Post-quantum Cryptography Market Global Forecast to 2030 Opportunities Driven by PQC Integration HPC Advancements Early Product Development Government Contracts and Post-Quantum Migration
Published on: 2025-11-21
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Post-Quantum Cryptography Market Global Forecast to 2030
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
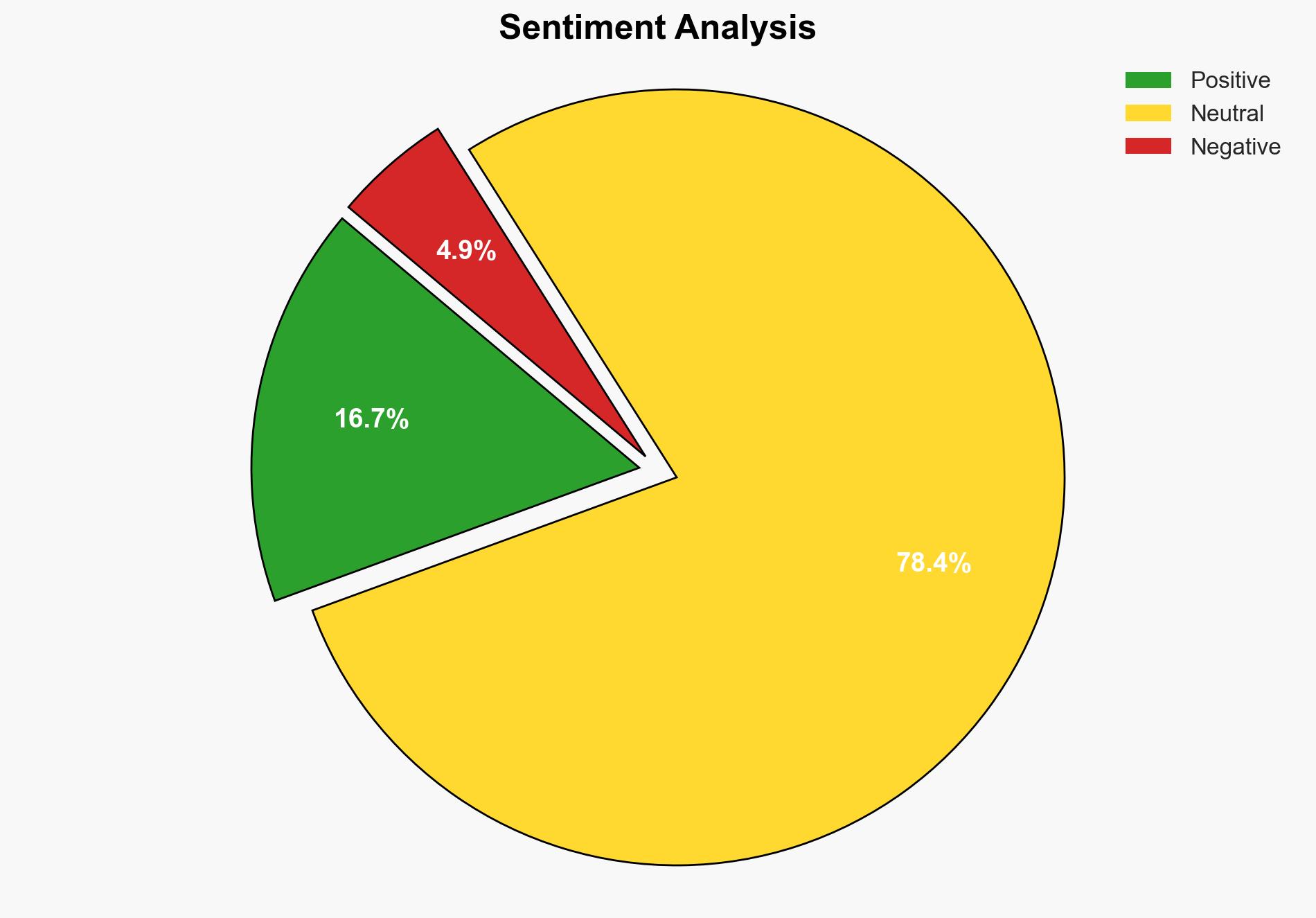
The post-quantum cryptography (PQC) market is poised for significant growth driven by advancements in high-performance computing (HPC), early product development, and government contracts. The most supported hypothesis is that the market will expand rapidly as enterprises strive to meet new cyber regulations and adopt quantum-resilient technologies. Confidence Level: High. Recommended action includes prioritizing investment in PQC technologies and fostering collaborations to enhance market readiness.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The PQC market will experience rapid growth due to increased demand for quantum-resilient solutions driven by regulatory requirements and emerging quantum threats.
Hypothesis 2: The PQC market growth will be slower than anticipated due to high implementation costs and technical challenges associated with integrating PQC into existing systems.
Hypothesis 1 is more likely due to strong indicators such as government initiatives, industry collaboration, and the proactive development of PQC solutions by major firms like IBM and Google. Hypothesis 2, while plausible, is less supported given the current momentum and investment in PQC technologies.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: It is assumed that quantum computing will advance to a level where current encryption methods become vulnerable. Additionally, it is assumed that regulatory bodies will enforce quantum-resilient standards.
Red Flags: Potential overestimation of quantum computing threats in the near term could lead to premature investments. Additionally, reliance on a few key players for PQC solutions could create bottlenecks.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The primary risk is the potential for a quantum computing breakthrough that could render current encryption obsolete, leading to significant cybersecurity threats. Economically, failure to adopt PQC could result in substantial financial losses and liability for enterprises. Politically, nations that lag in PQC adoption may face increased vulnerability to cyber espionage.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Actionable Steps: Encourage public-private partnerships to accelerate PQC development. Invest in workforce training to address technical integration challenges. Monitor regulatory developments closely to ensure compliance.
- Best Scenario: Rapid PQC adoption leads to enhanced cybersecurity and robust protection against quantum threats.
- Worst Scenario: Delayed PQC integration results in widespread data breaches and economic losses.
- Most-likely Scenario: Steady growth in PQC adoption as enterprises gradually transition to quantum-resilient solutions.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
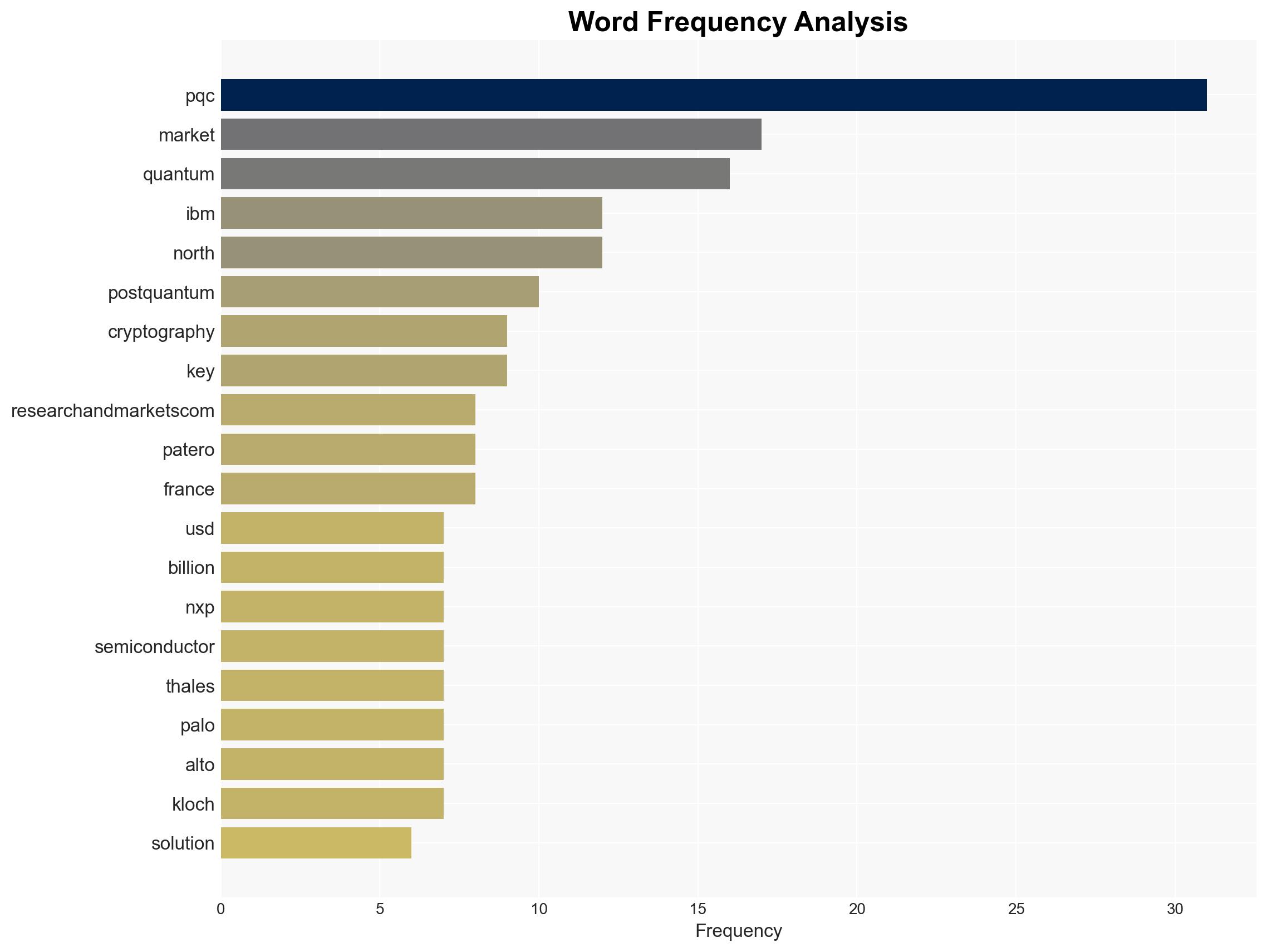
Key players include IBM, Google, AWS, NXP Semiconductor, Thales, and Palo Alto Networks. These entities are at the forefront of PQC development and integration.
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, Quantum Computing, Regulatory Compliance, Technology Innovation, Market Growth
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us