Notepad++ Implements Security Update to Counteract Exploited Update Mechanism for Targeted Malware Delivery
Published on: 2026-02-18
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Notepad Fixes Hijacked Update Mechanism Used to Deliver Targeted Malware
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
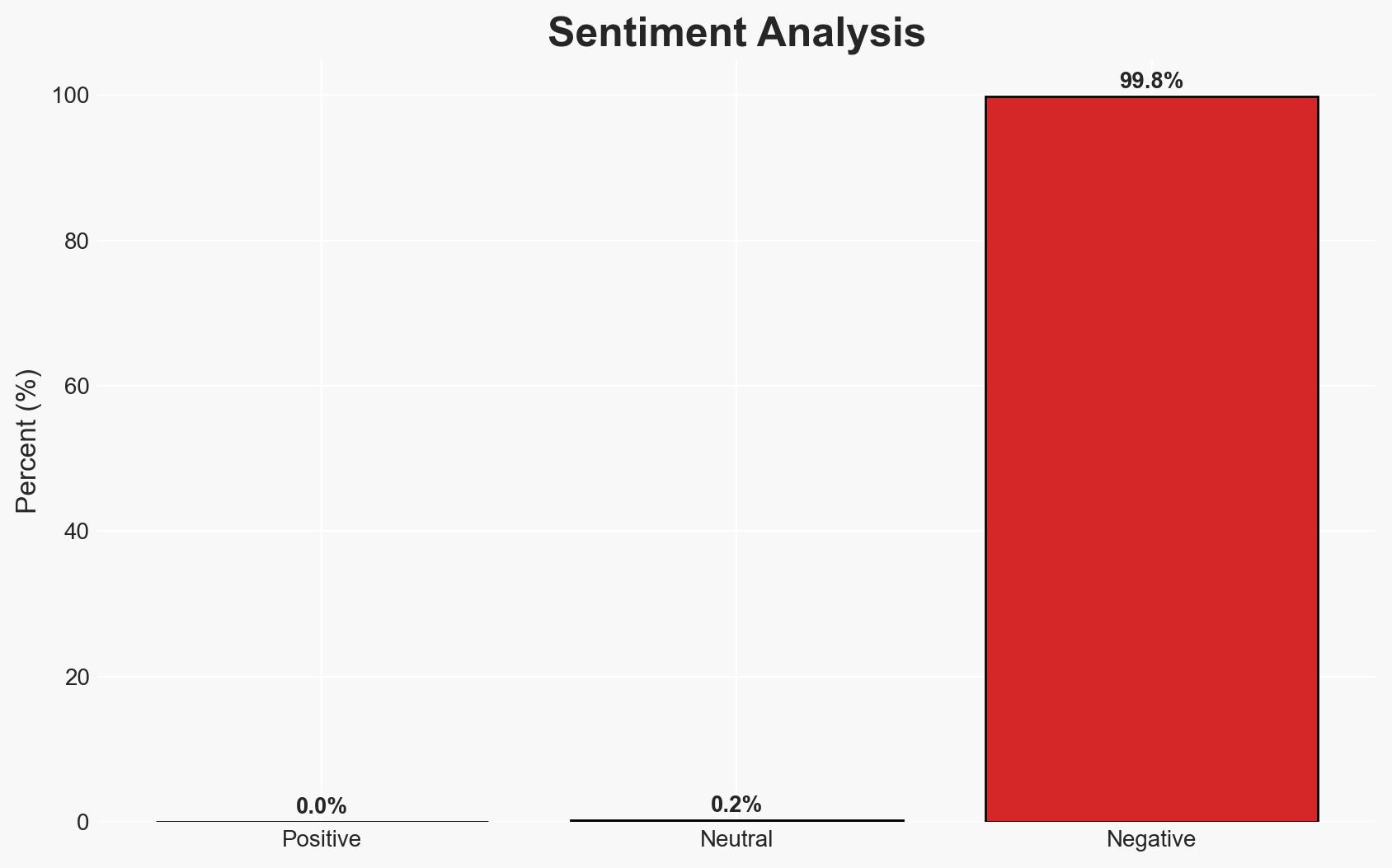
The recent security update by Notepad++ addresses a critical vulnerability exploited by a Chinese threat actor, Lotus Panda, to distribute malware via a hijacked update mechanism. This incident highlights significant risks in software supply chains affecting multiple sectors globally. The most likely hypothesis is that the attack aimed to gather intelligence from targeted sectors. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the available evidence and attribution to a known group.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The attack was primarily an intelligence-gathering operation by Lotus Panda targeting specific sectors. Supporting evidence includes the targeted nature of the attack and the sectors affected, which are typical intelligence targets. However, the exact objectives remain uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The attack was a broader attempt to disrupt operations in the affected sectors. This is less supported due to the selective targeting and the lack of widespread operational disruption reported.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the targeted nature of the attack and the involvement of a known Chinese cyber-espionage group. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of operational disruption or a broader range of affected sectors.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The attribution to Lotus Panda is accurate; the update mechanism vulnerability was the primary vector; the targeted sectors are accurately identified.
- Information Gaps: Specific objectives of the attack; full scope of affected entities; potential secondary payloads delivered.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Attribution bias towards known actors; potential misinformation from compromised sources; underreporting of affected entities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development underscores vulnerabilities in software supply chains and the potential for state-sponsored cyber-espionage to impact global sectors. It may prompt increased scrutiny and security measures in software update mechanisms.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential diplomatic tensions between China and affected countries; increased calls for international cybersecurity norms.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened awareness and defensive measures in targeted sectors; potential for copycat attacks.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on securing software supply chains; potential for further cyber-espionage activities.
- Economic / Social: Possible economic impacts on affected sectors; increased demand for cybersecurity solutions.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Encourage entities to update to Notepad++ version 8.9.2; monitor for further indicators of compromise; enhance supply chain security protocols.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for information sharing on cyber threats; invest in supply chain security technologies; conduct sector-specific threat assessments.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: No further incidents; improved global cybersecurity standards.
- Worst: Escalation of cyber-espionage activities; significant operational disruptions.
- Most-Likely: Continued targeted cyber-espionage with incremental improvements in defensive measures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Lotus Panda (China-nexus hacking group)
- Don Ho (Notepad++ maintainer)
- Rapid7 (Cybersecurity firm)
- Kaspersky (Cybersecurity firm)
- Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 (Cybersecurity research team)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, cyber-espionage, supply chain security, software vulnerabilities, China, Lotus Panda, malware distribution
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us