Patero and Carahsoft Collaborate to Enhance Federal and Commercial Cryptography for Post-Quantum Transition
Published on: 2025-12-08
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Patero and Carahsoft Partner to Inventory Cryptography of Federal and Commercial Organizations for Transition to Post-Quantum Cryptography
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The partnership between Patero and Carahsoft aims to facilitate the transition of federal and commercial organizations to post-quantum cryptography (PQC) by providing cryptographic inventory and risk assessment solutions. This initiative is crucial for compliance with U.S. and Canadian government mandates to protect against quantum computing threats. The most likely hypothesis is that this partnership will accelerate the adoption of PQC solutions in the public sector, with moderate confidence due to existing regulatory pressures and technological uncertainties.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The partnership will significantly expedite the transition to PQC across federal and commercial sectors, driven by regulatory compliance and the strategic distribution network of Carahsoft. Supporting evidence includes existing government mandates and the partnership’s alignment with these requirements. Key uncertainties involve the pace of quantum computing advancements and organizational readiness.
- Hypothesis B: The transition to PQC will face delays despite the partnership, due to technological challenges, budget constraints, and potential resistance from organizations. Contradicting evidence includes the urgency expressed by government mandates and the strategic importance of securing sensitive data.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to regulatory pressures and the strategic alignment of the partnership with government timelines. Indicators that could shift this judgment include breakthroughs in quantum computing or significant organizational resistance to change.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The development of quantum computing will continue to progress, posing a credible threat to current encryption methods. Government mandates will remain a driving force for PQC adoption. Organizations have the capability to implement the necessary changes within the specified timelines.
- Information Gaps: Detailed timelines for the development and deployment of quantum computing capabilities. The current readiness level of organizations to transition to PQC.
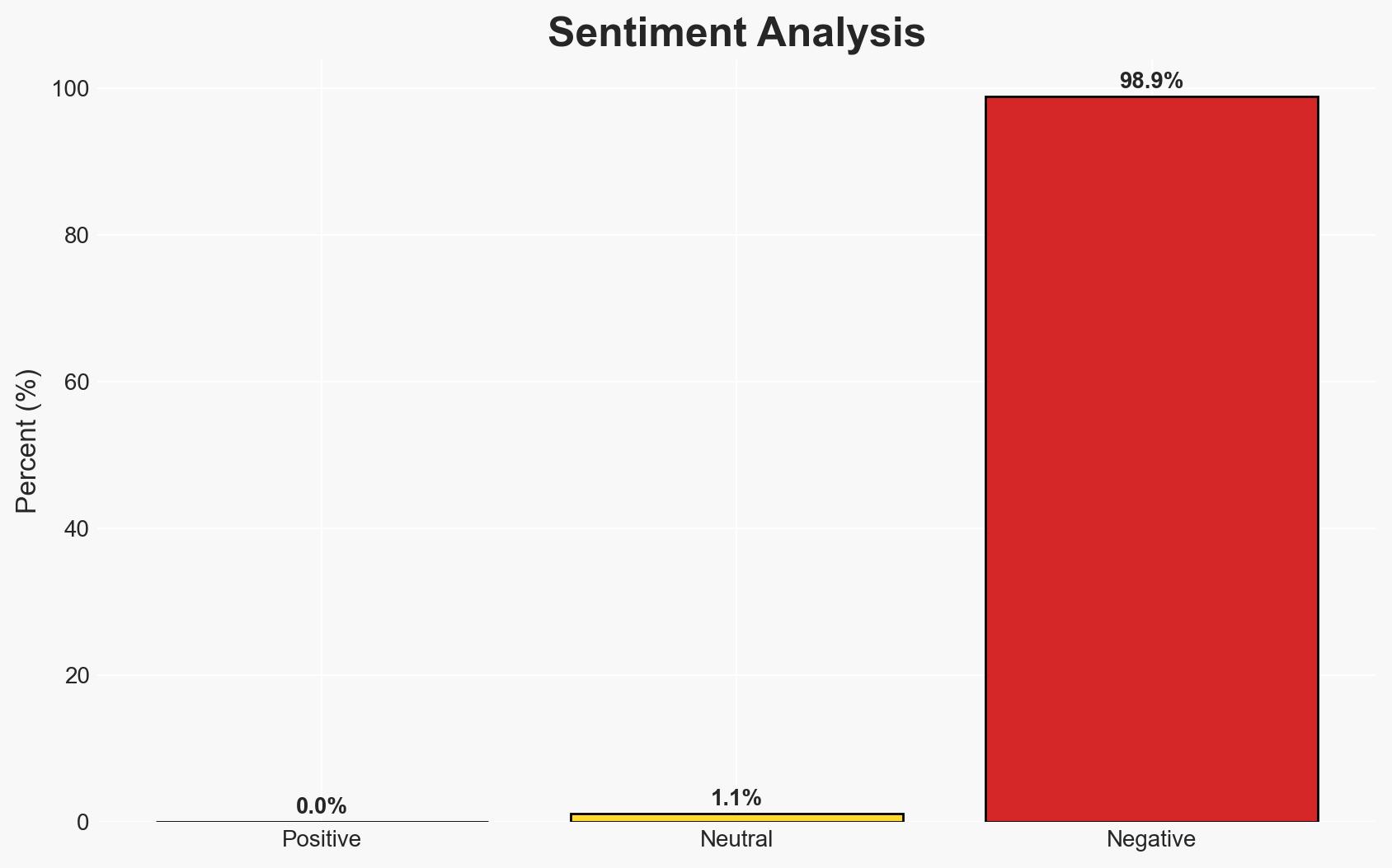
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential overestimation of the immediate threat posed by quantum computing to drive market demand. Source bias from commercial entities promoting their solutions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to accelerated PQC adoption, influencing global cryptographic standards and impacting national security strategies. The transition may also affect international relations as countries align their cryptographic policies.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased collaboration or tension between nations over cryptographic standards and cybersecurity policies.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced protection of sensitive data could reduce vulnerabilities to cyber threats and espionage.
- Cyber / Information Space: A shift in the cyber landscape as organizations adopt new encryption technologies, potentially leading to new vulnerabilities.
- Economic / Social: Economic implications for industries reliant on cryptographic technologies, with potential job creation in cybersecurity sectors.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor the implementation progress of PQC solutions in key sectors. Engage with stakeholders to assess readiness and identify potential barriers to adoption.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with technology providers to enhance PQC capabilities. Invest in training and awareness programs for organizations transitioning to PQC.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid adoption of PQC solutions, leading to enhanced data security and compliance.
- Worst: Significant delays in PQC adoption due to technological or budgetary constraints, increasing vulnerability to quantum threats.
- Most-Likely: Gradual transition to PQC, with some sectors advancing faster due to regulatory pressures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Peter Bentley, Chief Operating Officer at Patero
- Carahsoft Technology Corp.
- Patero Inc.
- U.S. Government Agencies
- Canadian Government Departments
7. Thematic Tags
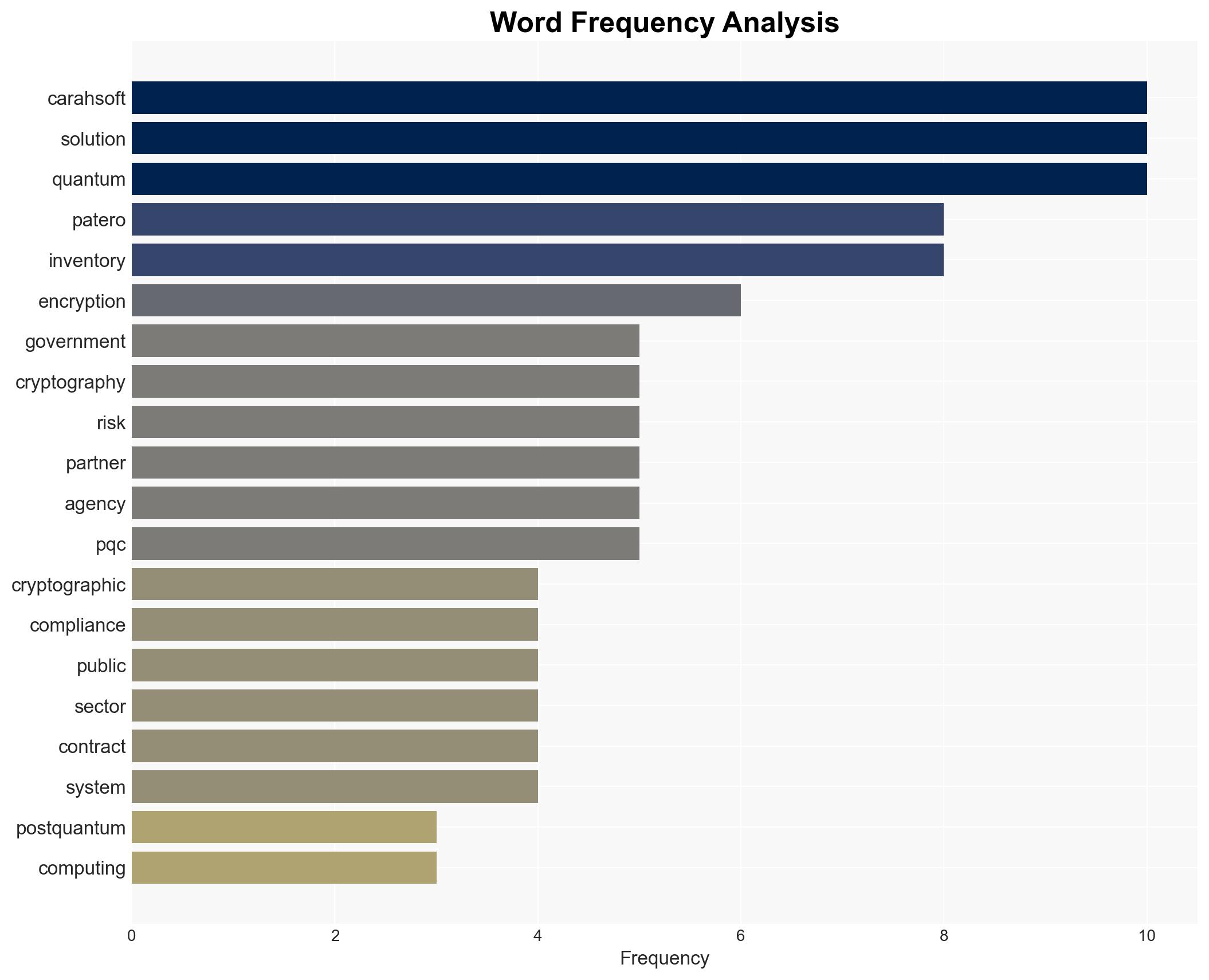
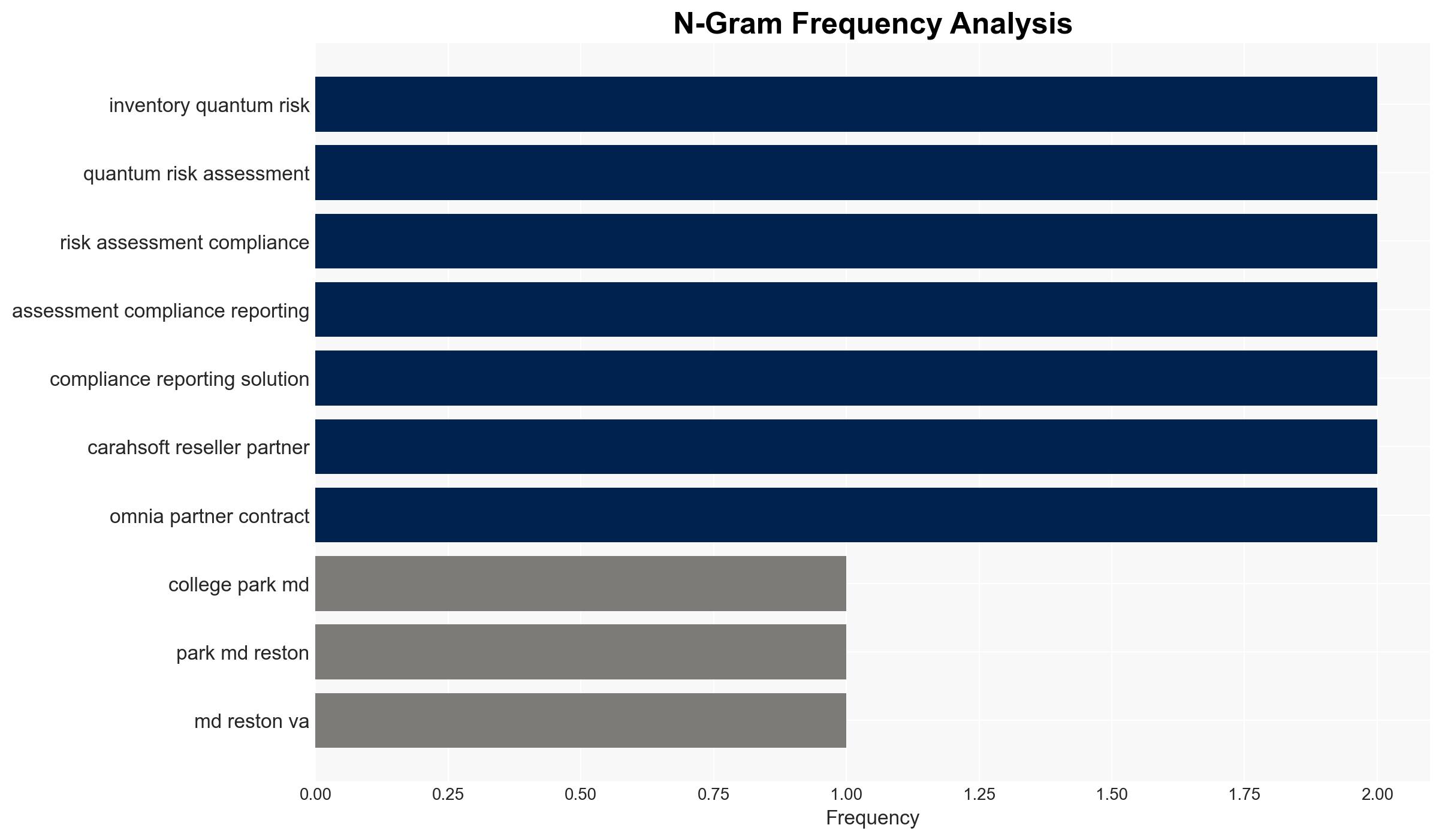
Cybersecurity, post-quantum cryptography, federal compliance, quantum computing, cryptographic inventory, public sector IT, data protection
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us