Over 260,000 Chrome Users Compromised by Malicious AI Extensions Masquerading as Productivity Tools
Published on: 2026-02-14
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
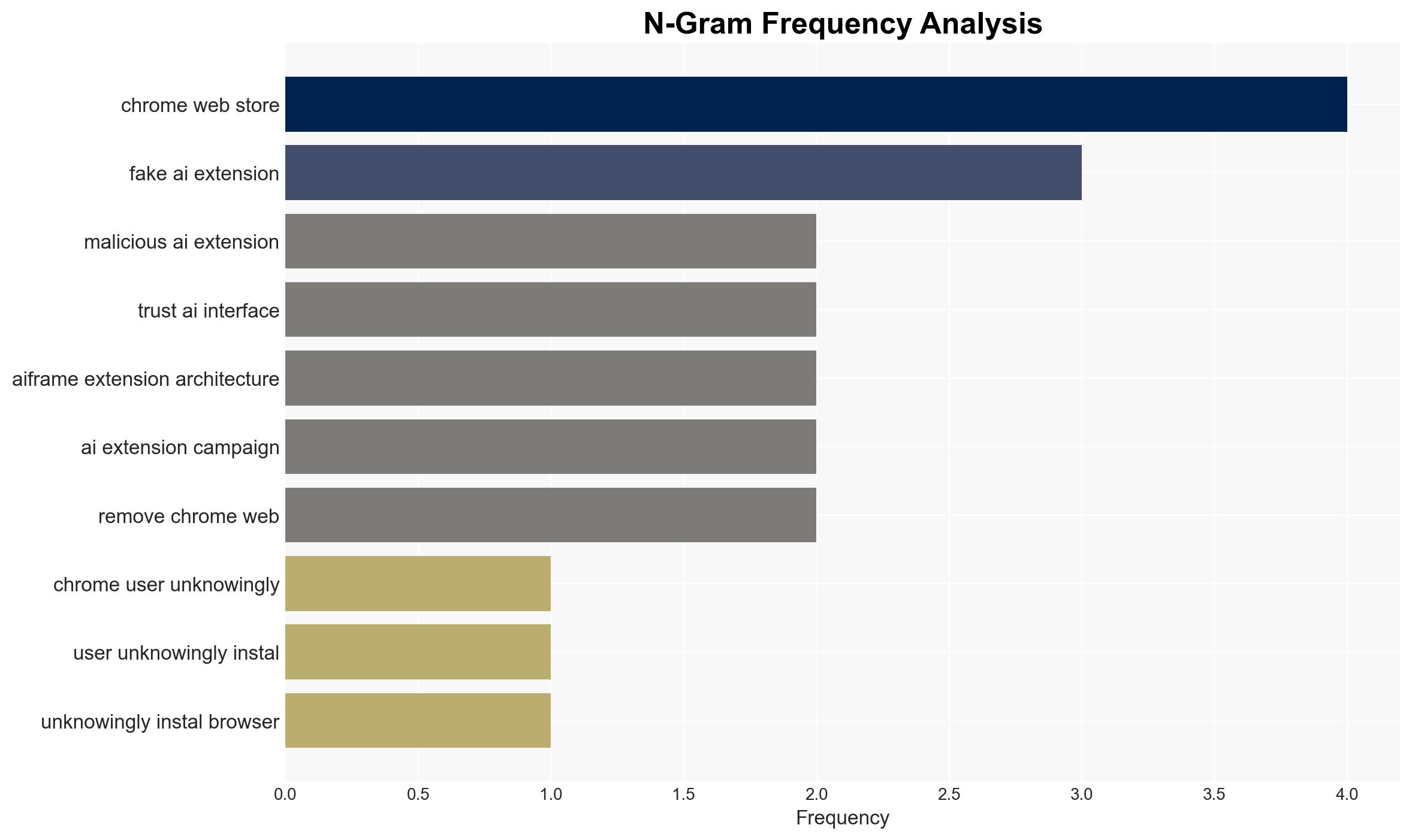
Intelligence Report: 260000 Chrome Users Exposed by Fake AI Extensions Targeting Gmail
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
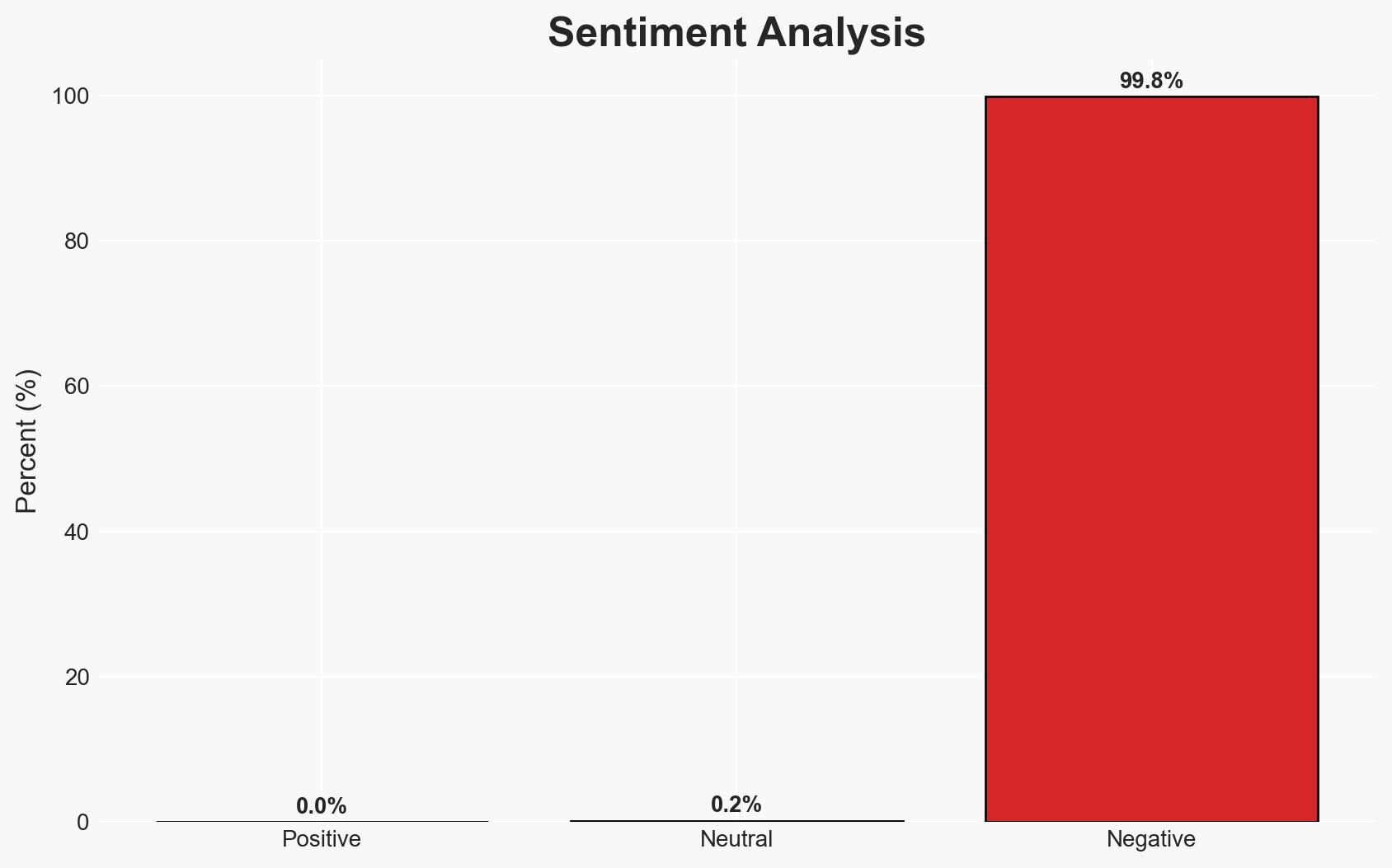
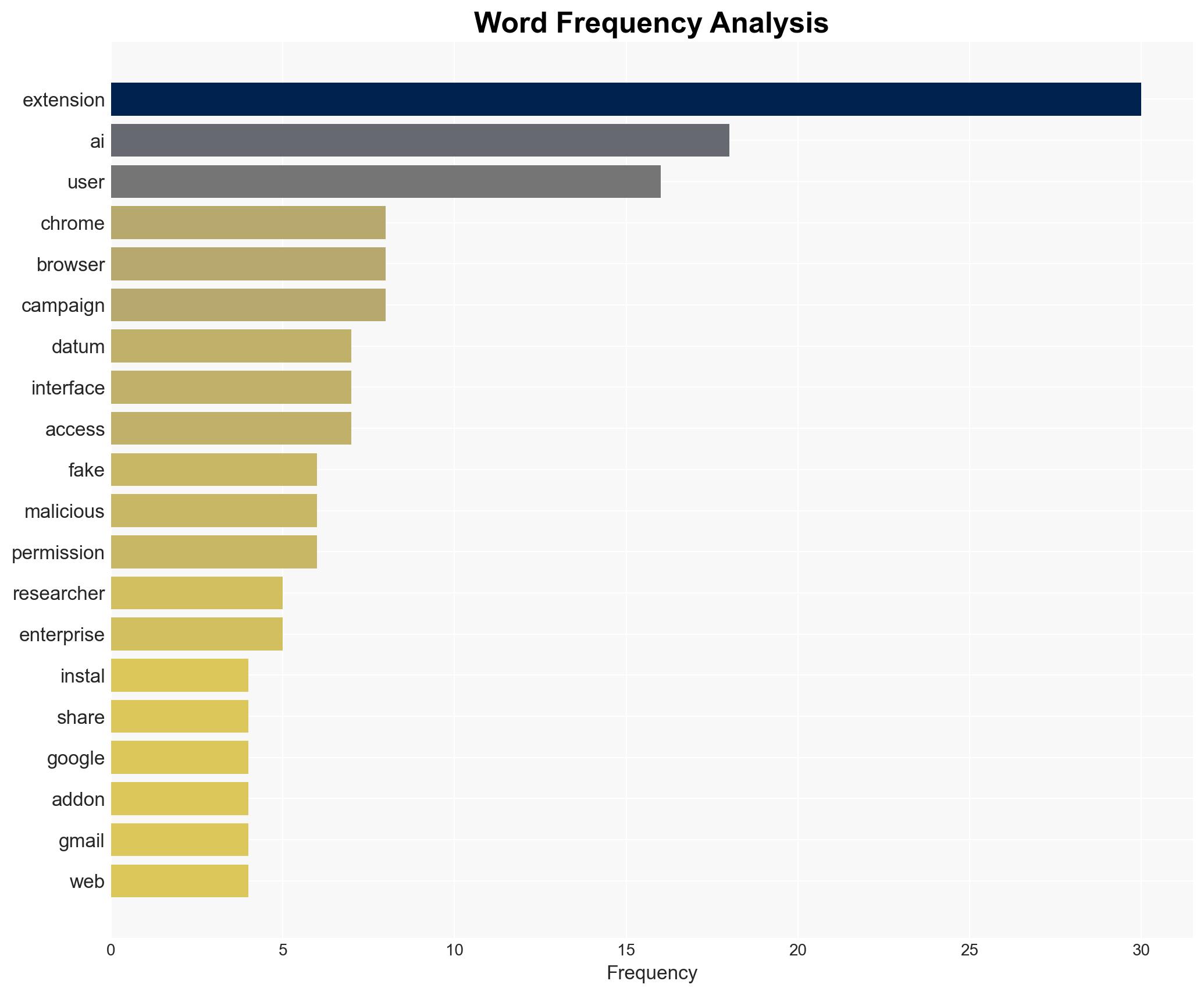
A coordinated campaign involving over 30 fake Chrome extensions has compromised more than 260,000 users by posing as AI productivity tools to deploy spyware. This operation primarily targeted Gmail data, exploiting user trust in AI interfaces. The most likely hypothesis is that this is a financially motivated cybercrime operation. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to incomplete attribution data.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The campaign is a financially motivated cybercrime operation aimed at stealing personal data for resale or fraud. Supporting evidence includes the use of spyware and the targeting of a large user base. However, the lack of direct financial transactions in the data leaves some uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: The campaign is a state-sponsored espionage operation aimed at gathering intelligence on a wide scale. This is less supported due to the broad targeting and lack of specific high-value targets, which are typical in espionage.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the nature of the data targeted and the operational setup, which aligns with typical cybercrime patterns. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of targeting specific high-value individuals or entities.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The extensions were primarily designed for data theft; the attackers are financially motivated; Google’s security measures were bypassed through sophisticated means.
- Information Gaps: Lack of information on the identity and location of the attackers; absence of data on the financial transactions or end-use of the stolen data.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential confirmation bias in attributing the operation to cybercrime without considering espionage; reliance on security researcher reports which may have inherent biases or incomplete data.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased scrutiny of Chrome extensions and pressure on Google to enhance security measures. It may also prompt similar future attacks exploiting AI trust.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential diplomatic tensions if state-sponsored involvement is suspected or proven.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of similar tactics being used in targeted attacks against critical infrastructure or government entities.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened awareness and potential regulatory actions on browser extension security; increased user skepticism towards AI tools.
- Economic / Social: Potential financial losses for affected users; erosion of trust in digital platforms and AI tools.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of Chrome extensions for suspicious activity; issue public advisories to affected users; collaborate with Google to remove remaining malicious extensions.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with tech companies for improved threat intelligence sharing; invest in user education on cybersecurity best practices.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid identification and neutralization of the threat actors, leading to decreased risk of similar attacks.
- Worst: Proliferation of similar attacks, leading to widespread data breaches and loss of trust in AI tools.
- Most-Likely: Continued sporadic attacks with gradual improvements in detection and prevention measures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, cybercrime, data theft, AI exploitation, browser security, information warfare, user trust
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us