Off-label AI The mental health risk no one is talking about
Published on: 2025-11-25
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Off-label AI in Mental Health
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
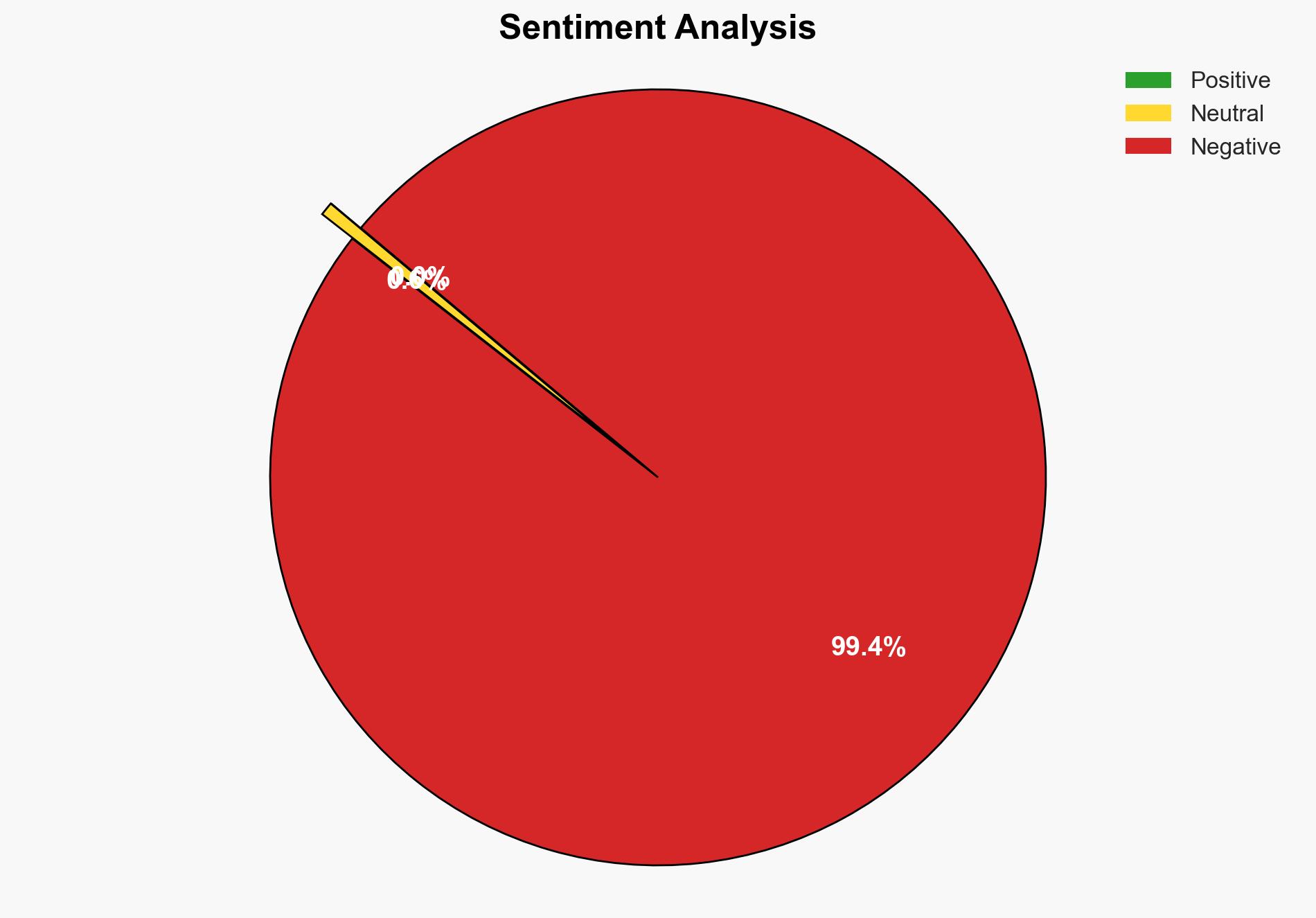
The rapid adoption of off-label AI tools in mental health care presents significant risks due to the lack of clinical validation and oversight. The most supported hypothesis is that the use of general-purpose AI tools without proper safeguards could lead to severe misclassification and privacy breaches, undermining trust and engagement. Recommended action includes the adoption of purpose-built AI systems with robust safety and compliance frameworks. Confidence Level: Moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The use of off-label AI tools in mental health care will lead to significant safety and privacy risks due to their lack of clinical validation and oversight.
Hypothesis 2: Off-label AI tools can be safely integrated into mental health care with minimal risk if supplemented with adequate human oversight and compliance measures.
Hypothesis 1 is more likely due to the inherent complexity of mental health issues and the current lack of robust safety protocols in general-purpose AI tools, as evidenced by the absence of escalation protocols and HIPAA compliance.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: AI tools are assumed to be capable of handling complex mental health scenarios without clinical validation. There is an assumption that AI can replace human oversight in sensitive contexts.
Red Flags: The rapid deployment of AI without adequate testing and validation, lack of transparency in AI tool capabilities, and insufficient regulatory frameworks.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The use of off-label AI tools in mental health care could lead to cascading threats, including:
- Political: Potential regulatory backlash and increased scrutiny from governmental bodies.
- Cyber: Increased risk of data breaches due to inadequate compliance with data protection standards.
- Economic: Loss of trust could lead to reduced adoption and financial losses for AI vendors.
- Informational: Spread of misinformation regarding AI capabilities in mental health care.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Adopt purpose-built AI systems with clinical validation and robust safety protocols.
- Implement comprehensive training for AI tool users and establish clear escalation procedures.
- Engage with regulatory bodies to ensure compliance with data protection and privacy standards.
- Best Scenario: Successful integration of AI tools with enhanced safety measures leads to improved mental health outcomes.
- Worst Scenario: Major data breach or misclassification incident results in loss of trust and regulatory intervention.
- Most-likely Scenario: Gradual adoption of AI tools with increased scrutiny and demand for compliance measures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
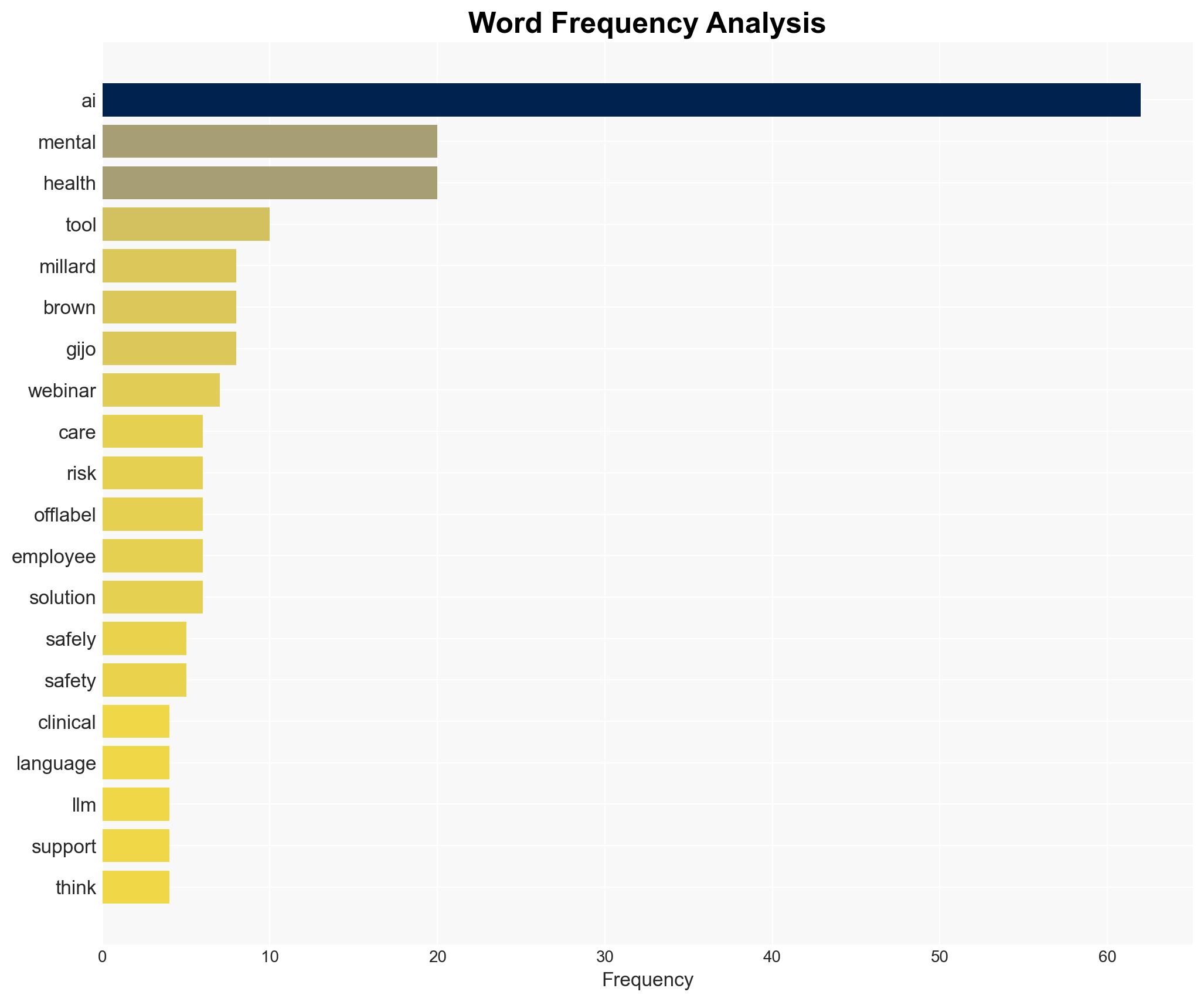
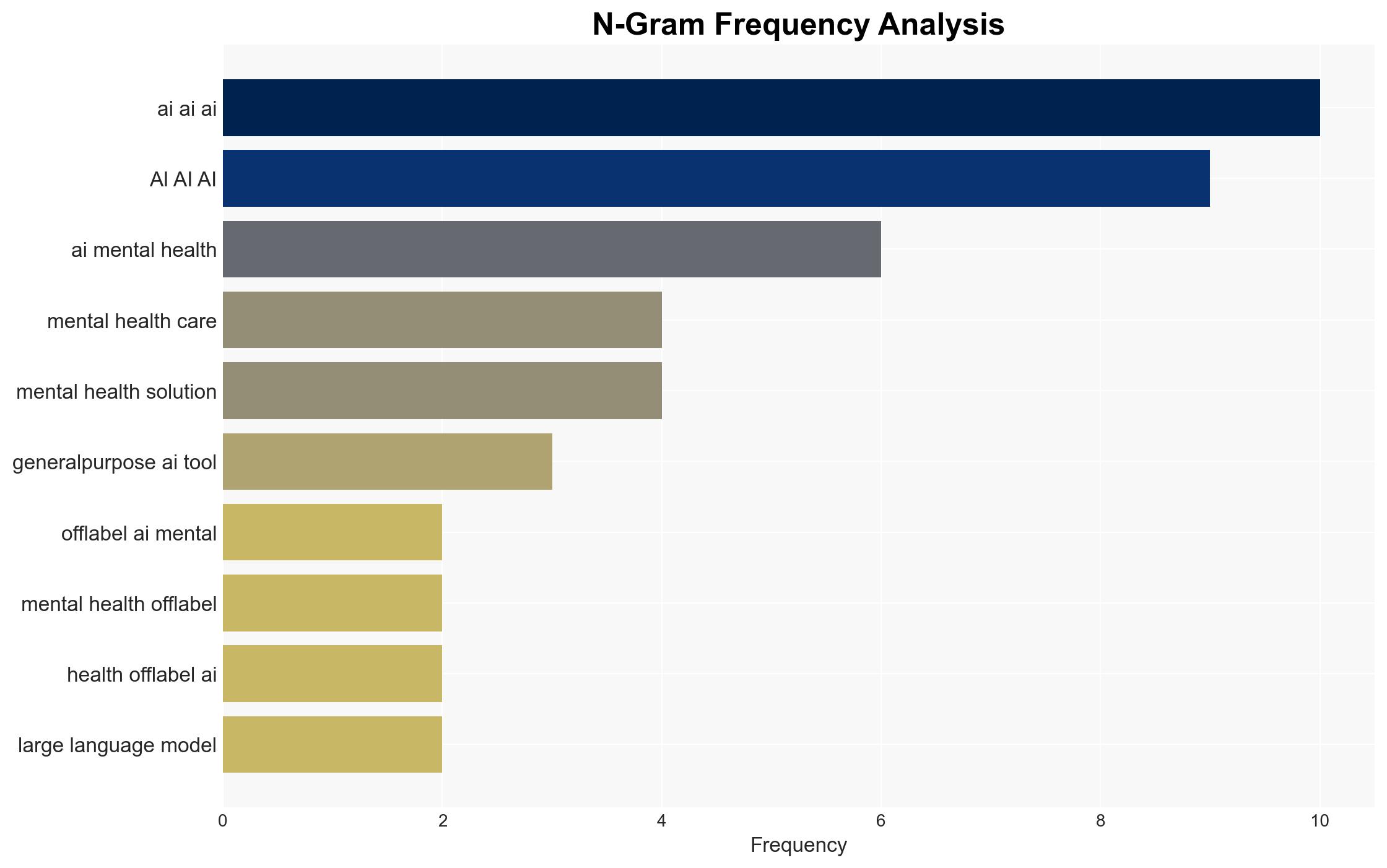
Dr. Millard Brown, Chief Medical Officer at Spring Health, advocates for ethical AI use in mental health.
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, Mental Health, Artificial Intelligence, Compliance, Data Privacy
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Structured challenge to expose and correct biases.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us