Parliament Seeks Industry Expertise for Review of Cyber Security and Resilience Bill
Published on: 2026-01-13
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Parliament Asks Security Pros to Shape Cyber Security and Resilience Bill
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
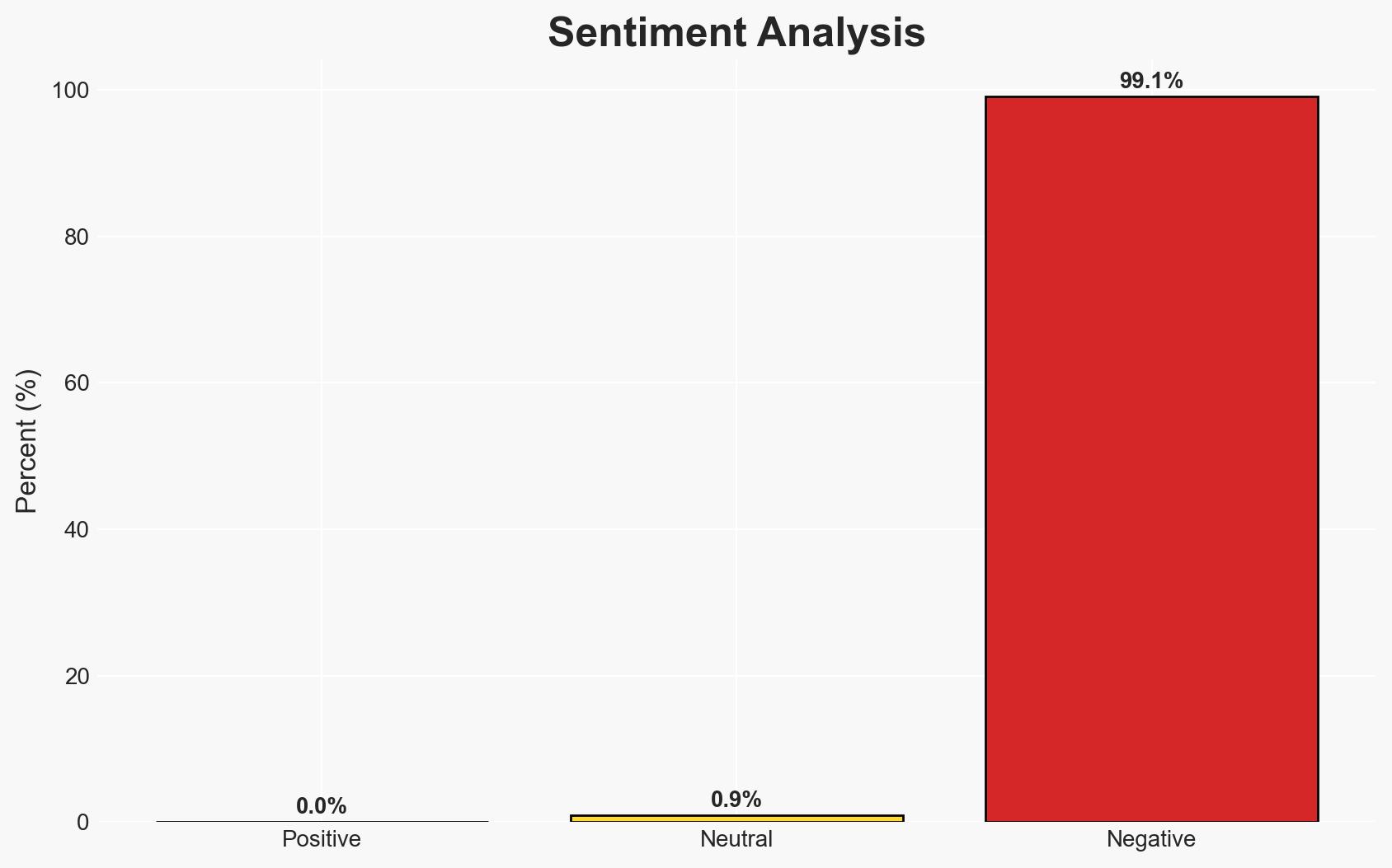
The UK Parliament is actively seeking industry input to refine the Cyber Security and Resilience Bill (CSRB), aiming to enhance regulations for critical infrastructure. The bill is likely to pass with minimal political resistance, but its effectiveness will depend on comprehensive industry engagement. Moderate confidence in the current trajectory of the bill’s development.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The CSRB will effectively strengthen UK cyber resilience by incorporating broad industry feedback, leading to robust regulatory updates. Evidence includes the committee’s active solicitation of input and cross-party support. Uncertainties include the extent of engagement from smaller entities and potential over-reporting issues.
- Hypothesis B: The CSRB may fall short of its objectives due to insufficient input from diverse industry stakeholders, particularly SMEs and MSPs, resulting in regulations that are either too broad or not adequately targeted. Supporting evidence includes concerns raised about the need for clearer definitions and streamlined reporting.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the structured approach of the parliamentary committee and the broad political backing. However, indicators such as limited SME participation or vague regulatory definitions could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The committee will genuinely incorporate industry feedback; cross-party support will remain stable; the bill will be implemented as scheduled.
- Information Gaps: Specific feedback from SMEs and MSPs; detailed definitions of new regulatory terms; clarity on enforcement mechanisms.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias towards larger tech companies in feedback; risk of over-reliance on existing frameworks without adaptation to new threats.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The CSRB’s development could significantly impact the UK’s cyber regulatory landscape, influencing both domestic and international cybersecurity practices.
- Political / Geopolitical: Strengthened cyber regulations may enhance the UK’s international standing as a leader in cybersecurity policy.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Improved regulations could reduce vulnerabilities in critical infrastructure, mitigating potential cyber-terrorism threats.
- Cyber / Information Space: Enhanced incident reporting and supply chain management could lead to better threat intelligence and response capabilities.
- Economic / Social: Effective implementation may bolster economic stability by protecting critical infrastructure, though compliance costs could impact smaller businesses.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Encourage diverse industry participation in the consultation process; monitor committee proceedings for emerging issues.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with industry bodies to facilitate compliance; invest in capacity-building for SMEs.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Comprehensive industry engagement leads to effective regulation, enhancing national cyber resilience.
- Worst: Limited stakeholder input results in ineffective regulations, increasing cyber risk exposure.
- Most-Likely: Moderate stakeholder engagement results in incremental improvements, with ongoing adjustments needed.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Jonathan Lee, Trend Micro’s UK cybersecurity director
- Public Bill Committee
- National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
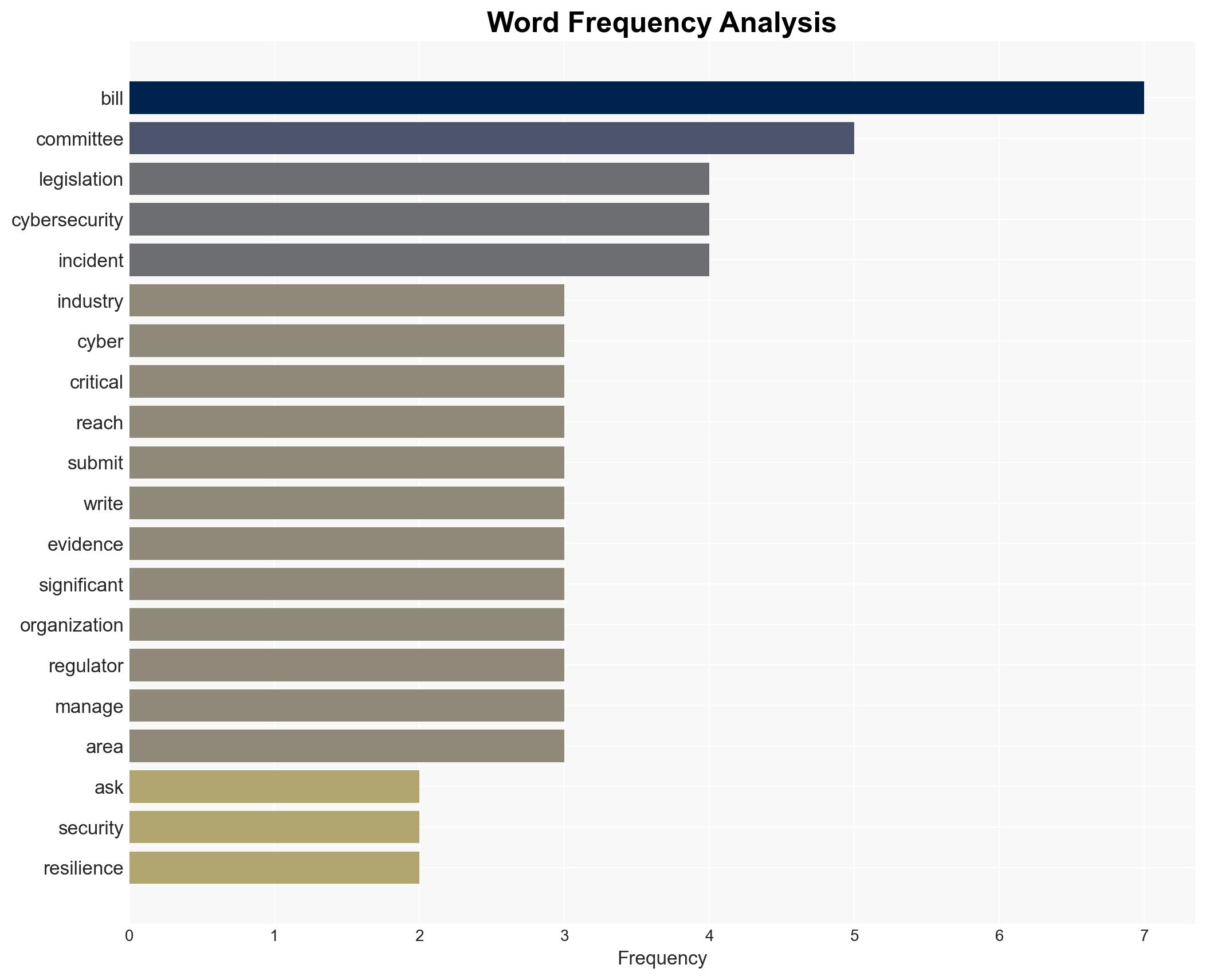
cybersecurity, legislation, critical infrastructure, UK Parliament, industry consultation, regulatory compliance, cyber resilience
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us