Proton VPN Issues Warning Over Fake Chrome Extensions That Compromise User Security
Published on: 2026-02-20
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Fake Proton VPN extensions slip into Chrome Web Store heres how to stay safe
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
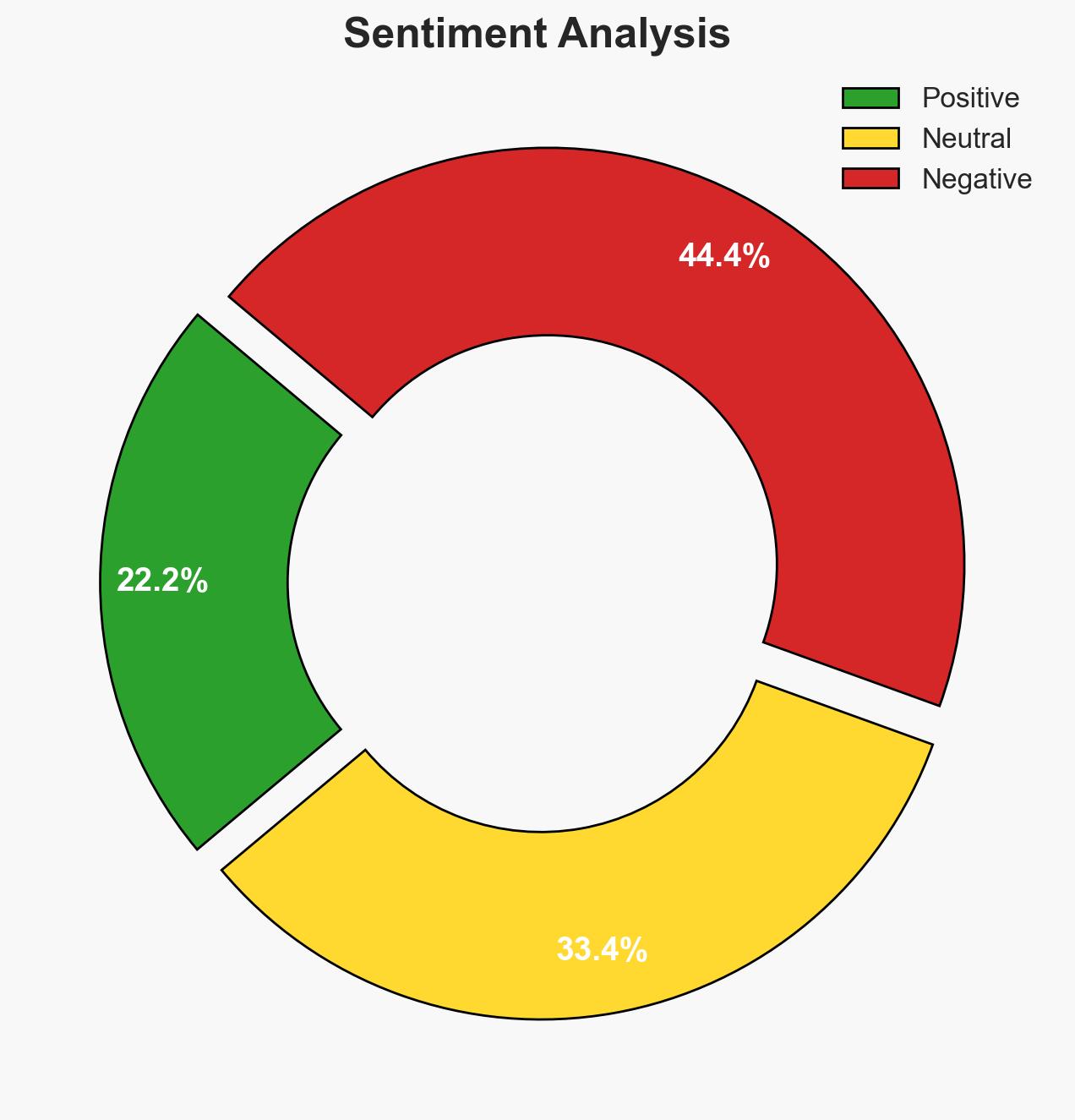
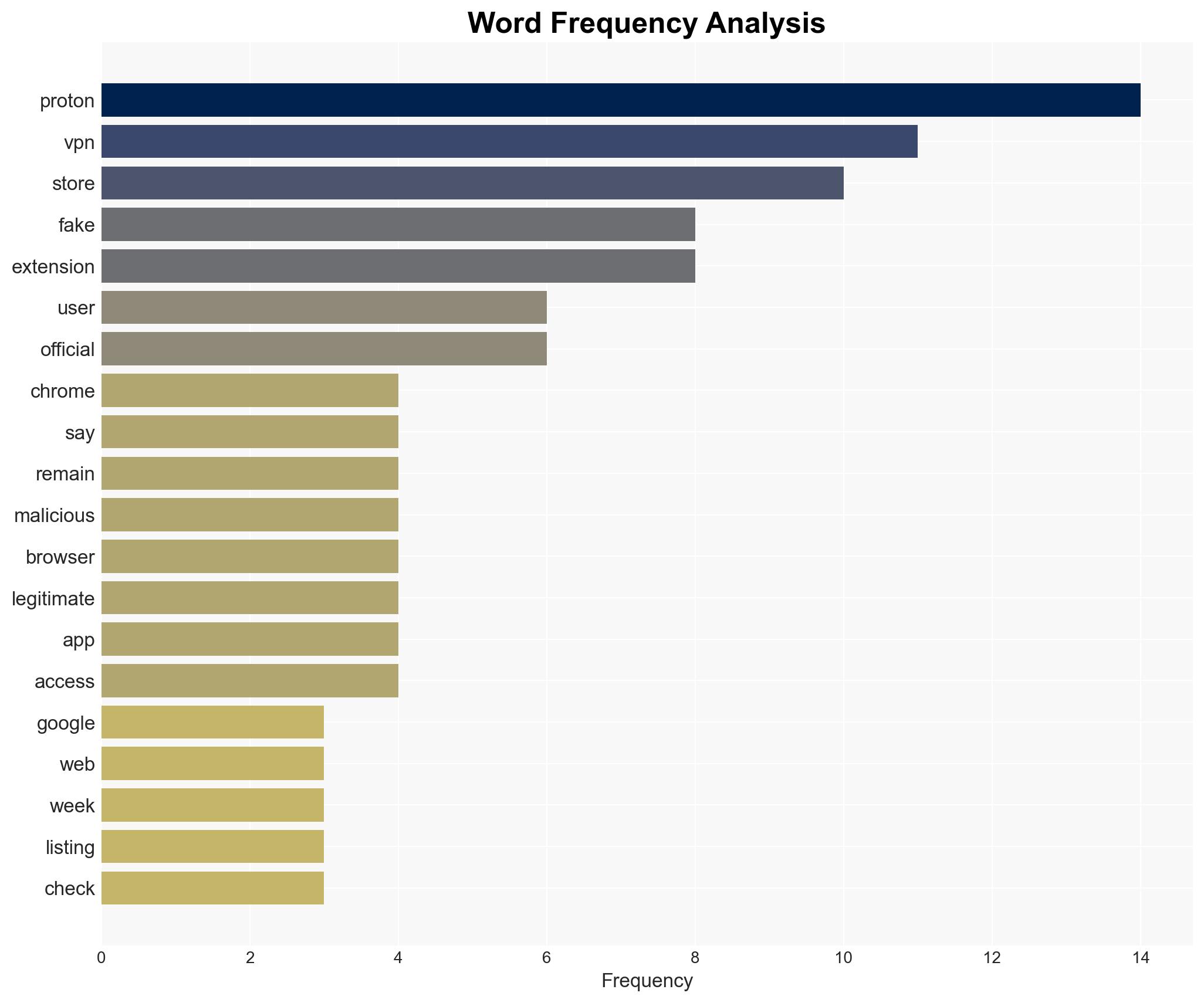
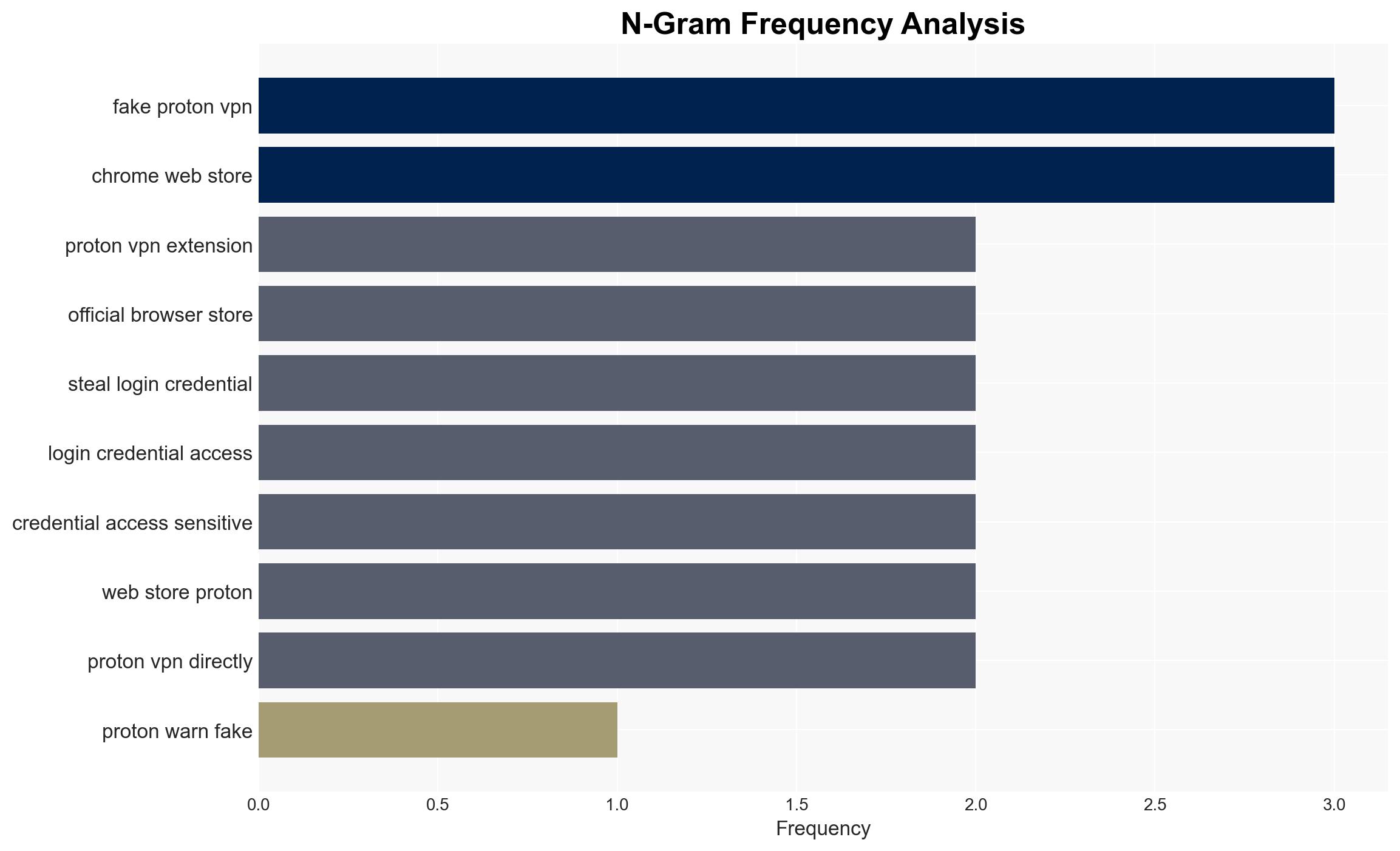
Fake Proton VPN extensions have been identified in the Chrome Web Store, posing significant security risks by impersonating a trusted provider to steal user data. The persistence of these malicious extensions highlights vulnerabilities in store moderation processes. This issue primarily affects users seeking secure VPN services, with a particular focus on the Russian market. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The fake extensions are the result of opportunistic cybercriminals exploiting weak moderation processes in the Chrome Web Store. Supporting evidence includes the repeated appearance of fake extensions despite notifications to Google. Key uncertainties involve the extent of Google’s internal processes and their responsiveness.
- Hypothesis B: The fake extensions are part of a coordinated effort to target specific user demographics, such as Russian users, for surveillance or data theft. This is supported by the targeting of the Russian market and the high demand for VPNs there. Contradicting evidence includes the lack of specific attribution to a coordinated group.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the repeated failures in store moderation and the general nature of the threat. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of coordinated efforts or state-sponsored involvement.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Users trust official browser stores; Google’s moderation processes are insufficient; demand for VPNs in Russia is high.
- Information Gaps: Details on Google’s internal review processes and the identity of the developers behind the fake extensions.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias from Proton in emphasizing risks to highlight their brand; deception risks from attackers using legitimate branding.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased scrutiny of browser store security and moderation processes. It may prompt users to seek alternative methods of obtaining software, impacting trust in official platforms.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased tensions in regions with high VPN demand, such as Russia, due to perceived targeting.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Potential exploitation by malicious actors to conduct surveillance or data theft.
- Cyber / Information Space: Highlighted vulnerabilities in digital marketplaces could lead to broader cyber hygiene campaigns.
- Economic / Social: Potential loss of consumer trust in digital marketplaces, impacting user behavior and market dynamics.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of browser store listings; engage with Google to improve moderation processes; educate users on safe download practices.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with tech companies to strengthen store security; invest in public awareness campaigns about digital security.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Improved store security and user awareness reduce incidents of fake extensions.
- Worst: Continued exploitation leads to significant data breaches and loss of trust in digital platforms.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in moderation with periodic incidents continuing to occur.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Proton AG
- Unverified developers (not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, digital marketplaces, VPN security, user data protection, browser extensions, cybercrime, online trust
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us