North Korean Cyber Actors Intensify Crypto Attacks with Advanced Malware and Social Engineering Tactics
Published on: 2026-02-11
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Google Cloud flags North Korea-linked crypto malware campaign
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
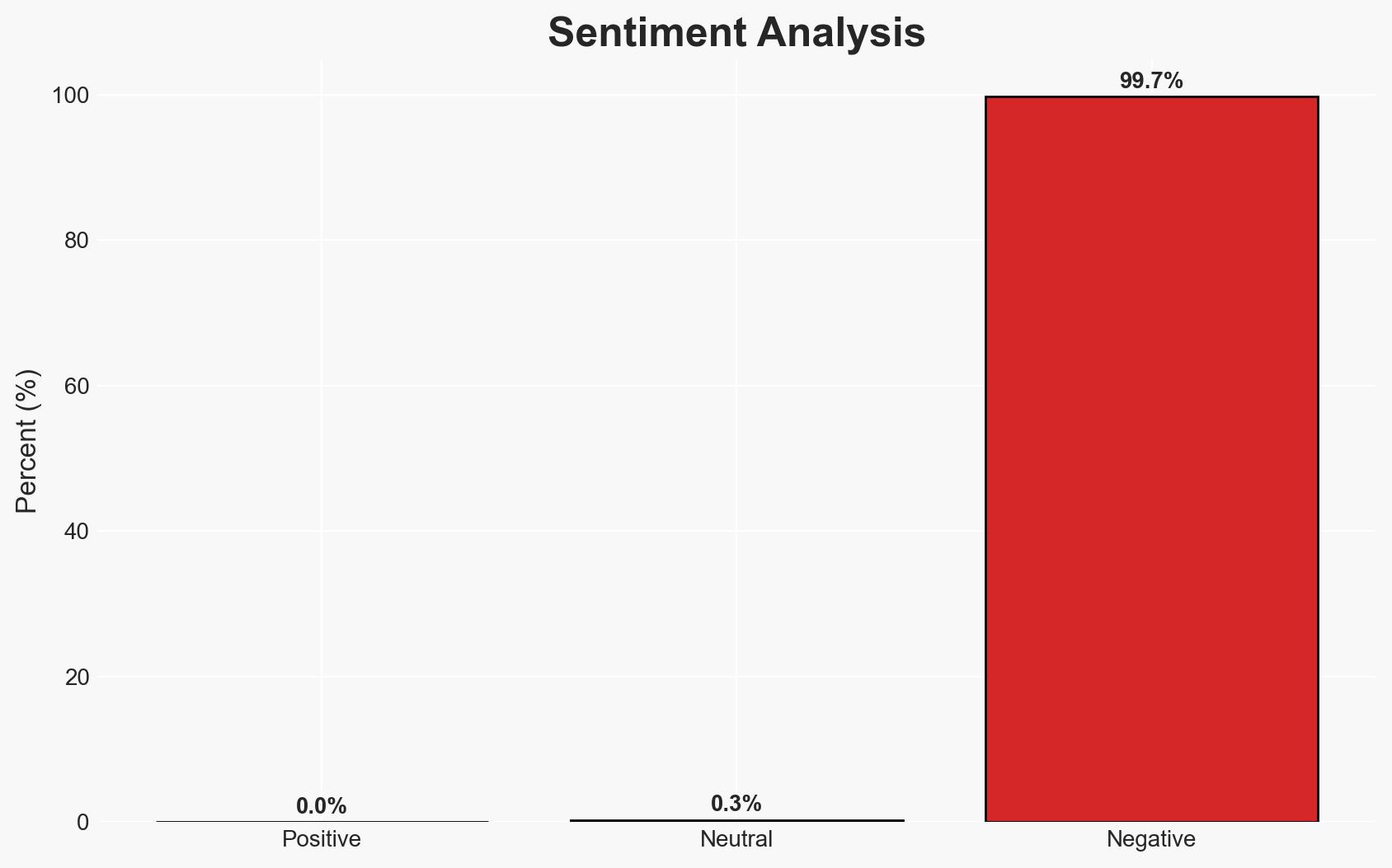
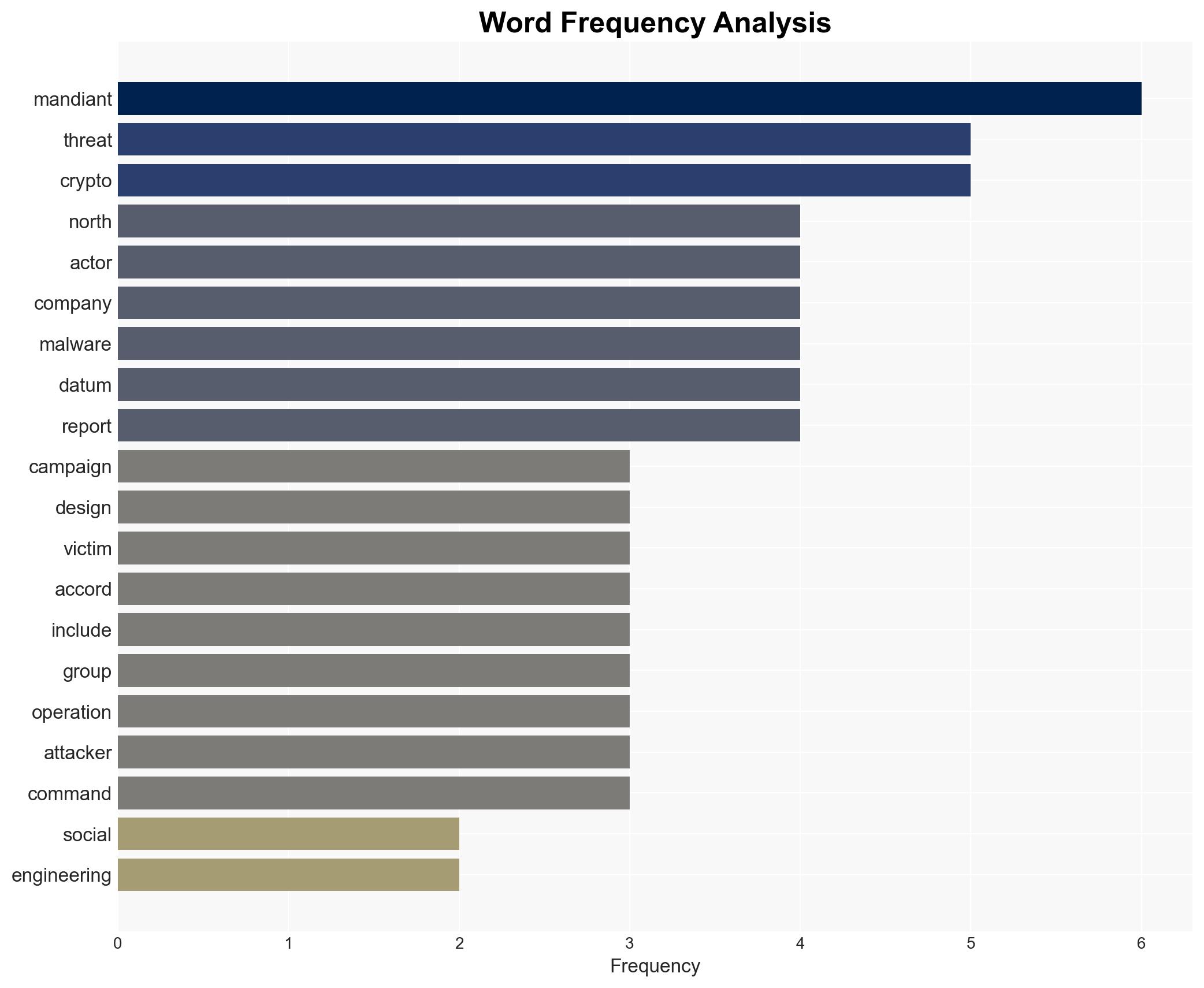
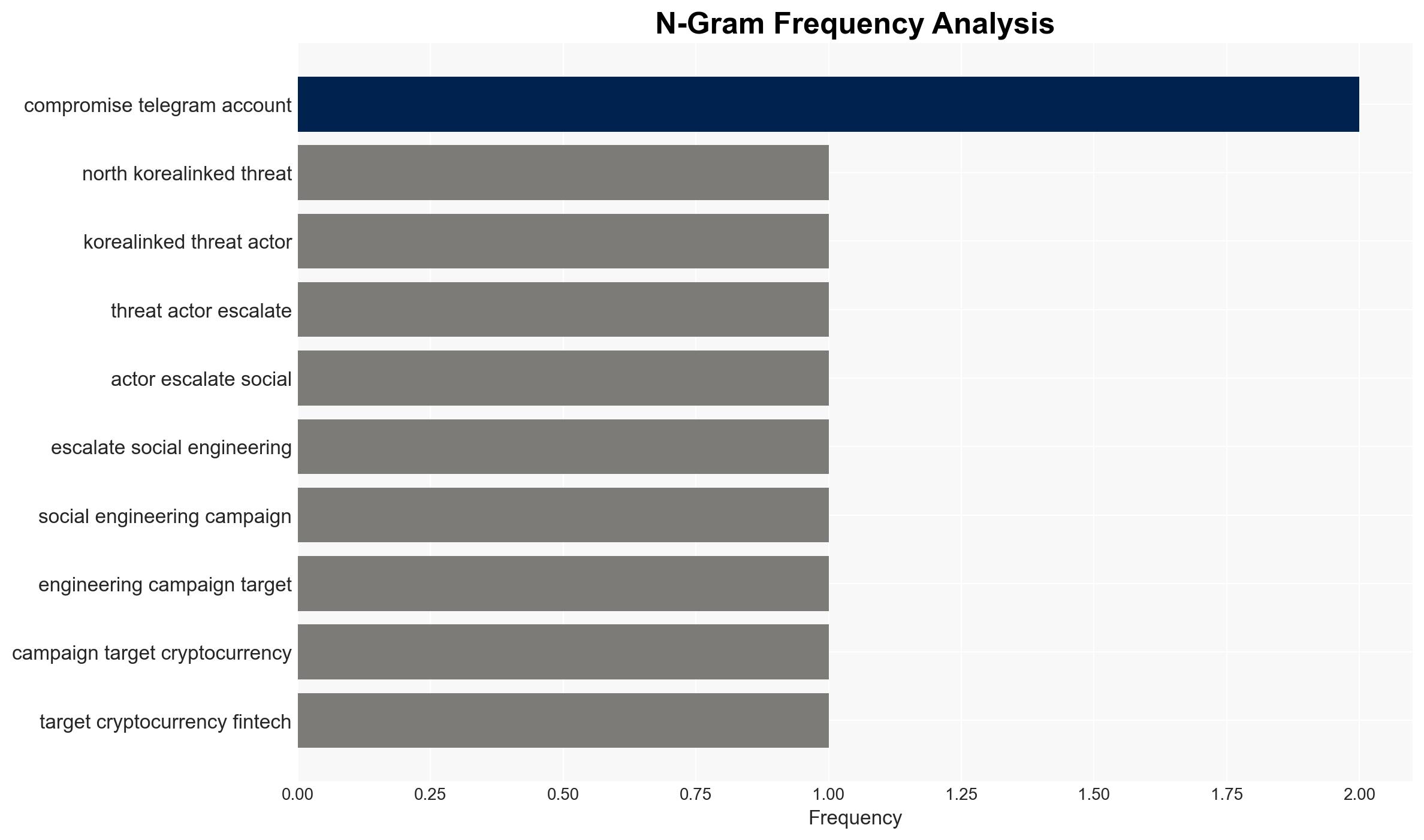
North Korea-linked threat actors are intensifying their cyber operations against cryptocurrency and fintech sectors, utilizing advanced social engineering and AI tools to deploy sophisticated malware. This campaign, identified by Mandiant, highlights a significant escalation in cyber capabilities and targeting strategies. The primary victims are crypto companies, software developers, and venture capital entities. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the reliance on open-source reporting and potential attribution challenges.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: North Korean state-sponsored actors are deliberately targeting the cryptocurrency sector to fund national objectives. This is supported by the sophistication of the malware and historical patterns of North Korean cyber activity. However, the exact level of state involvement remains uncertain due to potential proxy use.
- Hypothesis B: Independent cybercriminals with loose affiliations to North Korean entities are conducting these operations primarily for financial gain. The use of AI tools and social engineering could be indicative of broader cybercriminal trends rather than state sponsorship. Contradicting this is the scale and coordination typical of state-backed operations.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the alignment with known North Korean cyber tactics and strategic objectives. Indicators such as increased sophistication and targeting of financial assets suggest state-level coordination. Future attribution clarity and operational patterns could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The operations are centrally coordinated by North Korean state actors; AI tools are enhancing the effectiveness of traditional cyber tactics; the primary motive is financial gain to support state objectives.
- Information Gaps: Direct evidence of state sponsorship; detailed technical analysis of malware capabilities; comprehensive attribution data.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Confirmation bias towards state involvement due to historical patterns; potential misinformation from compromised sources; deception through AI-generated content.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased tensions in cyberspace, with potential retaliatory measures by affected states or companies. The use of AI in cyber operations may set a precedent for future campaigns.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential diplomatic fallout and increased sanctions against North Korea; heightened cyber defense collaboration among targeted nations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Escalation in cyber threat levels; increased demand for cybersecurity measures in the financial sector.
- Cyber / Information Space: Enhanced AI-driven cyber operations; potential for widespread adoption of similar tactics by other threat actors.
- Economic / Social: Financial instability in targeted sectors; erosion of trust in digital financial systems.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of North Korean cyber activities; implement advanced threat detection systems; increase awareness and training on social engineering tactics.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for intelligence sharing; invest in AI and machine learning for threat detection; strengthen international cyber norms and cooperation.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Improved international cooperation reduces threat impact. Worst: Escalation leads to significant financial losses and geopolitical tensions. Most-Likely: Continued cyber operations with incremental improvements in defense measures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, North Korea, cryptocurrency, social engineering, AI tools, malware, financial sector
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us