Phishing Scheme Targets LastPass Users to Steal Master Passwords Through Fake Maintenance Alerts
Published on: 2026-01-21
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
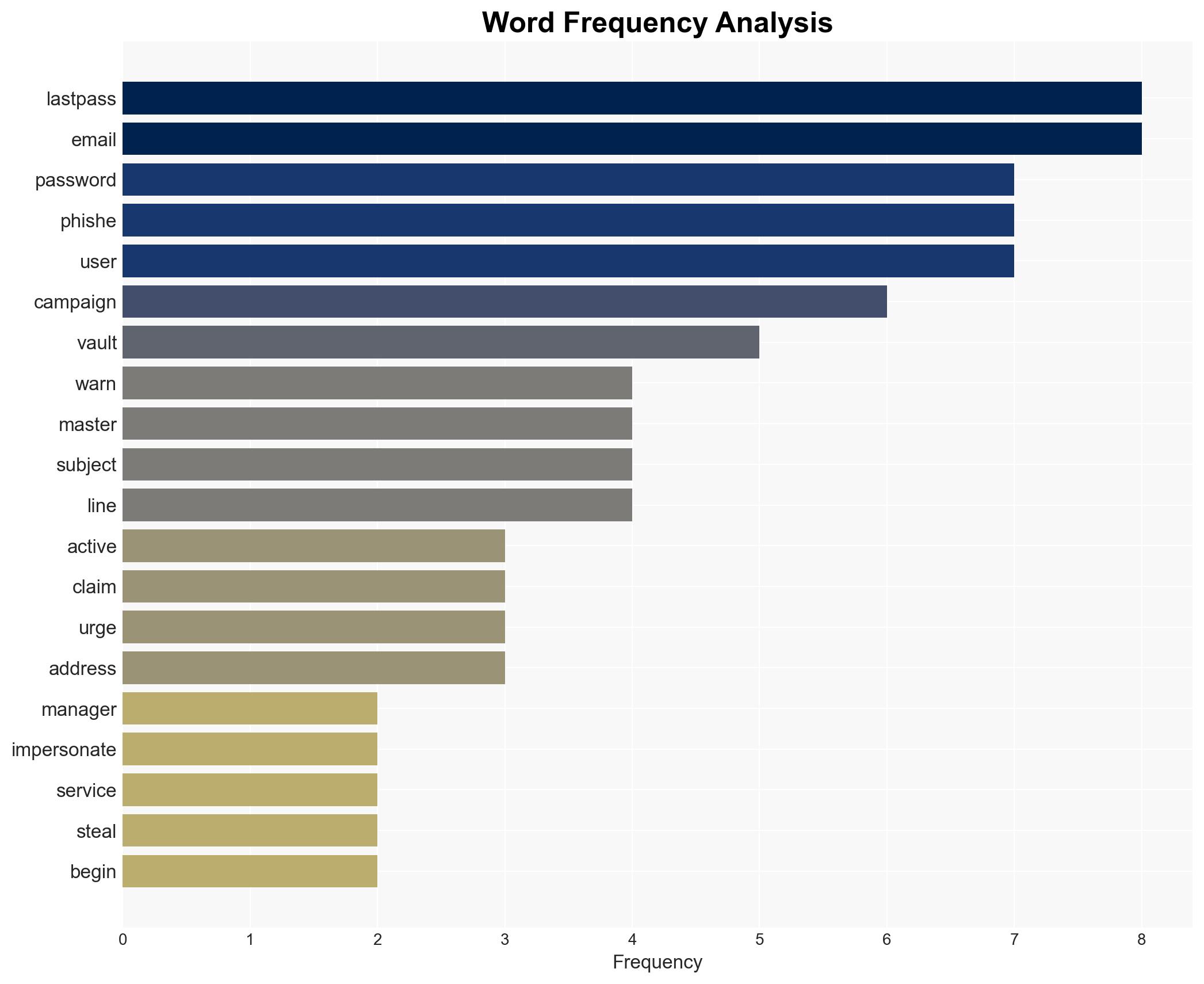
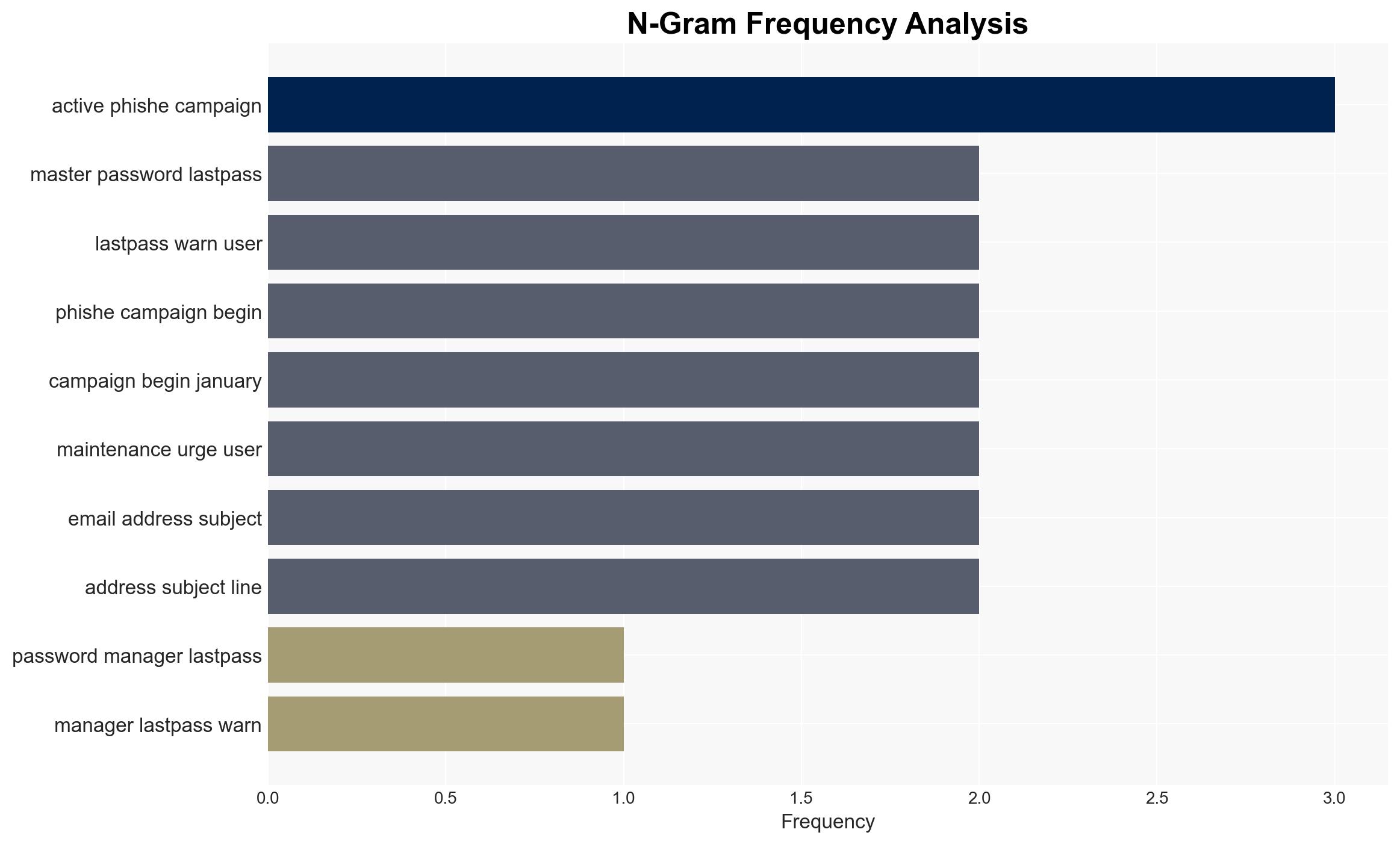
Intelligence Report: Crooks impersonate LastPass in campaign to harvest master passwords
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
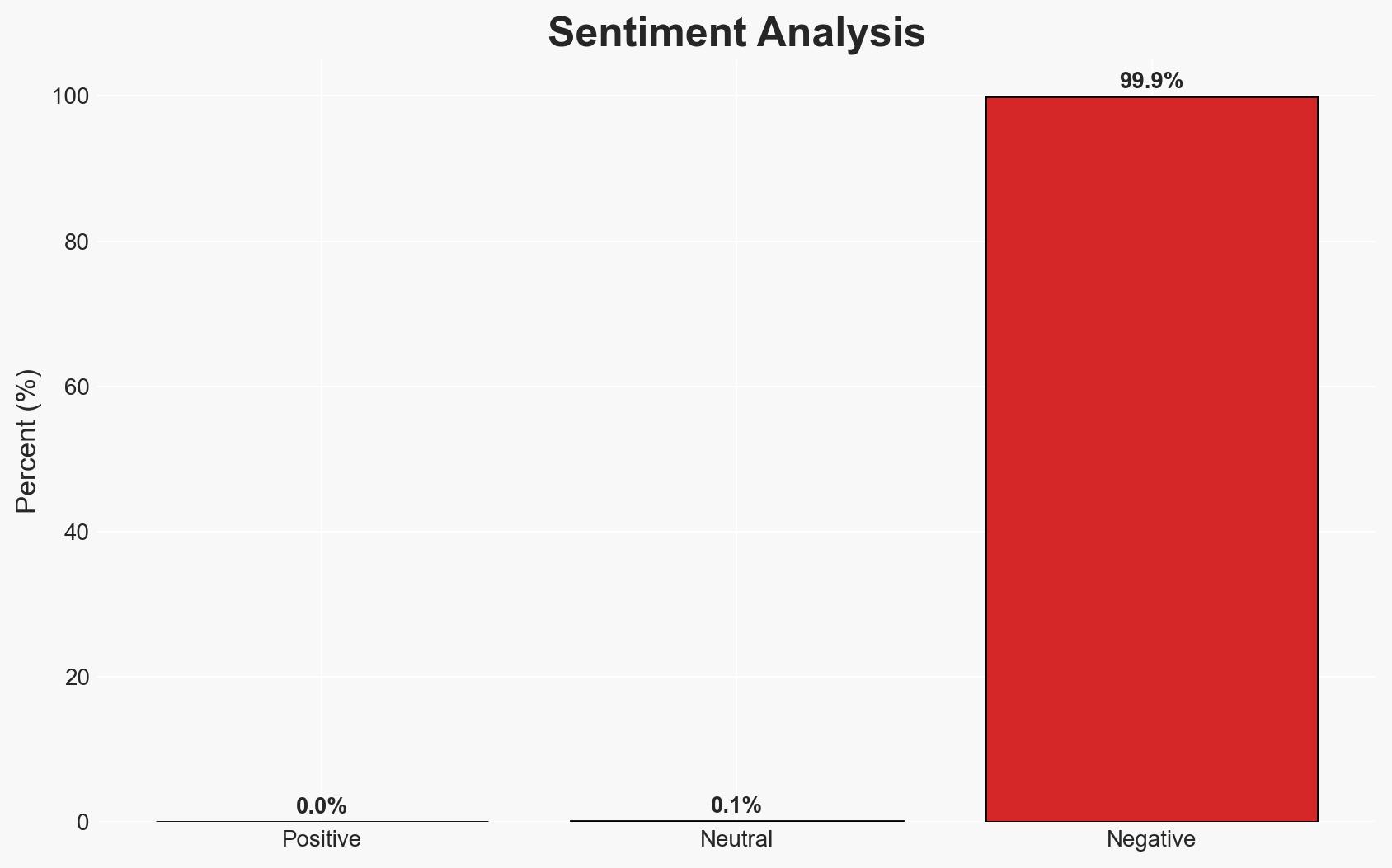
There is an active phishing campaign targeting LastPass users by impersonating the service to steal master passwords. The campaign exploits reduced staffing during a US holiday weekend to delay detection and response. The most likely hypothesis is that this is a financially motivated cybercrime operation. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to limited information on the threat actors and their capabilities.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The phishing campaign is a financially motivated cybercrime operation exploiting LastPass’s previous vulnerabilities and user trust. Supporting evidence includes the timing of the attack over a holiday weekend and the use of fake domains to mimic LastPass. Key uncertainties include the identity of the threat actors and their potential connections to previous breaches.
- Hypothesis B: The campaign is a state-sponsored operation aimed at gathering credentials for broader espionage activities. This is less supported due to the lack of evidence linking the campaign to state actors and the focus on financial gain indicated by the tactics used.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the financial nature of the phishing tactics and the exploitation of known vulnerabilities. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of state actor involvement or broader strategic objectives beyond financial theft.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The attackers are primarily financially motivated; LastPass users are the primary targets; the phishing campaign’s timing was strategically chosen to exploit reduced staffing.
- Information Gaps: The identity and origin of the threat actors; the full scope of affected users; potential connections to other cyber incidents.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Confirmation bias towards financial motives due to the nature of the phishing; potential underestimation of the attackers’ sophistication and broader objectives.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This phishing campaign could lead to significant data breaches, financial losses, and erosion of trust in password management services. It may also encourage similar attacks by other threat actors.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential diplomatic tensions if state-sponsored involvement is discovered.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased threat to cybersecurity infrastructure and potential for escalated cybercrime activities.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened awareness and potential regulatory scrutiny on password management services and their security practices.
- Economic / Social: Financial losses for individuals and businesses; potential decrease in consumer confidence in digital security solutions.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of phishing activity; collaborate with cybersecurity firms to identify and mitigate threats; inform users of security best practices.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures, including improved user authentication methods; strengthen partnerships with tech companies and law enforcement.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Rapid mitigation and increased user awareness reduce impact. Worst: Prolonged campaign leads to significant breaches and financial losses. Most-Likely: Continued phishing attempts with moderate success, prompting increased security measures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, phishing, cybercrime, password management, digital security, threat intelligence, financial fraud
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us