Notepad++ Enhances Update Security Following Recent Supply Chain Attack
Published on: 2026-02-18
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
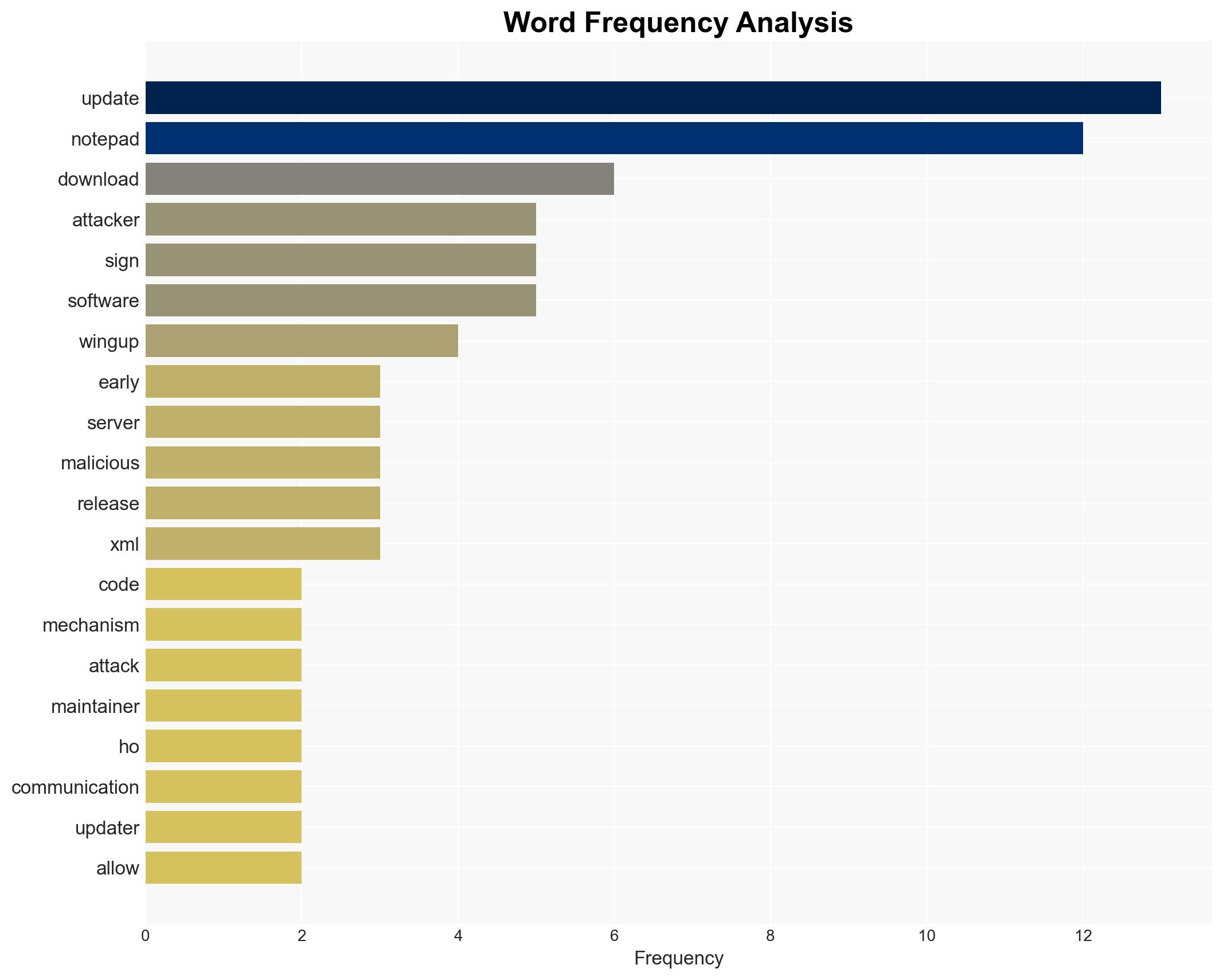
Intelligence Report: Notepad secures update channel in wake of supply chain compromise
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
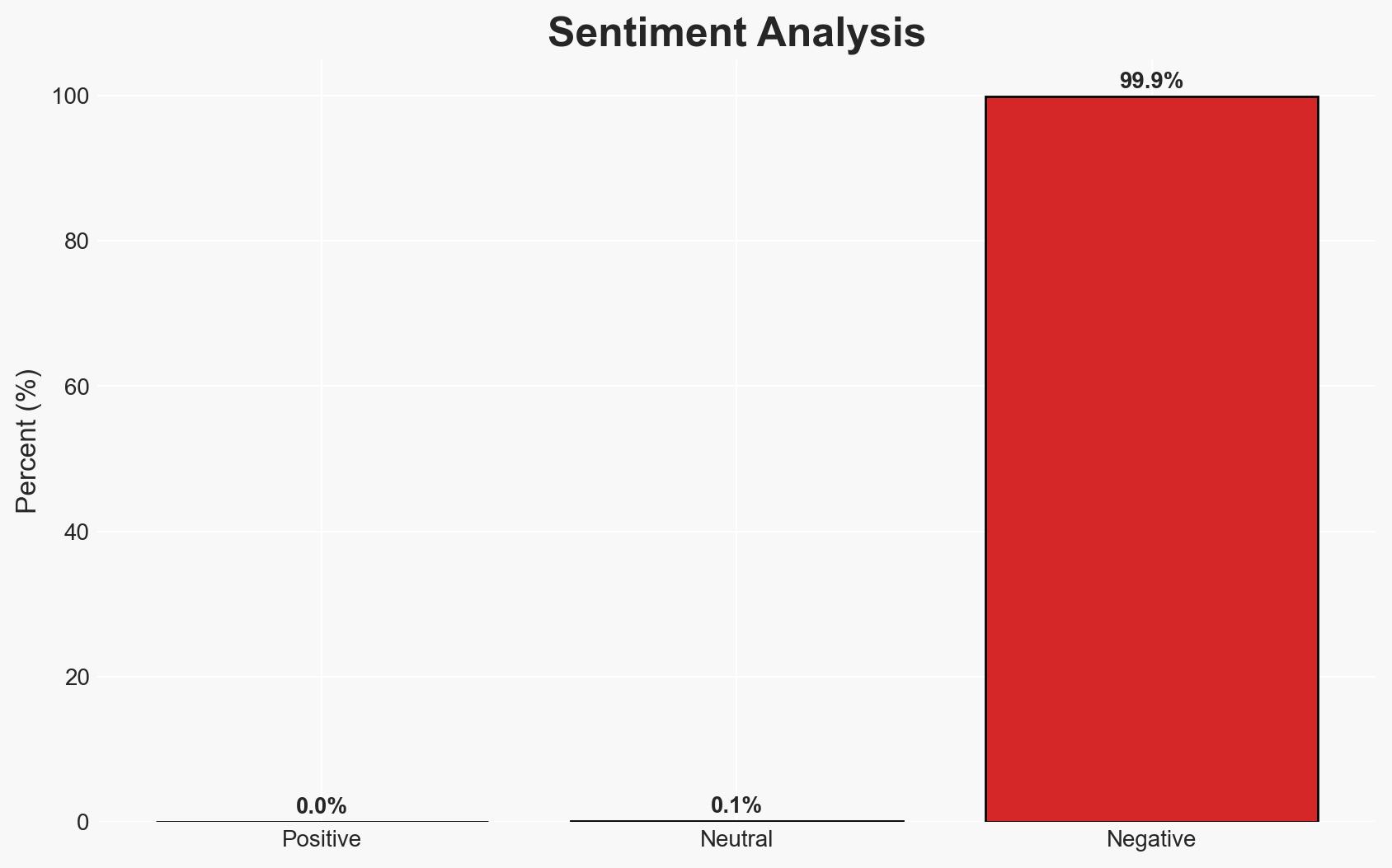
The recent security enhancements to Notepad++’s update mechanism significantly reduce the risk of future supply chain attacks. The most likely hypothesis is that these changes will effectively prevent similar compromises, impacting users globally. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the improvements made and the potential for unknown vulnerabilities.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The security updates to Notepad++ will prevent future supply chain attacks. This is supported by the implementation of signed XML files and installer verification, which address previously exploited vulnerabilities. However, the possibility of undiscovered vulnerabilities remains a key uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: Despite the updates, Notepad++ remains vulnerable to sophisticated supply chain attacks. This hypothesis is supported by the complexity of cyber threats and the potential for attackers to find new methods of exploitation. The lack of detailed information on the attackers’ capabilities and intentions is a significant uncertainty.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the comprehensive security measures implemented. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include new reports of successful attacks or the discovery of additional vulnerabilities in the update process.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Notepad++’s security measures are correctly implemented and effective; attackers lack immediate alternative methods to compromise the update process; users will update to the latest version promptly.
- Information Gaps: Detailed technical analysis of the new security measures’ effectiveness; insights into the attackers’ current capabilities and intentions.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential overconfidence in the security measures’ effectiveness; reliance on information from the software maintainer, which could be biased.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The security enhancements could deter future attacks and influence broader software security practices. However, if vulnerabilities persist, it could undermine trust in software supply chains.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased scrutiny and regulation of software supply chains, particularly in regions affected by the compromise.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced security may reduce the risk of cyber tools being used for espionage or sabotage.
- Cyber / Information Space: The situation highlights the ongoing threat of supply chain attacks and the need for robust cybersecurity measures.
- Economic / Social: Continued vulnerabilities could impact user trust and adoption rates, affecting the software’s market position.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor for any reports of new vulnerabilities or attacks; encourage users to update to the latest version promptly.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for ongoing threat analysis; invest in user education on secure software practices.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: No new vulnerabilities are discovered, and user trust is restored. Worst: New vulnerabilities are exploited, leading to further attacks. Most-Likely: Security measures are effective, but vigilance is required to address emerging threats.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Don Ho (Notepad++ maintainer)
- Rapid7 (Cybersecurity firm)
- Kaspersky (Cybersecurity firm)
- Palo Alto Networks (Cybersecurity firm)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, supply chain security, cyber defense, software vulnerabilities, cyber-espionage, software updates, cybersecurity practices
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us