Not replacing jobs or homework Harvard study reveals how students and professionals are actually using AI tools – The Times of India
Published on: 2025-10-26
Intelligence Report: Not replacing jobs or homework Harvard study reveals how students and professionals are actually using AI tools – The Times of India
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
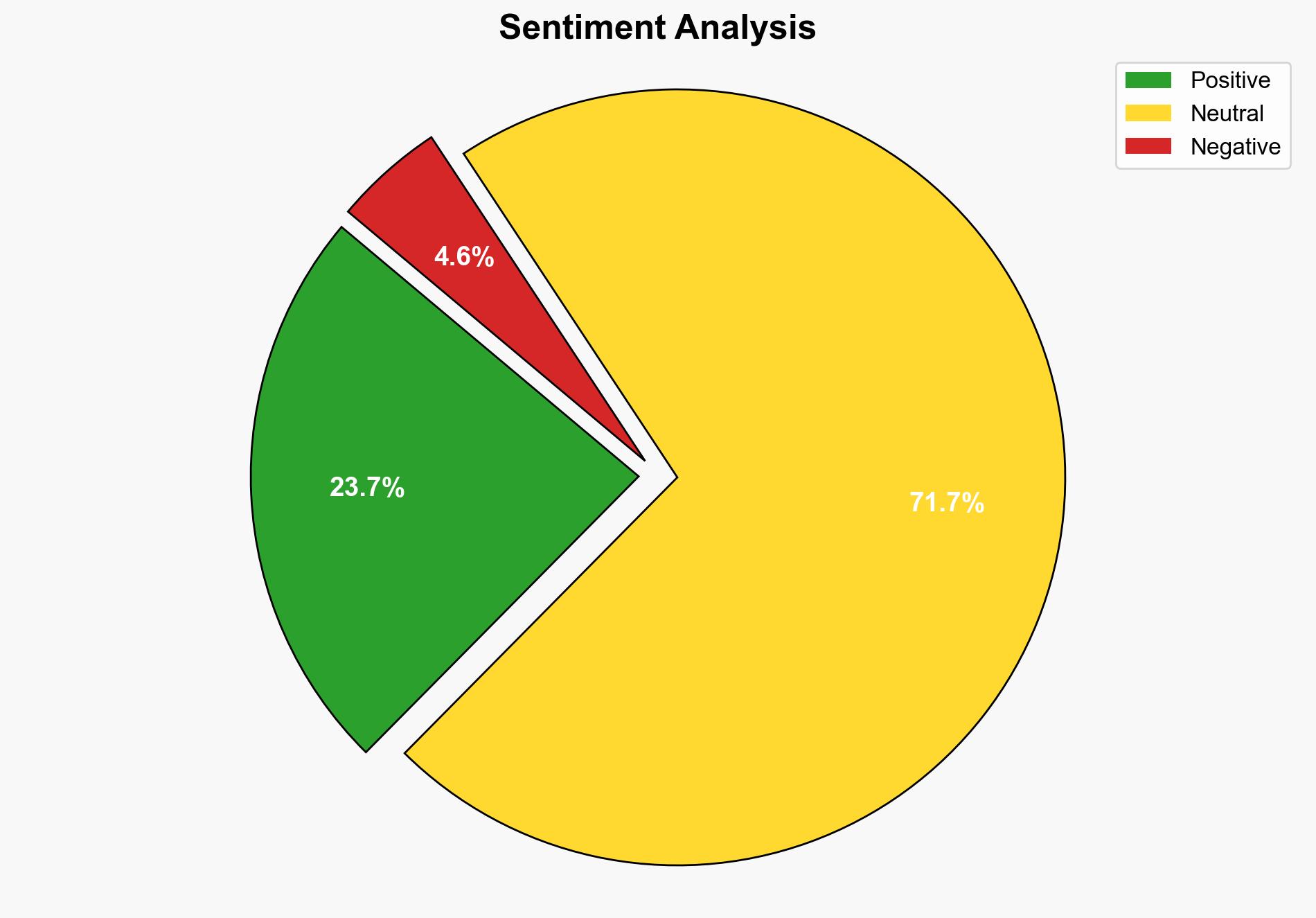
The strategic judgment is that AI tools like ChatGPT are currently being integrated as supportive aids rather than replacements in educational and professional settings. The most supported hypothesis is that AI enhances productivity and learning rather than displacing jobs or academic efforts. Confidence level: Moderate. Recommended action: Encourage the responsible integration of AI tools to enhance human capabilities while monitoring for potential misuse.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **AI as a Supportive Tool Hypothesis**: AI tools are primarily used to augment human capabilities, facilitating learning and productivity without replacing jobs or academic efforts. This hypothesis is supported by evidence of AI being used for clarifying concepts, summarizing information, and aiding in task management.
2. **AI as a Disruptive Force Hypothesis**: AI tools are subtly replacing human roles and efforts, potentially leading to job displacement and academic dishonesty. This hypothesis considers the potential for AI to automate tasks traditionally performed by humans, thereby reducing the need for human intervention.
Using ACH 2.0, the first hypothesis is better supported due to the lack of evidence indicating significant job displacement or widespread academic dishonesty directly attributed to AI use.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: It is assumed that AI tools are used ethically and that users are motivated to enhance rather than replace their efforts. Another assumption is that AI tools are accessible to a diverse range of users.
– **Red Flags**: Potential cognitive bias includes over-reliance on self-reported data from users. There is a risk of underestimating the long-term impact of AI on job markets and education systems. Inconsistencies may arise from varying levels of AI adoption across different regions and industries.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The integration of AI tools could lead to significant shifts in workforce dynamics, requiring new skill sets focused on AI collaboration. Economically, industries may face pressure to adapt or risk obsolescence. Psychologically, there may be increased anxiety over job security. Strategically, the risk of AI misuse in academic settings could undermine educational integrity.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Promote AI literacy programs to ensure ethical and effective use of AI tools.
- Encourage industries to develop frameworks for integrating AI without displacing workers.
- Monitor AI adoption trends to identify and mitigate potential negative impacts on job markets and education.
- Scenario-based projections:
- Best: AI tools enhance productivity and learning without significant job displacement.
- Worst: AI leads to widespread job loss and academic dishonesty.
- Most Likely: AI tools become integral to workflows, requiring adaptation but not causing major disruptions.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
David Deming, Danoff Dean of Harvard College, is a key individual mentioned in the study, providing insights into AI’s role in education and professional settings.
7. Thematic Tags
AI integration, educational technology, workforce adaptation, ethical AI use