Old authentication habits die hard – Help Net Security
Published on: 2025-10-06
Intelligence Report: Old Authentication Habits Die Hard – Help Net Security
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
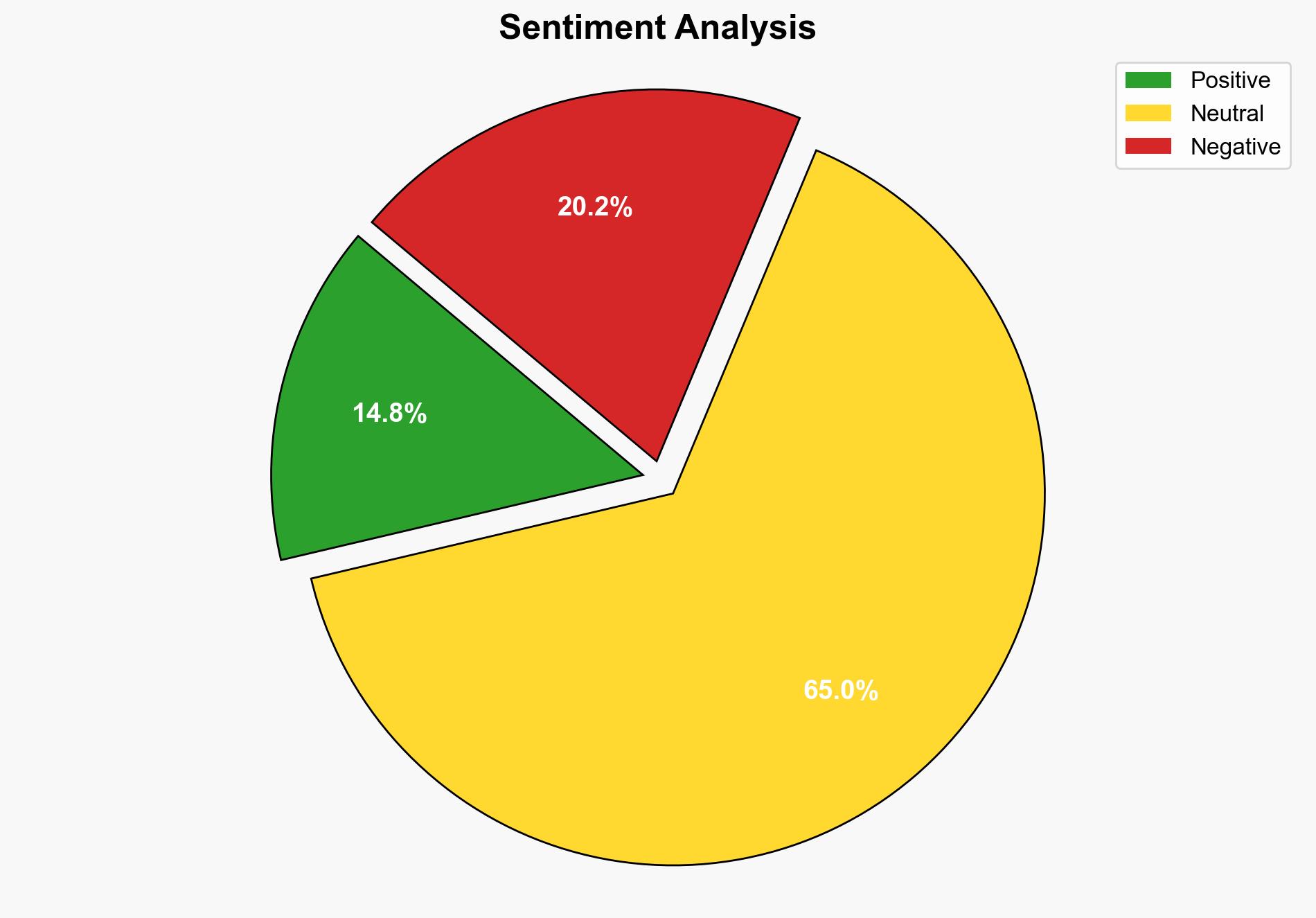
The most supported hypothesis is that outdated authentication practices and employee habits significantly increase organizational vulnerability to cyber threats. This is due to a combination of delayed policy updates and inadequate training. Confidence level: Moderate. Recommended action: Immediate overhaul of cybersecurity training and authentication protocols, with a focus on deploying stronger, phishing-resistant methods such as device-bound passkeys.
2. Competing Hypotheses
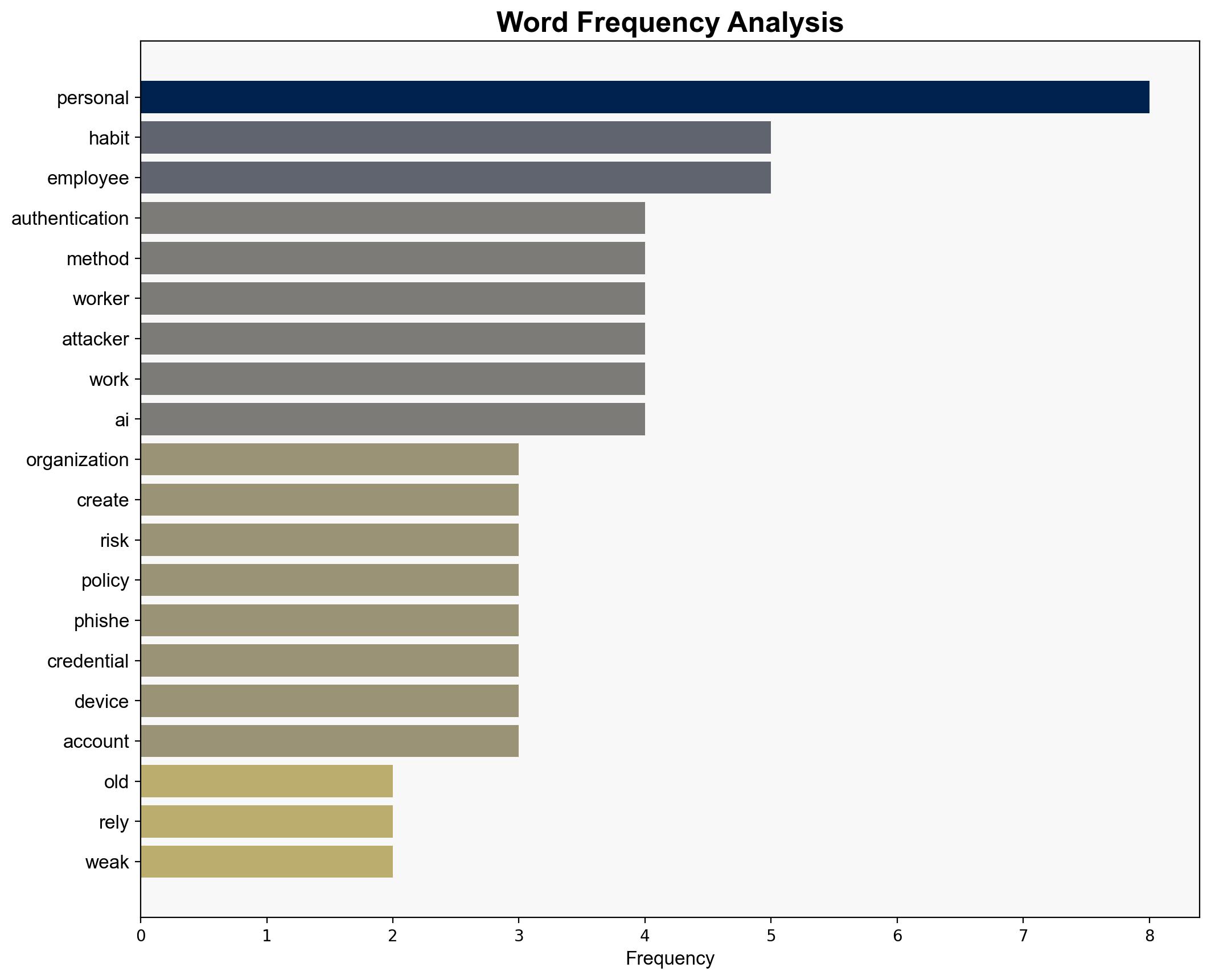
1. **Hypothesis A**: Organizations’ reliance on weak authentication methods is primarily due to outdated security policies and delayed updates, which leave employees unprepared and reliant on familiar, insecure practices.
2. **Hypothesis B**: The persistence of weak authentication methods is largely driven by employee resistance to change and preference for convenience, despite the availability of more secure options.
Using ACH 2.0, Hypothesis A is better supported as the source highlights systemic issues such as policy delays and outdated training, which are organizationally driven rather than purely individual choices.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: It is assumed that organizations have the capability to update policies promptly but choose not to. It is also assumed that employees are aware of the risks associated with outdated methods but continue to use them due to habit.
– **Red Flags**: Lack of specific data on how many organizations have updated their policies recently. Potential bias in survey data regarding employee perceptions and behaviors.
– **Blind Spots**: The role of management in enforcing updated practices and the impact of organizational culture on security policy adherence.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The continued use of weak authentication methods poses significant cyber risks, including increased susceptibility to phishing, credential theft, and social engineering attacks. This can lead to data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage. The generational gap in technology adoption may exacerbate these risks as younger employees may be more adaptable to new methods, leaving older employees as potential weak links.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- **Immediate Action**: Organizations should prioritize updating their security policies and training programs to include stronger authentication methods.
- **Medium-Term**: Implement mandatory use of device-bound passkeys and MFA across all platforms.
- **Long-Term**: Foster a culture of continuous cybersecurity awareness and adaptability to emerging threats.
- **Scenario Projections**:
– **Best Case**: Rapid adoption of secure methods reduces vulnerability and enhances organizational resilience.
– **Worst Case**: Continued reliance on outdated methods leads to a major breach.
– **Most Likely**: Gradual improvement in security posture as policies and training catch up with technological advancements.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
No specific individuals are mentioned in the source text. Key entities include organizations relying on outdated authentication methods and those responsible for cybersecurity policy and training.
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, regional focus