Organizations Embrace Remote Privileged Access Management to Enhance Security in Hybrid Work Environments
Published on: 2025-11-28
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Why Organizations Are Turning to RPAM
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
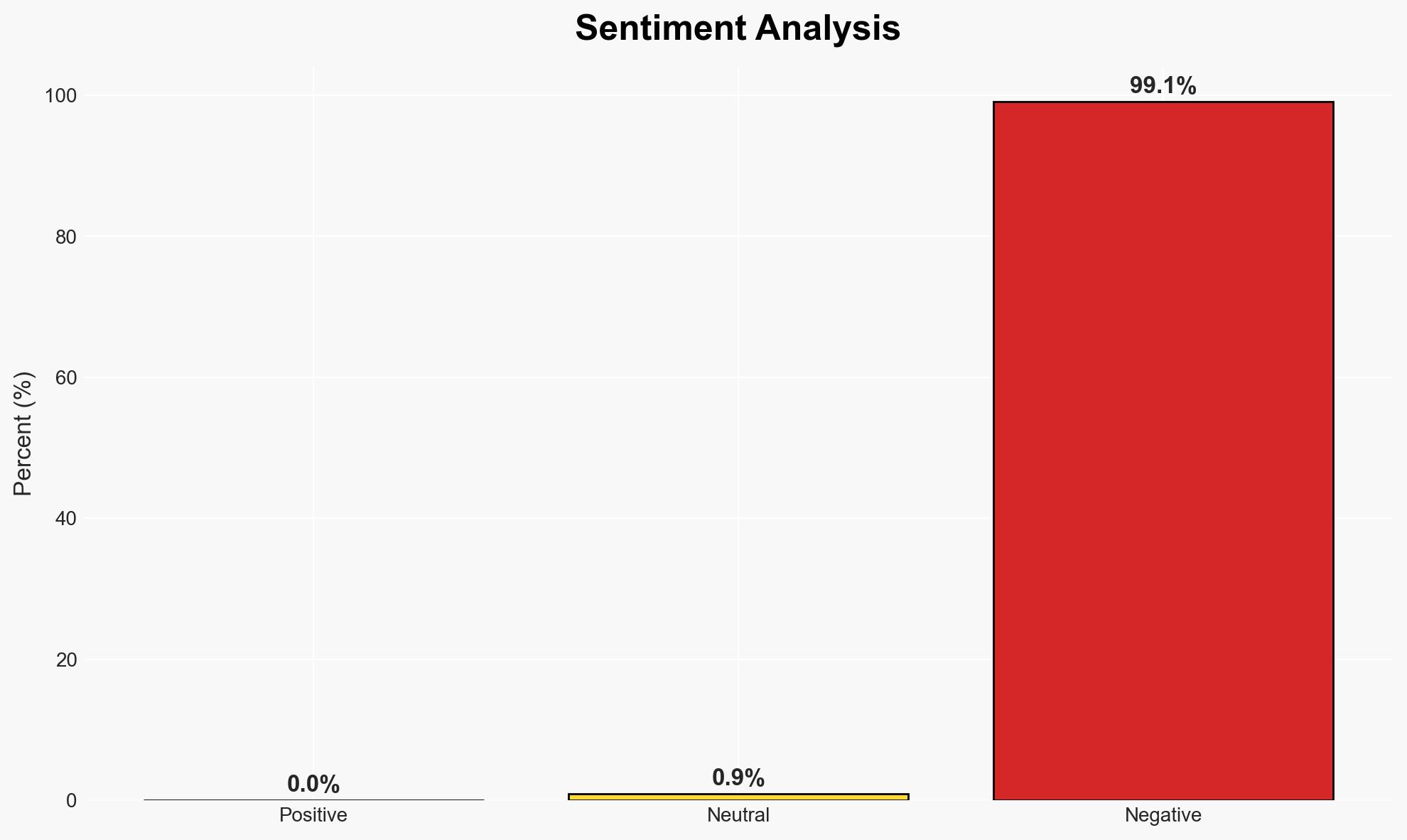
Organizations are increasingly adopting Remote Privileged Access Management (RPAM) to address security challenges posed by hybrid and remote work environments. RPAM offers enhanced security features over traditional Privileged Access Management (PAM) solutions, particularly in distributed and cloud-based infrastructures. The shift is driven by the need for secure, flexible access controls and compliance with regulatory requirements. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Organizations are adopting RPAM primarily due to the inadequacy of traditional PAM solutions in securing remote and hybrid work environments. This is supported by the increased need for secure remote access and the limitations of legacy PAM in distributed infrastructures. However, the extent of RPAM’s adoption across different sectors remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The adoption of RPAM is driven more by regulatory compliance pressures rather than inherent security advantages. While compliance requirements are a factor, the evidence suggests that security and operational flexibility are more significant drivers.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported, as the primary motivation appears to be the security challenges of remote work environments. Indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in regulatory landscapes or significant security breaches exploiting traditional PAM vulnerabilities.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Organizations prioritize security over cost in adopting RPAM; hybrid work environments will persist; RPAM solutions are effectively more secure than traditional PAM.
- Information Gaps: Detailed adoption rates of RPAM across different industries; specific regulatory requirements influencing adoption; comparative security performance metrics between RPAM and PAM.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias from RPAM vendors promoting their solutions; lack of independent verification of RPAM’s efficacy; possible underreporting of PAM vulnerabilities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The adoption of RPAM could significantly alter organizational security postures and influence broader cybersecurity strategies. As RPAM becomes more prevalent, it may drive further innovation in access management technologies.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased reliance on cloud-based solutions may raise sovereignty and data privacy concerns, potentially leading to regulatory scrutiny.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced security measures could reduce the risk of cyber intrusions, but also shift threat actor tactics towards exploiting new vulnerabilities.
- Cyber / Information Space: RPAM adoption supports zero-trust architectures, potentially reducing attack surfaces but requiring continuous monitoring and adaptation.
- Economic / Social: Investment in RPAM could drive economic growth in cybersecurity sectors but may also increase operational costs for organizations.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a risk assessment of current access management solutions; monitor for emerging RPAM vulnerabilities; engage with RPAM vendors for solution demonstrations.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms specializing in RPAM; invest in training for IT staff on RPAM deployment and management; evaluate compliance impacts of RPAM adoption.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: RPAM adoption leads to significant reductions in security breaches and compliance violations.
- Worst: RPAM solutions introduce new vulnerabilities, leading to high-profile breaches.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in security posture with RPAM adoption, accompanied by ongoing adjustments to address emerging threats.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, remote work, access management, cloud security, regulatory compliance, zero-trust, hybrid environments
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us