Over 6,000 SmarterMail servers vulnerable to critical authentication bypass, risking admin account hijacking
Published on: 2026-01-27
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Over 6000 SmarterMail servers exposed to automated hijacking attacks
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
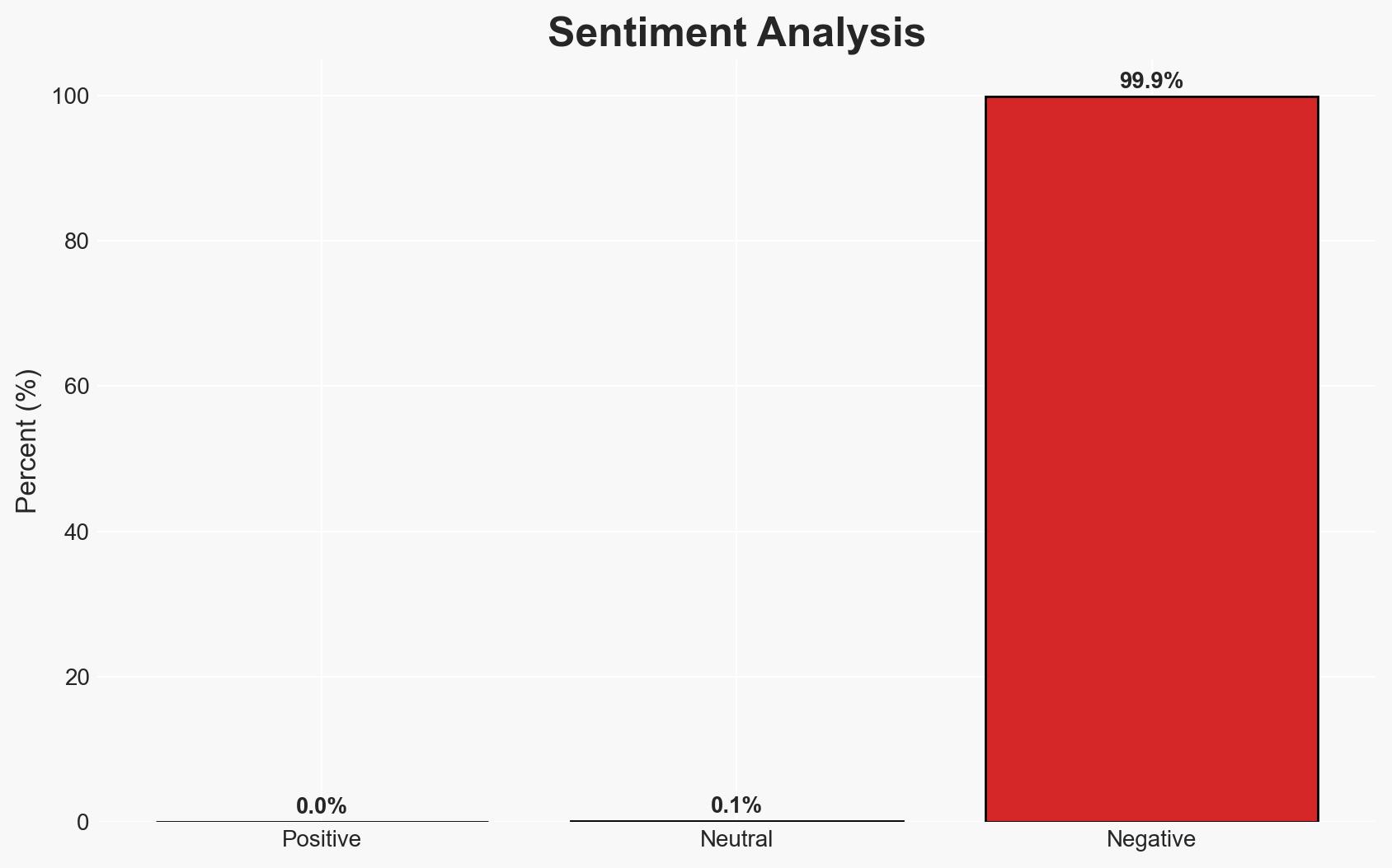
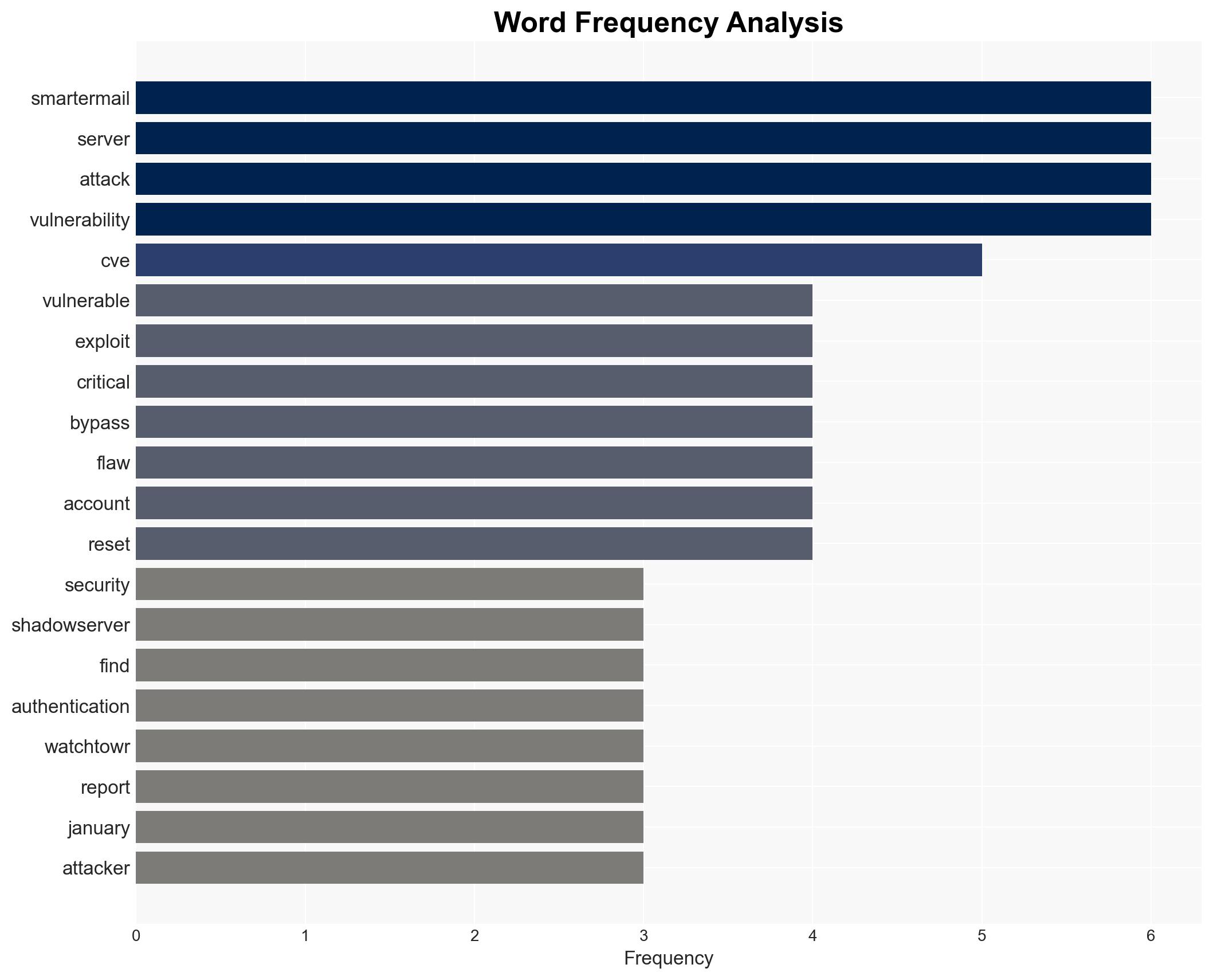
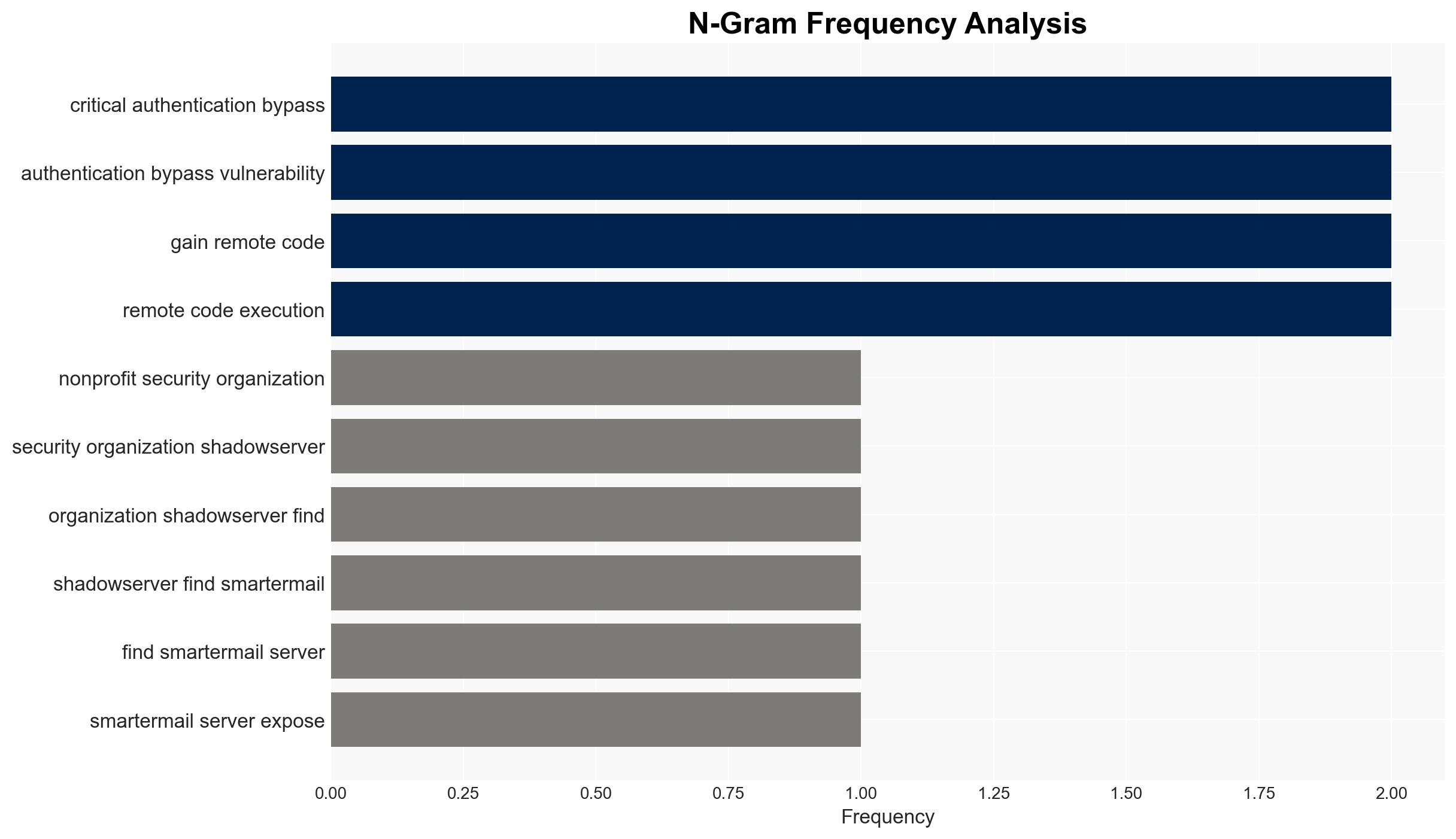
Over 6,000 SmarterMail servers are vulnerable to a critical authentication bypass vulnerability, posing significant cyber risks, particularly in North America and Asia. The vulnerability allows unauthenticated attackers to gain administrative control, potentially leading to mass exploitation. The situation requires urgent mitigation, with moderate confidence in the assessment due to incomplete data on the full scope of exploitation.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The vulnerability is being actively exploited by cybercriminals for financial gain or data theft. Supporting evidence includes reports of automated attacks and the presence of a proof-of-concept exploit. However, the exact scale and intent of these attacks remain uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The vulnerability is primarily being exploited by state-sponsored actors for espionage or strategic disruption. While the critical nature of the vulnerability supports this hypothesis, there is currently no direct evidence linking state actors to the exploitation.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the observed automated exploitation patterns and the lack of specific indicators of state-sponsored involvement. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include attribution evidence or changes in the targeting pattern.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The vulnerability affects all unpatched SmarterMail servers; attackers have the capability to exploit the vulnerability at scale; mitigation measures are not uniformly applied across affected entities.
- Information Gaps: Comprehensive data on the identity and objectives of the attackers; detailed impact assessments from affected organizations; the extent of mitigation efforts undertaken by SmarterMail users.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting due to reliance on cybersecurity firms with vested interests; risk of deception by attackers using false flags to obscure their identity.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The exploitation of this vulnerability could lead to significant disruptions in affected organizations, particularly if critical infrastructure or sensitive data is targeted. The situation may evolve into a broader cybersecurity crisis if not contained.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if state-sponsored involvement is confirmed, especially if critical infrastructure is affected.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment as organizations scramble to patch vulnerabilities and secure systems.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased cyber threat activity and potential for misinformation campaigns exploiting the vulnerability.
- Economic / Social: Economic impacts from disrupted services and increased cybersecurity costs; potential social unrest if public services are affected.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Urgent patching of vulnerable SmarterMail servers; enhanced monitoring for signs of exploitation; dissemination of threat intelligence to affected sectors.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures, including regular security audits and incident response planning; foster partnerships for information sharing and threat intelligence.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Vulnerability is rapidly mitigated with minimal impact. Worst: Widespread exploitation leads to significant disruptions. Most-Likely: Continued targeted attacks with gradual mitigation as patches are applied.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Shadowserver, SmarterTools, watchTowr, CISA, Huntress, Macnica, NIST
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, vulnerability management, cyber threats, information security, critical infrastructure, cyber espionage, threat intelligence
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us