Phishing Campaigns Exploit Fake PayPal Alerts to Compromise Credentials and Deploy RMM Tools
Published on: 2026-01-14
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Hackers Use Fake PayPal Notices to Steal Credentials Deploy RMMs
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
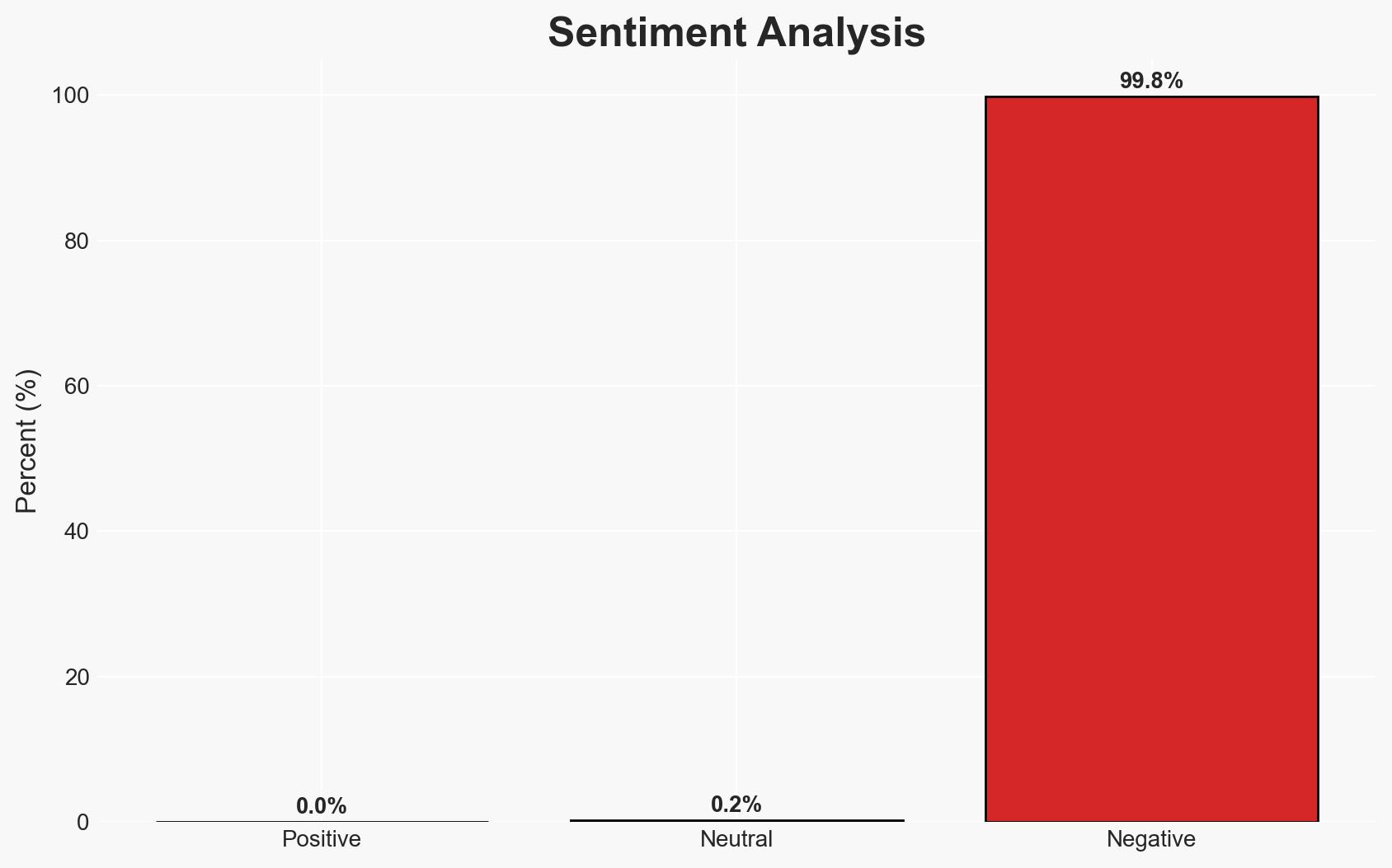
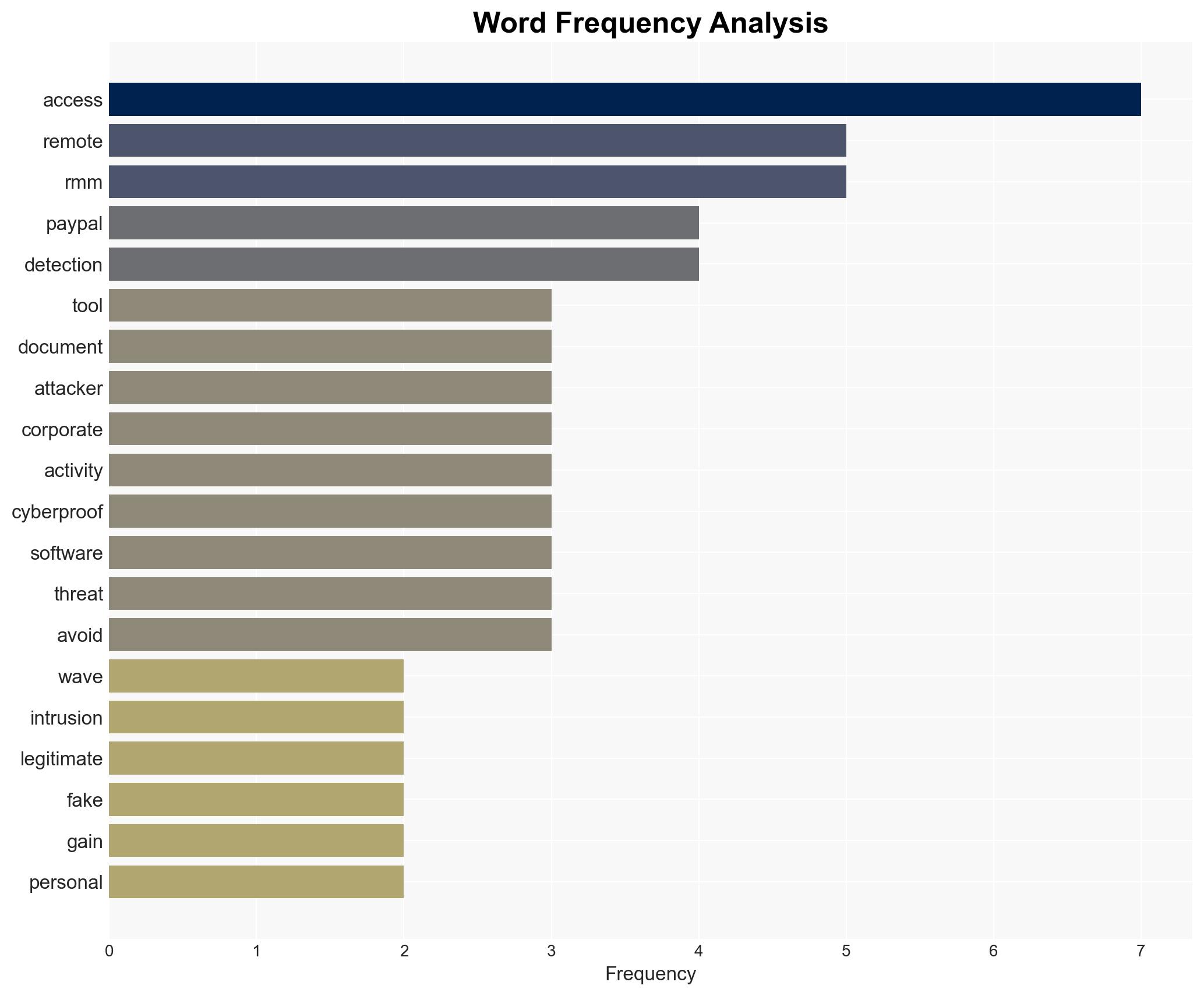
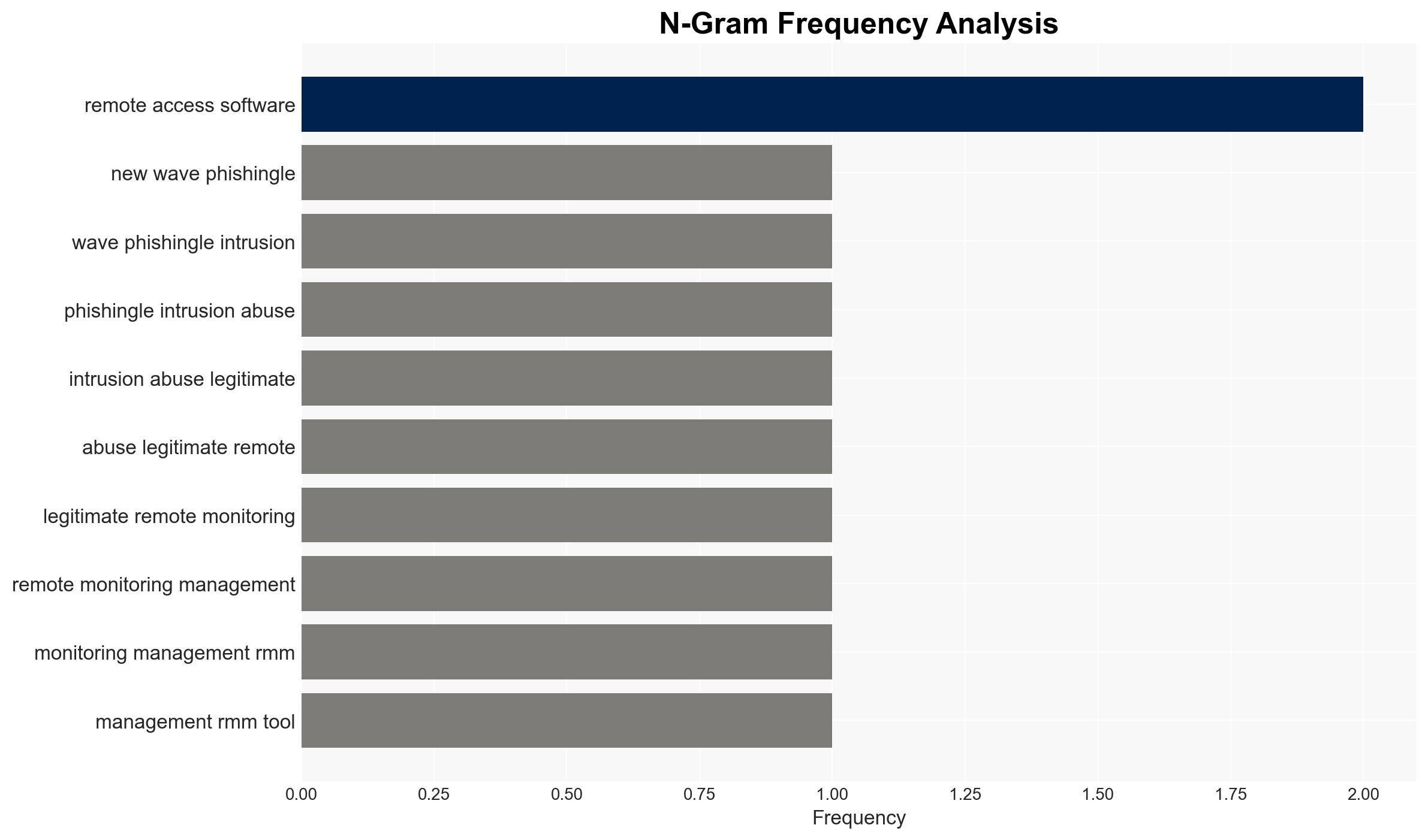
Recent phishing campaigns have shifted to using fake PayPal alerts to deploy Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tools, posing a significant threat to both personal and corporate security. This tactic leverages legitimate software to evade detection, with potential long-term risks including corporate compromise and ransomware attacks. The most likely hypothesis is that financially motivated cybercriminals are exploiting these methods, with moderate confidence in this assessment.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Financially motivated cybercriminals are using fake PayPal notices to deploy RMM tools for immediate financial gain. Evidence includes the use of financial-themed phishing and the deployment of RMM tools without triggering EDR alerts. However, the long-term sale of access to APT actors remains speculative.
- Hypothesis B: State-sponsored actors are using these tactics as a precursor to broader espionage or disruptive operations. This is less supported due to the primary financial theme and lack of direct state actor indicators.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the immediate financial focus and typical cybercriminal tactics observed. Indicators such as changes in phishing themes or the involvement of known APT groups could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The primary motivation is financial gain; RMM tools are chosen for their ability to evade detection; the campaign is not currently linked to state actors.
- Information Gaps: Specific attribution to threat actors; detailed analysis of the economic impact; potential links to broader campaigns.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Confirmation bias towards financial motives; potential underestimation of state actor involvement; reliance on limited incident samples.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased sophistication in phishing attacks and broader adoption of RMM tools by cybercriminals, potentially escalating to more severe corporate breaches.
- Political / Geopolitical: Minimal direct impact unless state actors are involved, which could escalate tensions.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased threat to corporate security environments, necessitating enhanced defensive measures.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for wider adoption of RMM tools in cybercrime, complicating detection and response efforts.
- Economic / Social: Potential financial losses for individuals and companies, leading to broader economic implications if widespread.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance phishing detection capabilities, restrict RMM tool access, and conduct user training on phishing awareness.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for threat intelligence sharing, invest in advanced detection technologies, and review third-party tool risks.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Campaigns are mitigated with minimal impact; Worst: Widespread corporate breaches and ransomware attacks; Most-Likely: Continued financial targeting with gradual sophistication increase.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, phishing, cybercrime, remote access tools, financial fraud, threat detection, information security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us