Poland restricts Chinese vehicles at military sites amid rising espionage and data security concerns
Published on: 2026-02-21
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Poland bans Chinese vehicles from military sites over espionage fears
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
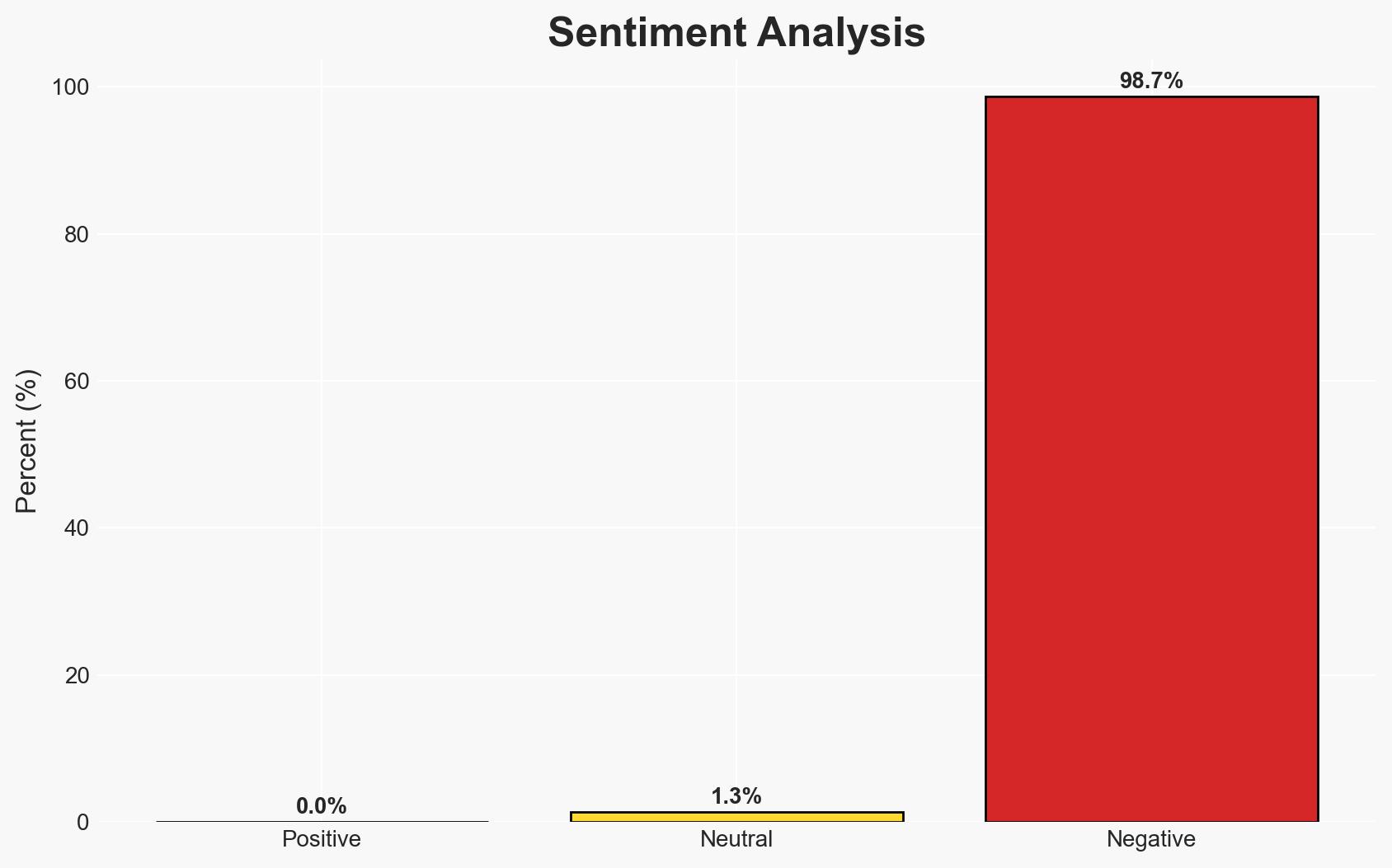
Poland has banned Chinese-made vehicles from military sites due to espionage concerns, aligning with broader Western distrust of Chinese technology. This decision is primarily driven by fears of data theft via integrated digital systems in vehicles. The move reflects a global trend prioritizing security over economic convenience, impacting Chinese automakers’ expansion in Europe. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Poland’s ban on Chinese vehicles is primarily a security measure to prevent espionage and data theft, supported by the integration of digital systems in vehicles and alignment with similar actions by other NATO members. However, the specific evidence of espionage activities remains unclear.
- Hypothesis B: The ban is a strategic move to curb China’s growing influence in Europe and protect domestic industries, rather than a direct response to an immediate espionage threat. The rapid growth of Chinese automakers in Poland supports this view, though it does not fully explain the security-focused rhetoric.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the alignment with broader Western security measures against Chinese tech and the explicit focus on espionage risks. Indicators such as increased incidents of data breaches or new intelligence reports could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Poland’s security assessments are accurate; Chinese vehicles pose a genuine espionage risk; Western nations share a unified stance on Chinese tech threats.
- Information Gaps: Specific evidence of espionage activities via Chinese vehicles; details on Poland’s risk assessment methodology; China’s actual capabilities and intentions regarding vehicle-based surveillance.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential confirmation bias in Western assessments of Chinese tech; source bias from entities with economic interests in reducing Chinese market share; possible Chinese disinformation to downplay espionage capabilities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased tensions between China and Western nations, influencing global tech policies and economic relations. The ban may prompt further restrictions on Chinese technology in critical infrastructure.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential diplomatic strain between Poland and China; reinforcement of NATO’s collective security posture against perceived Chinese threats.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced security protocols for military sites; potential increase in counter-intelligence activities targeting Chinese tech.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened focus on cybersecurity measures for digital systems in vehicles; potential cyber retaliation from China.
- Economic / Social: Impact on Chinese automakers’ market share in Europe; possible economic repercussions for Poland if China retaliates economically.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor Chinese diplomatic and economic responses; enhance cybersecurity measures for military and critical infrastructure.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with allies for shared intelligence on Chinese tech threats; invest in domestic tech capabilities to reduce reliance on foreign systems.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Strengthened Western alliances and improved domestic tech industries.
- Worst: Escalation into broader economic conflict with China.
- Most-Likely: Continued diplomatic tensions with incremental policy adjustments by both sides.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Polish Military
- Chinese Foreign Ministry
- Chinese Automakers
- Polish Automotive Industry Association (PZPM)
- Huawei
- Guo Jiakun (Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesperson)
7. Thematic Tags
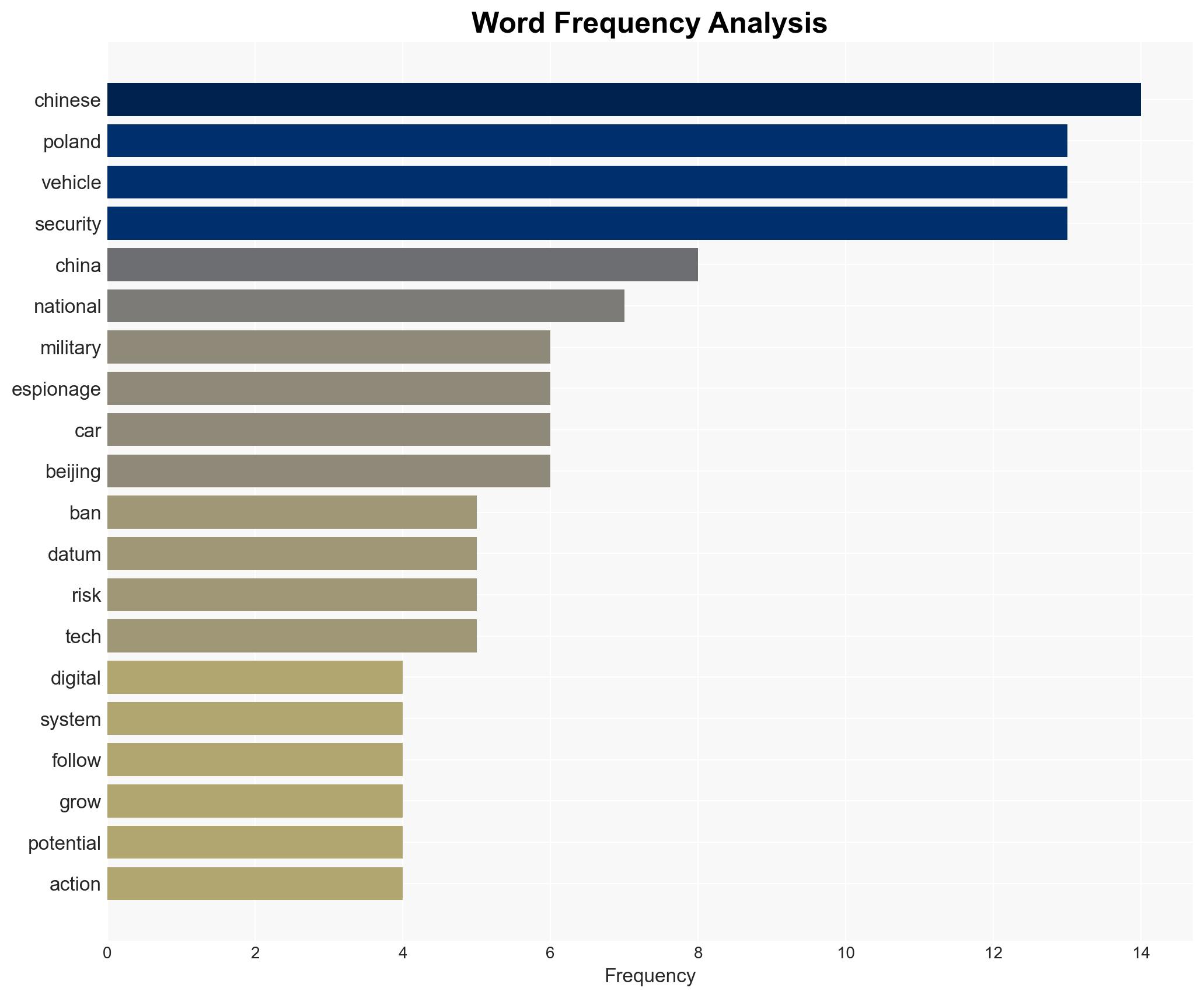
cybersecurity, national security, espionage, Chinese technology, NATO, economic impact, geopolitical tensions
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us