Patched FortiGate firewalls compromised due to unresolved authentication bypass vulnerability
Published on: 2026-01-21
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Fortinet admins report patched FortiGate firewalls getting hacked
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
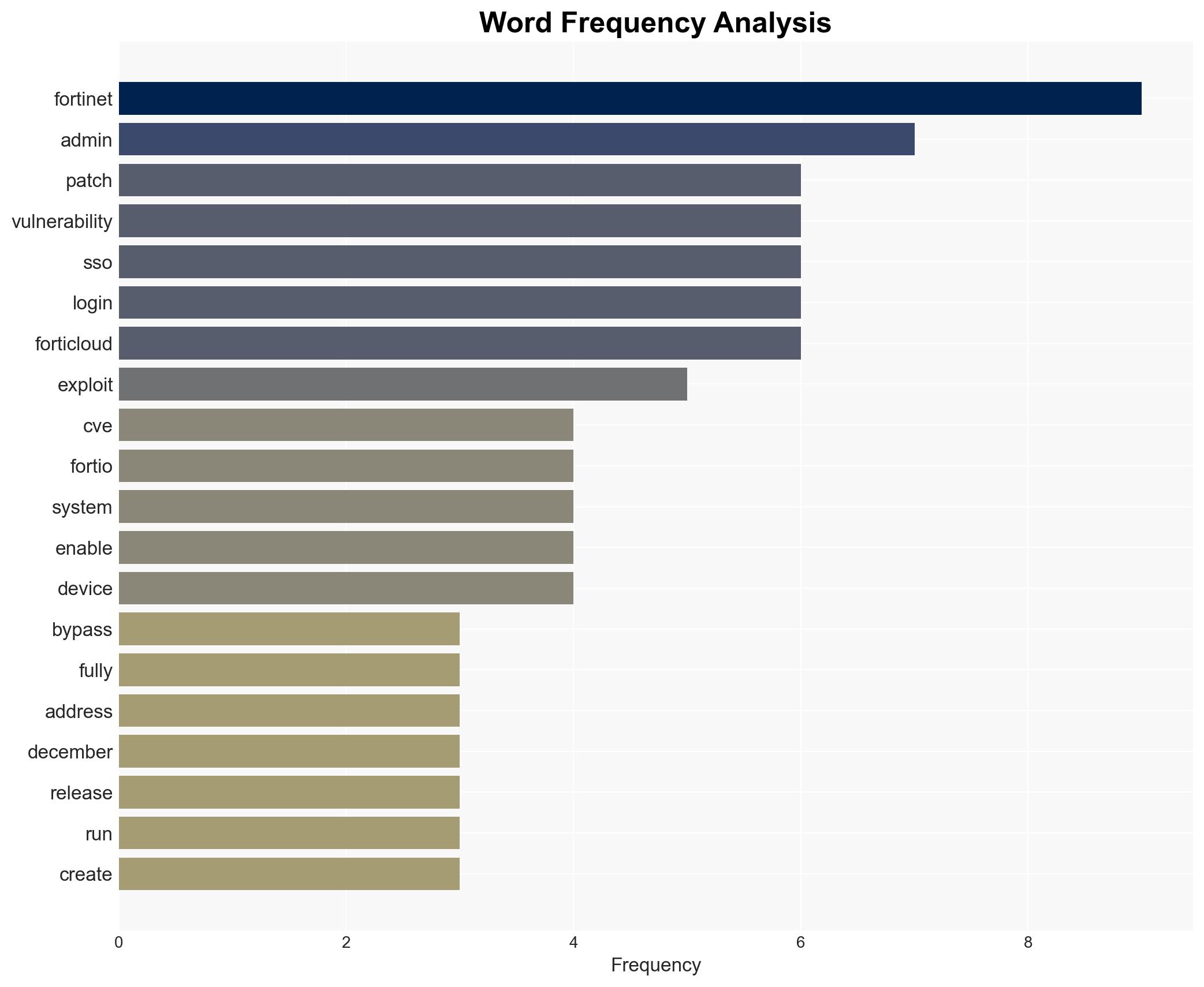
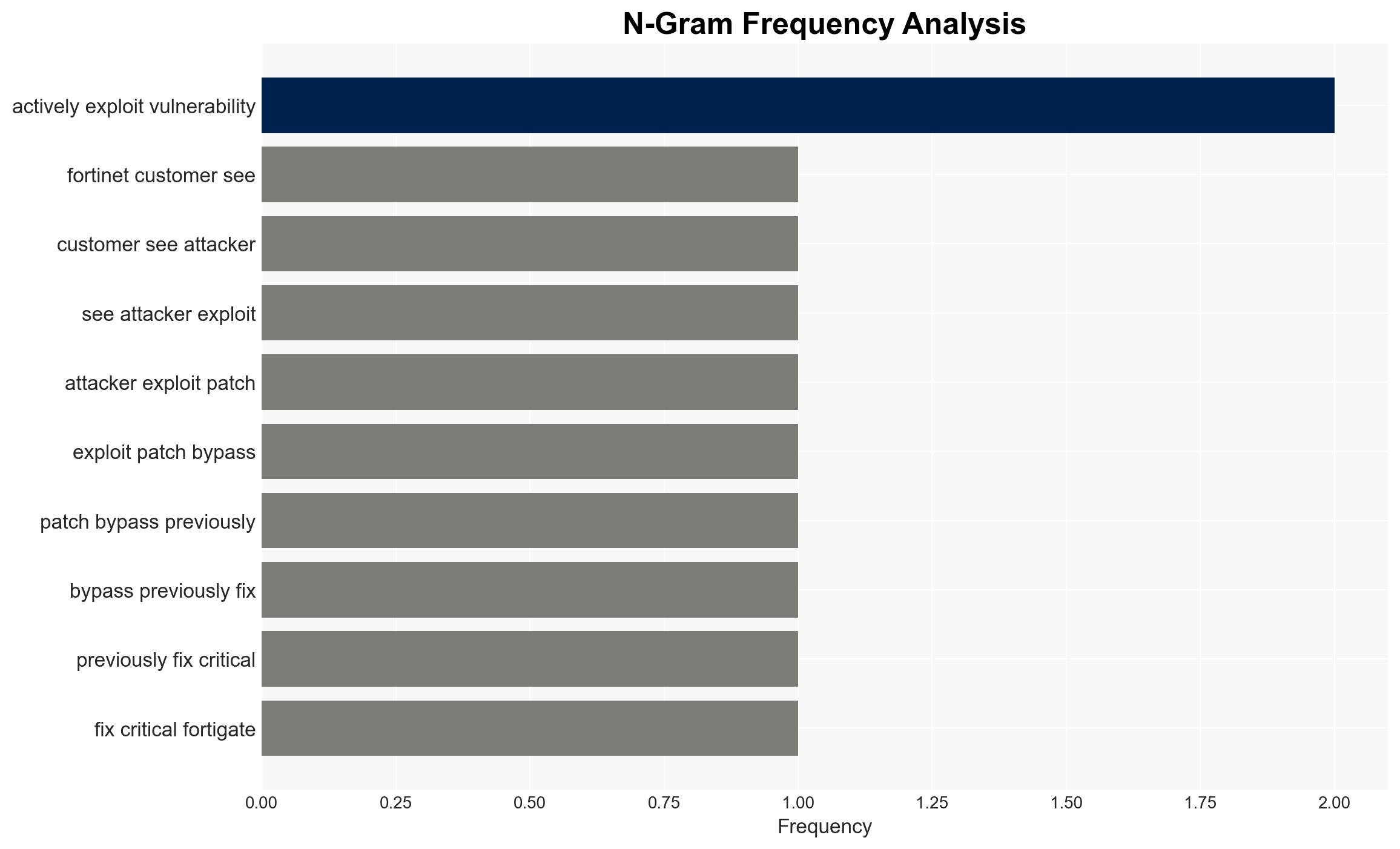
Fortinet firewalls, despite being patched, are reportedly still vulnerable due to a bypass of a critical authentication flaw (CVE-2025-59718). This issue affects organizations using FortiGate firewalls, potentially compromising their security posture. The most likely hypothesis is that the patch was incomplete, leaving systems exposed. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the lack of direct confirmation from Fortinet.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The patch for the FortiGate authentication vulnerability was incomplete, allowing attackers to exploit the flaw. Evidence includes reports from multiple admins experiencing similar breaches post-patch and Fortinet’s plan to release further updates. Key uncertainty lies in the lack of direct confirmation from Fortinet.
- Hypothesis B: There is a new, undisclosed vulnerability being exploited, rather than a bypass of the existing one. This is less supported due to the similarity in attack patterns and the admin reports aligning with previous exploitation methods.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to consistent reports of similar attack patterns and Fortinet’s acknowledgment of a persistent issue. Confirmation from Fortinet or evidence of a new vulnerability could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Fortinet’s forthcoming updates will address the vulnerability; the attack patterns reported are accurate and representative; Fortinet’s lack of response indicates ongoing investigation.
- Information Gaps: Direct confirmation from Fortinet regarding the nature of the vulnerability; detailed technical analysis of the exploit method.
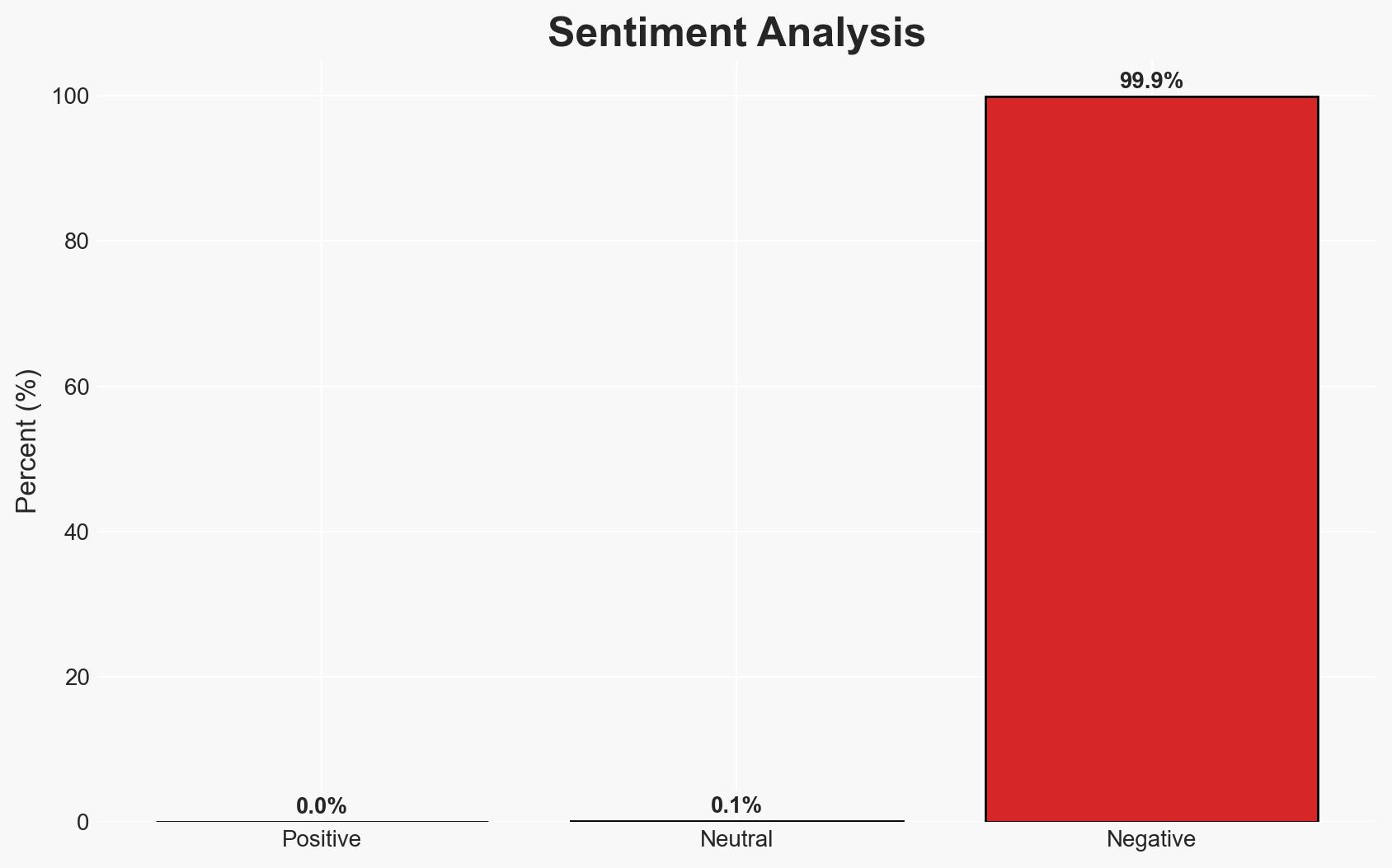
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias from affected admins seeking to shift responsibility; possibility of misinformation from attackers to obfuscate their methods.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This vulnerability could lead to increased cyber threats and exploitation if not addressed promptly, affecting organizational security and trust in Fortinet’s products.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased scrutiny on cybersecurity practices and vendor accountability.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Elevated risk of unauthorized access to sensitive systems, potentially impacting critical infrastructure.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased cyber espionage and data breaches, with potential for misinformation campaigns exploiting the vulnerability.
- Economic / Social: Financial losses for affected organizations and reputational damage to Fortinet, impacting market confidence.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Disable vulnerable features as advised, monitor systems for unusual activity, and apply forthcoming patches promptly.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen incident response capabilities, review vendor security practices, and enhance network monitoring.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Fortinet releases a comprehensive patch, restoring security and trust.
- Worst: Exploitation continues, leading to significant breaches and loss of sensitive data.
- Most-Likely: Fortinet addresses the issue with patches, but reputational damage persists, prompting increased scrutiny.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Fortinet
- Arctic Wolf (cybersecurity company)
- Shadowserver (tracking organization)
- CISA (Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, vulnerability management, Fortinet, network security, patch management, cyber threat, information security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us