Protecting Your Vehicle: Understanding the Risks of Car Hacking and How to Safeguard Against It
Published on: 2026-02-18
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Your car can get hacked here’s how to protect yourself
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
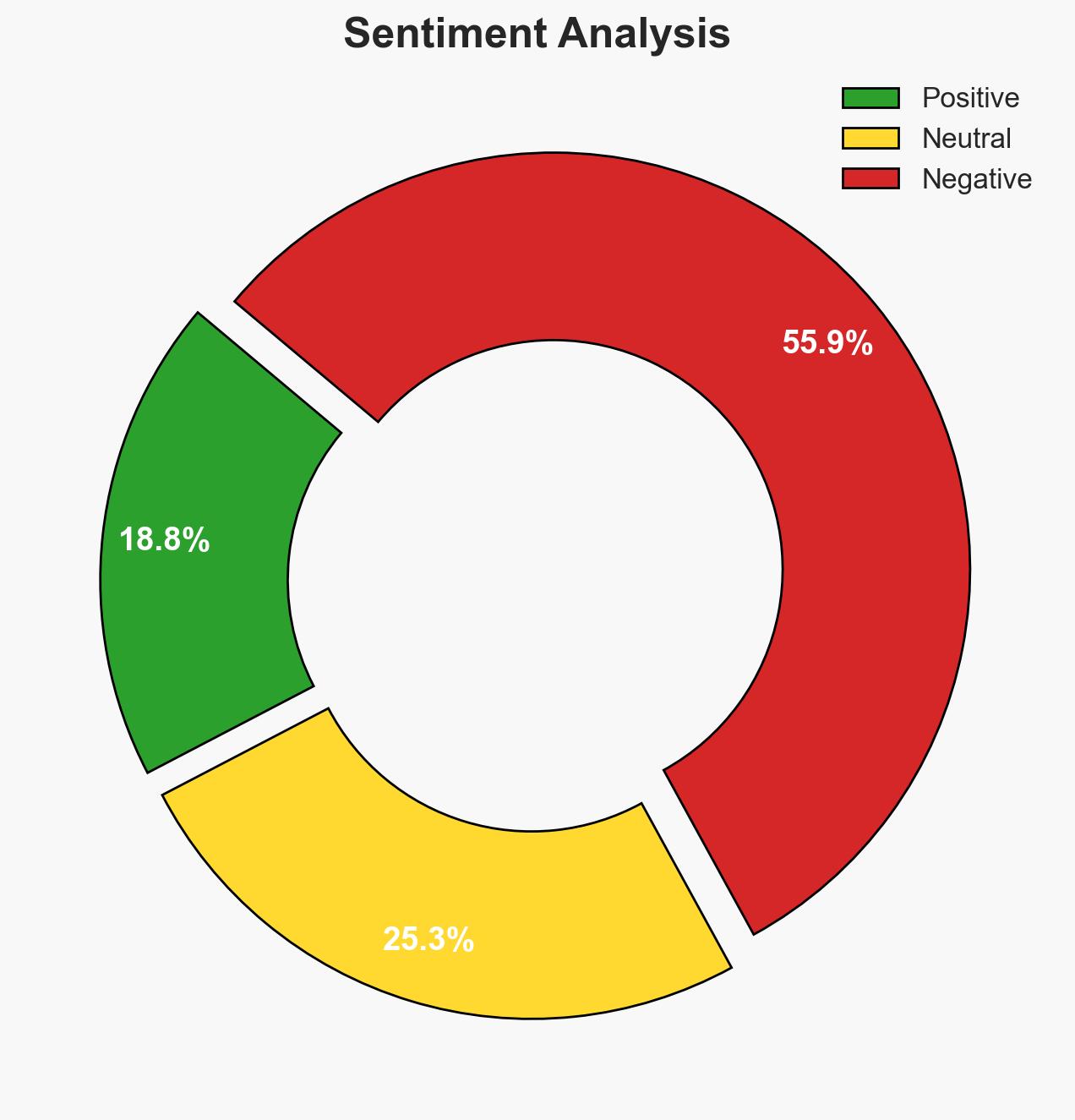
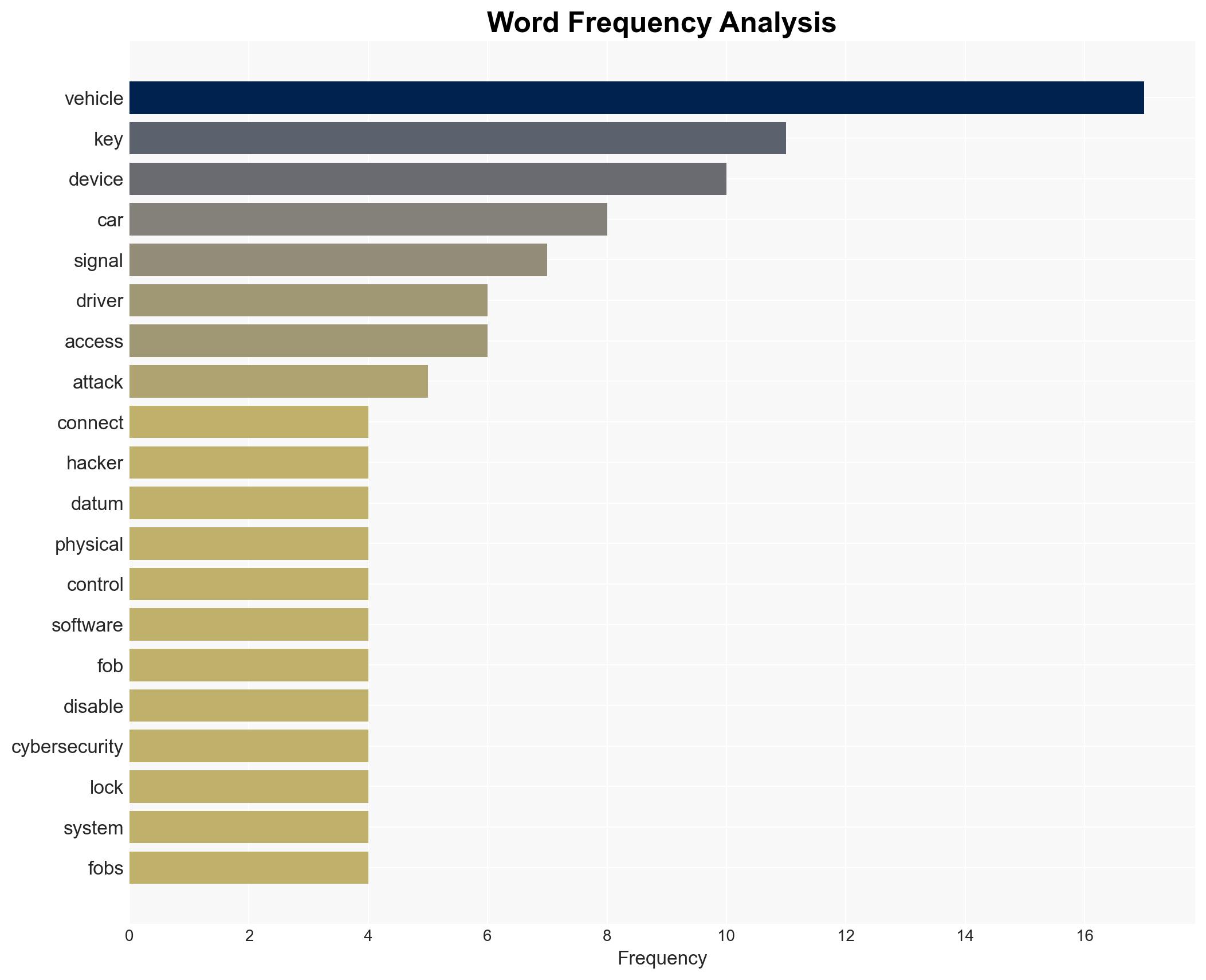
The increasing connectivity of modern vehicles introduces significant cybersecurity vulnerabilities, exposing drivers to risks of data theft, financial fraud, and unauthorized vehicle control. The most likely hypothesis is that cybercriminals will continue to exploit these vulnerabilities, affecting vehicle owners and manufacturers. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Cybercriminals will increasingly target vehicles as they become more connected, exploiting vulnerabilities in software, key fobs, and telematics systems. This is supported by historical incidents and the rise in sophisticated attacks. However, the extent of future attacks is uncertain due to potential improvements in vehicle cybersecurity.
- Hypothesis B: Automakers will successfully mitigate vehicle cybersecurity risks through enhanced security measures, reducing the frequency and impact of cyberattacks. While there is evidence of increased security efforts post-2015, the rapid evolution of cyber threats poses a challenge to this hypothesis.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the ongoing sophistication of attacks and the existing vulnerabilities in vehicle systems. Indicators such as increased investment in cybersecurity by automakers or new regulatory measures could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Vehicles will continue to integrate advanced connectivity features; cybercriminals will prioritize exploiting these systems; automakers will not significantly outpace threat actors in cybersecurity measures.
- Information Gaps: Specific data on the frequency and success rate of vehicle cyberattacks; detailed information on automakers’ cybersecurity strategies and investments.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from cybersecurity firms with vested interests; lack of transparency from automakers regarding vulnerabilities and breaches.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of vehicle cybersecurity threats could lead to increased regulatory scrutiny and influence consumer trust in automotive technology. The interplay between technological advancement and threat mitigation will shape the future landscape.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for international regulatory frameworks on vehicle cybersecurity; impact on trade if certain manufacturers are perceived as less secure.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of cyberterrorism targeting critical transportation infrastructure; potential for vehicles to be used as vectors in broader cyberattacks.
- Cyber / Information Space: Expansion of attack surfaces in the cyber domain; potential for misinformation campaigns exploiting vehicle vulnerabilities.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact on the automotive industry; erosion of consumer confidence in smart vehicle technologies.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of vehicle cybersecurity incidents; encourage automakers to disclose vulnerabilities and collaborate on solutions.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships between government, industry, and cybersecurity experts to enhance vehicle security; invest in public awareness campaigns about vehicle cybersecurity risks.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Automakers implement robust cybersecurity measures, significantly reducing attack success rates.
- Worst: Major cyberattack on vehicles leads to widespread disruption and loss of life.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in vehicle security, with ongoing but manageable cyber threats.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, automotive industry, data protection, cybercrime, vehicle technology, regulatory compliance, consumer safety
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us