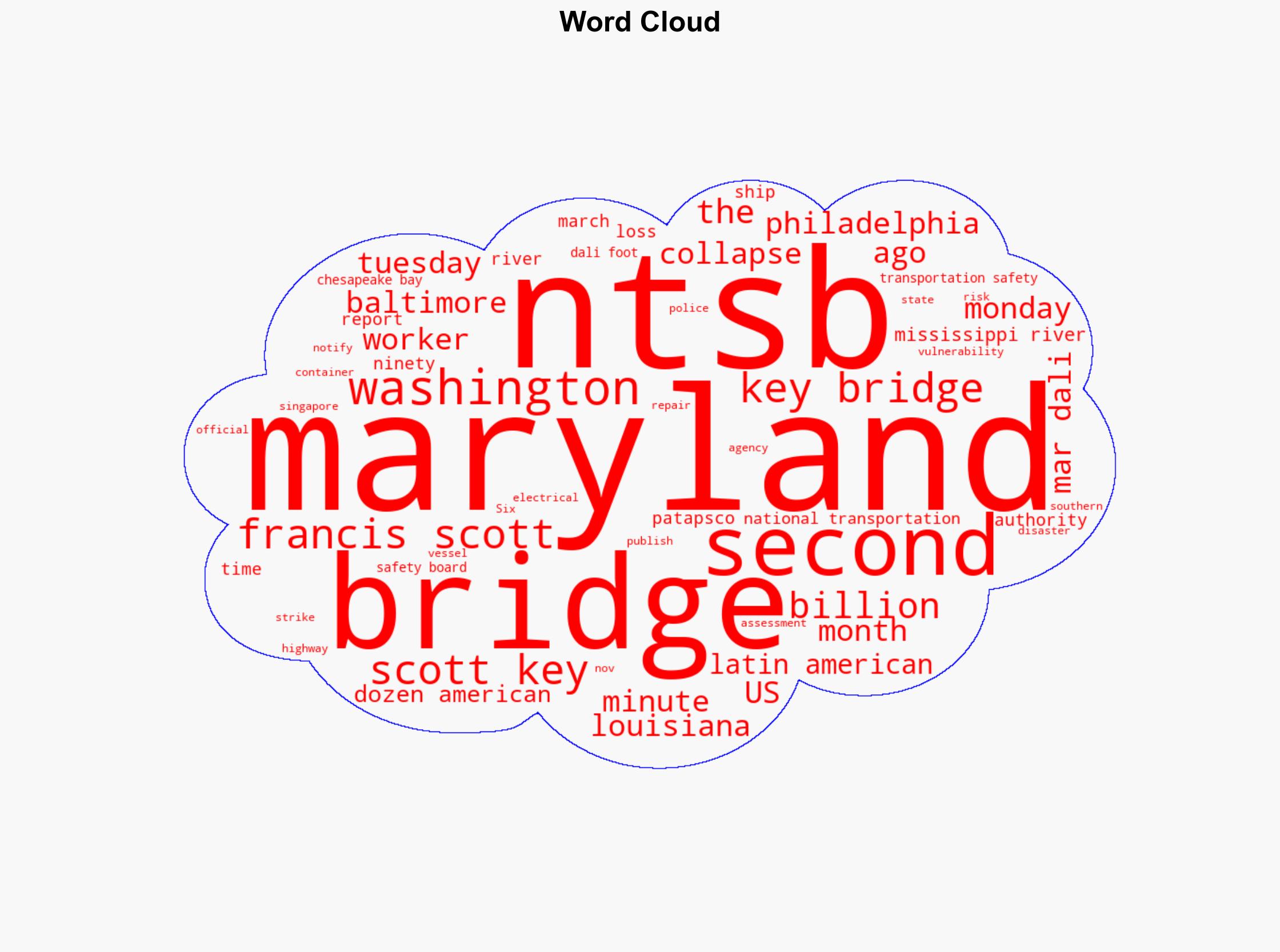
The most supported hypothesis is that the disaster on the Francis Scott Key Bridge was primarily due to systemic failures in communication and infrastructure vulnerability assessment. The confidence level in this hypothesis is moderate, given the available evidence and identified gaps. Immediate strategic recommendations include enhancing communication protocols and conducting comprehensive vulnerability assessments on critical infrastructure to prevent similar incidents.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The incident was primarily caused by a failure in communication and infrastructure vulnerability assessment.
Hypothesis 2: The incident was primarily due to unforeseen technical failures on the container ship, with communication and infrastructure issues being secondary.
Assessment: Hypothesis 1 is more likely given the NTSB findings that highlight a lack of effective communication and failure to conduct a vulnerability assessment. While technical failures on the ship were significant, the systemic issues in communication and infrastructure management appear to be the root cause.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: It is assumed that the NTSB’s findings are comprehensive and unbiased. There is also an assumption that the Maryland authority’s previous reports were accurate and complete.
Red Flags: The potential for bias in NTSB reporting due to political or organizational pressures. The possibility of incomplete data regarding the ship’s technical failures and the bridge’s structural integrity.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The incident underscores significant strategic risks, including the potential for similar infrastructure failures across the United States. Politically, there could be increased scrutiny on transportation safety regulations and funding allocations. Economically, the cost of repairs and potential litigation could strain state budgets. Informationally, public confidence in infrastructure safety may erode, leading to increased demand for transparency and accountability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Conduct immediate and thorough vulnerability assessments on all critical infrastructure, particularly those identified by the NTSB as at risk.
- Enhance communication protocols between maritime and highway authorities to ensure timely alerts and responses to potential threats.
- Best-case scenario: Successful implementation of recommendations leads to improved infrastructure safety and public confidence.
- Worst-case scenario: Failure to address systemic issues results in further incidents and loss of life.
- Most-likely scenario: Incremental improvements in communication and infrastructure assessments, with gradual restoration of public trust.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
NTSB officials, Maryland transportation authorities, and the operators of the Singapore-flagged container ship are central to the incident and subsequent investigations.
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, Infrastructure Safety, Communication Failures, Risk Assessment, Public Safety, Transportation Policy
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us