npm Enhances Supply Chain Security Amid Ongoing Vulnerabilities and Malware Risks
Published on: 2026-02-13
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: npms Update to Harden Their Supply Chain and Points to Consider
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
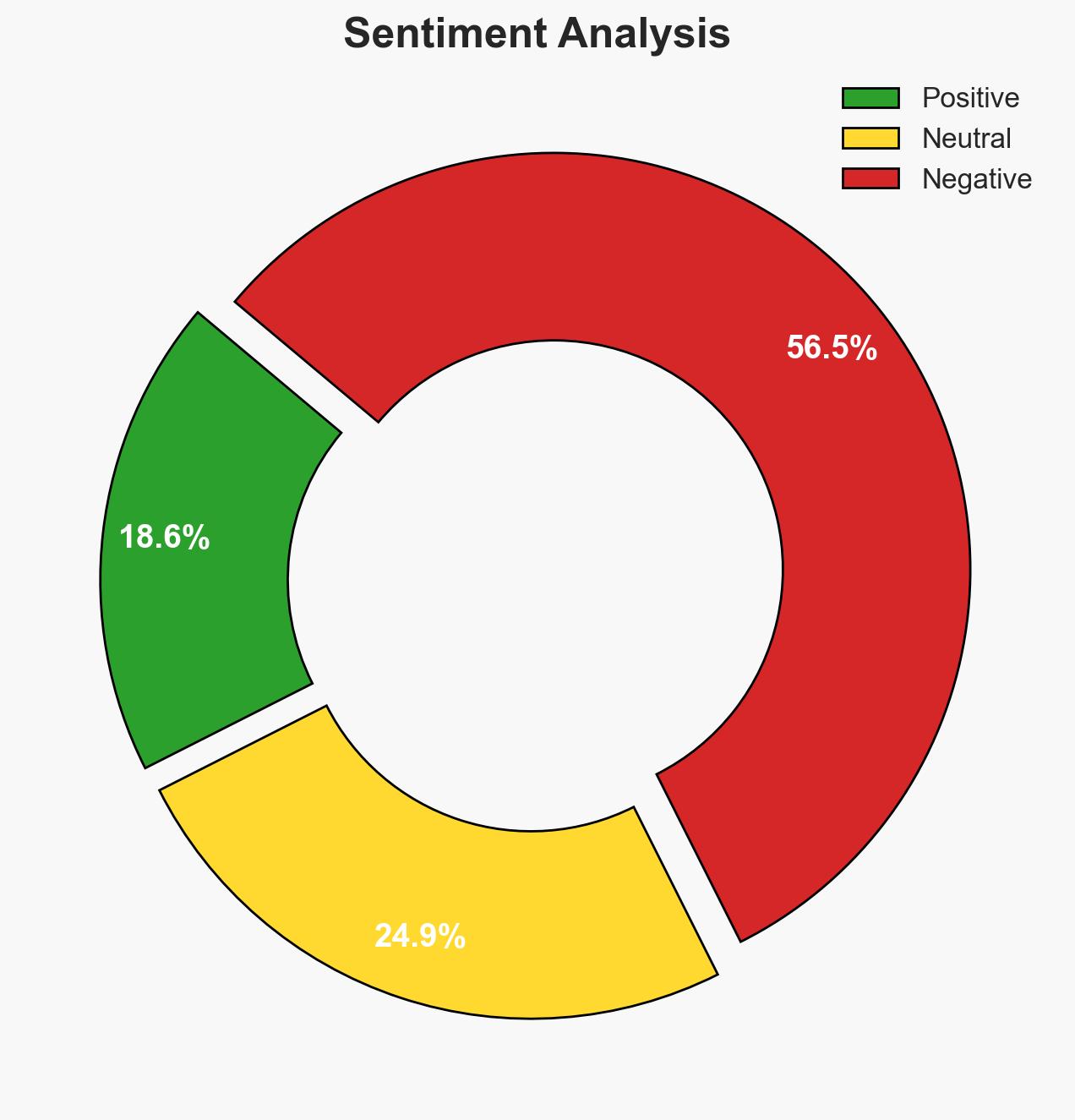
The npm authentication overhaul aims to mitigate supply-chain attacks by implementing session-based tokens and encouraging MFA, but vulnerabilities remain due to optional MFA and potential phishing attacks. The changes are a positive step, but the risk of exploitation persists. This affects developers and users within the Node.js community. Overall confidence in the effectiveness of these measures is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The npm authentication overhaul significantly reduces the risk of supply-chain attacks by enforcing session-based tokens and promoting MFA. Evidence supporting this includes the revocation of classic tokens and the introduction of short-lived session tokens. However, the optional nature of MFA and the history of successful phishing attacks contradict this hypothesis.
- Hypothesis B: Despite the overhaul, npm remains vulnerable to supply-chain attacks due to optional MFA and the potential for phishing attacks to obtain short-lived tokens. This hypothesis is supported by the continued ability to create 90-day tokens with MFA bypass and past successful phishing incidents. The main contradiction is the improved security measures that could deter less sophisticated attacks.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the persistent vulnerabilities associated with optional MFA and phishing risks. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include mandatory MFA implementation and a reduction in successful phishing attempts.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Developers will adopt MFA; phishing attacks will continue to target npm; short-lived tokens are more secure than long-lived ones; npm will maintain current security practices.
- Information Gaps: The extent of developer adoption of MFA; detailed data on recent phishing attack success rates; npm’s future plans for mandatory security measures.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Confirmation bias in assessing the effectiveness of security measures; potential underreporting of successful attacks due to reputational concerns.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The npm security changes could lead to a temporary reduction in supply-chain attacks, but persistent vulnerabilities may allow sophisticated actors to exploit the system. Over time, this could influence broader cybersecurity practices and standards.
- Political / Geopolitical: Limited direct implications, but could influence international cybersecurity policy discussions.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Potential for increased targeting of npm by cybercriminals and state actors seeking to exploit supply-chain vulnerabilities.
- Cyber / Information Space: May prompt other platforms to adopt similar security measures, influencing the broader cybersecurity landscape.
- Economic / Social: Continued vulnerabilities could undermine trust in open-source software, impacting developer communities and software adoption.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Encourage npm to make MFA mandatory; increase awareness and training on phishing risks for developers.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms to enhance threat detection; invest in research for more secure authentication methods.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Mandatory MFA and improved phishing defenses lead to a significant reduction in attacks.
- Worst: Continued optional MFA and successful phishing attacks result in major supply-chain breaches.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in security with occasional breaches due to persistent vulnerabilities.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- npm (Node Package Manager)
- Developers and maintainers within the Node.js community
- Cybersecurity teams and firms
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
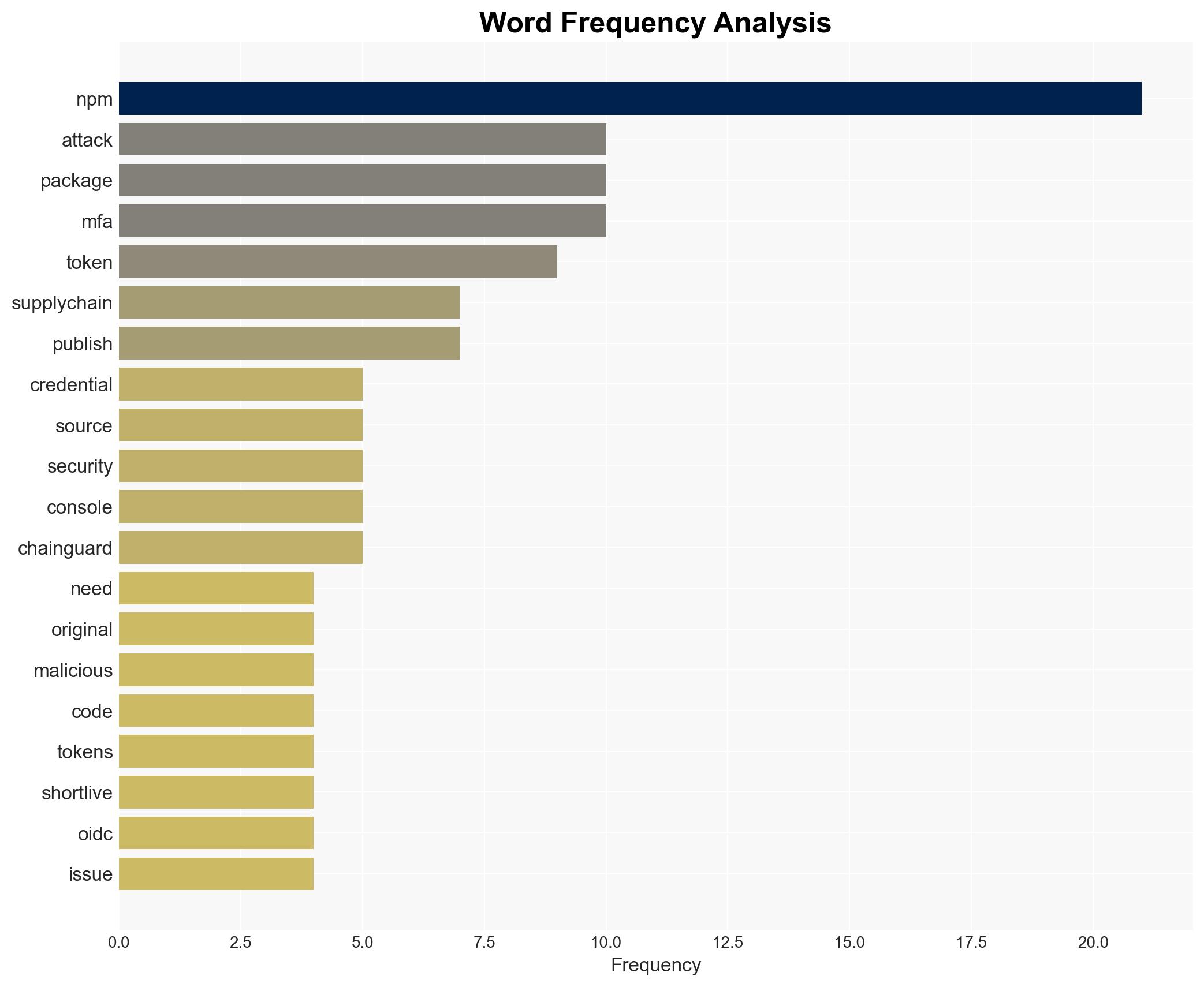
cybersecurity, supply-chain security, cyber vulnerabilities, MFA, phishing attacks, open-source software, npm, Node.js
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us