Oxford University boffins created an AI tool to help discover the needles in a cosmic haystack reducing its astronomer’s workloads dramatically – Windows Central
Published on: 2025-09-13
Intelligence Report: Oxford University boffins created an AI tool to help discover the needles in a cosmic haystack reducing its astronomer’s workloads dramatically – Windows Central
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
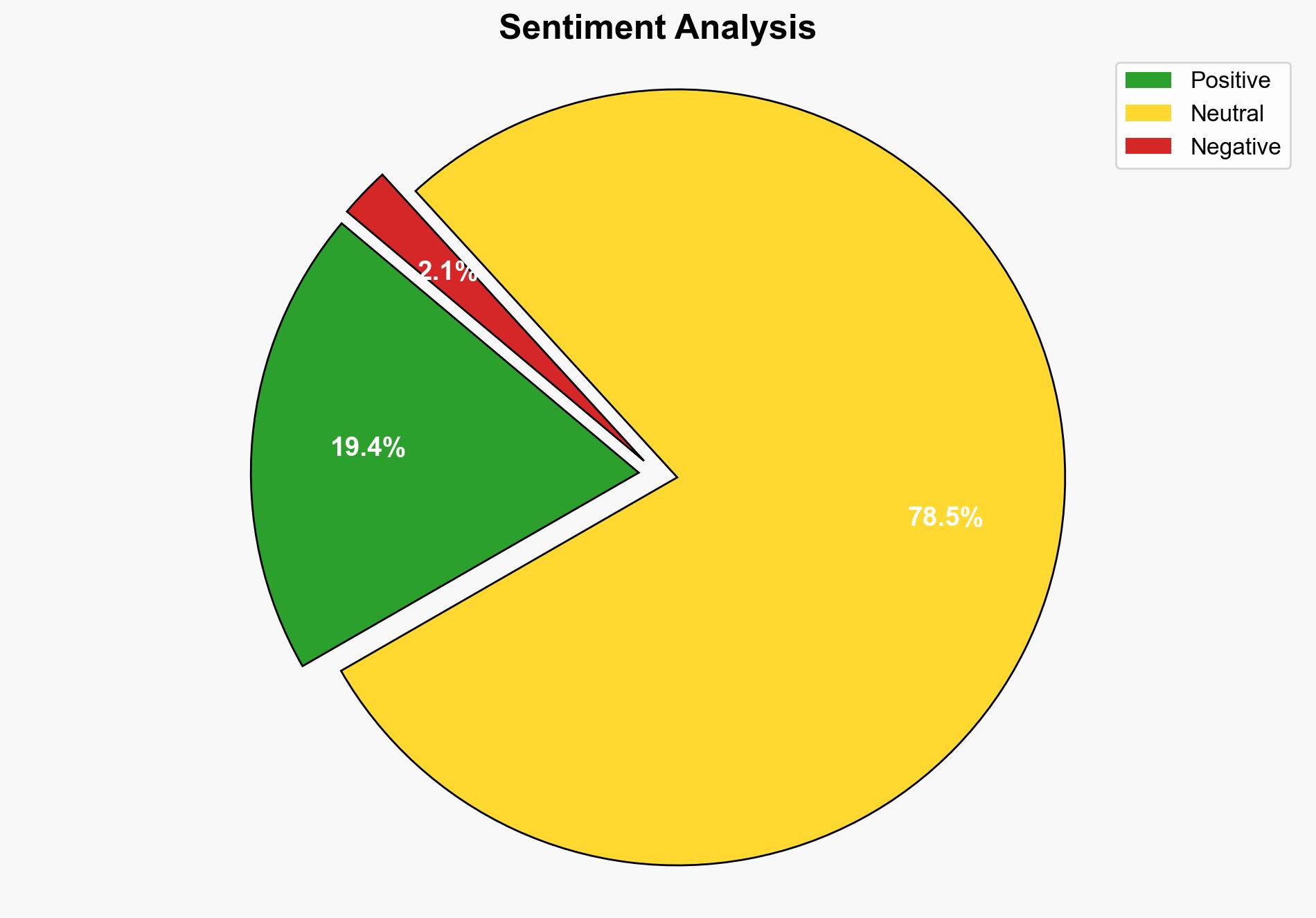
The AI tool developed by Oxford University represents a significant advancement in astronomical research efficiency, with a high confidence level in its potential to transform data analysis in this field. The most supported hypothesis is that the tool will effectively reduce workloads and improve accuracy in identifying cosmic phenomena. Recommended action includes monitoring the tool’s integration and performance in real-world applications to validate its efficacy and explore further applications in other scientific domains.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis A**: The AI tool will significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of astronomical research by reducing the manual workload and improving the identification of supernovae.
2. **Hypothesis B**: The AI tool may not deliver the expected improvements due to potential limitations in data processing capabilities or unforeseen technical challenges.
Using the Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (ACH) 2.0, Hypothesis A is better supported. The tool’s design, which leverages a lean data approach and decision-tree algorithms, aligns with current trends in AI efficiency and suggests a high likelihood of success.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: The tool’s algorithms are assumed to be robust enough to handle the complexity of astronomical data. It is also assumed that the training data is representative and sufficient for accurate model performance.
– **Red Flags**: Potential over-reliance on AI could lead to complacency in human verification processes. There is also a risk of data bias if the training set is not comprehensive.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The successful implementation of this AI tool could set a precedent for similar applications in other scientific fields, potentially revolutionizing data analysis processes. However, failure to deliver on its promises could lead to skepticism about AI’s role in scientific research, affecting future funding and development. Additionally, if the tool is not adequately secured, it could become a target for cyber threats, compromising sensitive data.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- **Mitigation**: Implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect the AI tool and its data.
- **Exploitation**: Explore partnerships with other research institutions to expand the tool’s application and gather diverse datasets.
- **Scenario Projections**:
- **Best Case**: The tool significantly enhances research efficiency, leading to breakthroughs in cosmic discovery.
- **Worst Case**: Technical failures undermine trust in AI applications, stalling further development.
- **Most Likely**: Gradual improvement in research processes with incremental validation of the tool’s capabilities.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Richard Devine, mentioned as a managing editor at Windows Central, provides context but is not directly involved in the AI tool’s development.
7. Thematic Tags
artificial intelligence, scientific research, data analysis, cybersecurity, technological innovation