Qrator Labs Mitigated Record L7 DDoS Attack from 576M-Device Botnet – HackRead
Published on: 2025-09-13
Intelligence Report: Qrator Labs Mitigated Record L7 DDoS Attack from 576M-Device Botnet – HackRead
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
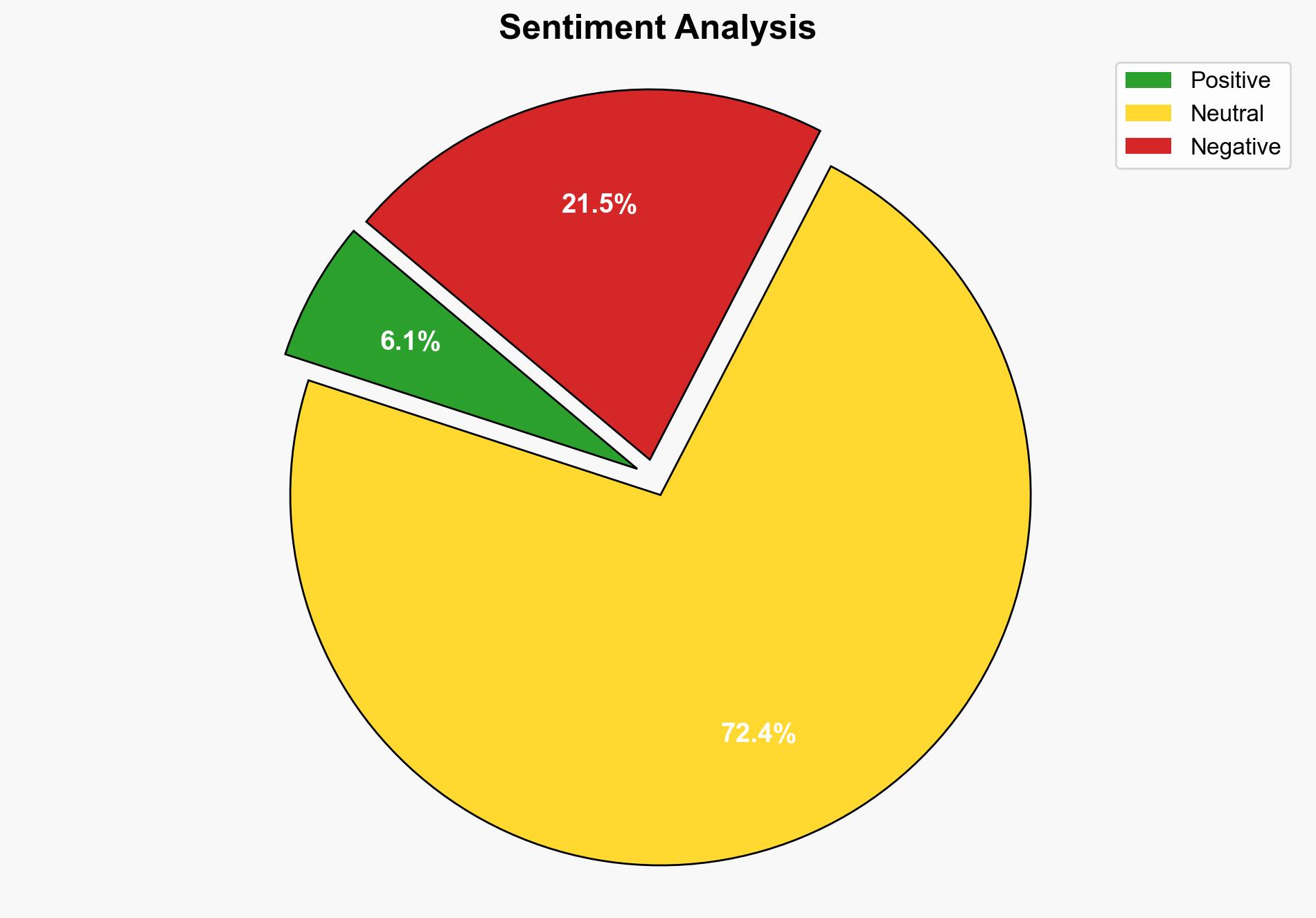
The analysis suggests that the DDoS attack mitigated by Qrator Labs, involving a 576 million-device botnet, represents a significant escalation in cyber threat capabilities, potentially indicating either a state-sponsored operation or a highly organized cybercriminal group. The most supported hypothesis is that this attack is a precursor to more targeted disruptions against critical infrastructure. Confidence level: Moderate. Recommended action: Enhance international collaboration on cybersecurity defenses and invest in advanced threat detection technologies.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The attack was orchestrated by a state actor aiming to test the resilience of government and critical infrastructure systems globally. This hypothesis is supported by the scale and sophistication of the attack, as well as the targeting of government organizations.
Hypothesis 2: The attack was conducted by a cybercriminal group seeking financial gain through extortion or disruption of services. This is supported by the involvement of online betting services and the potential for ransom demands.
Using ACH 2.0, Hypothesis 1 is more supported due to the strategic targeting and global distribution of the botnet, suggesting a motive beyond financial gain.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions include the belief that the scale of the botnet correlates with state-level resources, and that the attack’s timing aligns with geopolitical tensions. A red flag is the lack of direct attribution to a specific actor, which introduces uncertainty. There is also a potential blind spot in assuming that financial motives are secondary without concrete evidence.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The incident highlights a growing trend in the severity of DDoS threats, with implications for national security and economic stability. The potential for cascading effects on interconnected systems poses a strategic risk, especially if critical infrastructure is targeted. The geopolitical dimension suggests possible escalation if state involvement is confirmed, potentially leading to retaliatory cyber actions.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Enhance cybersecurity frameworks through international cooperation, focusing on intelligence sharing and joint response strategies.
- Invest in AI-driven threat detection systems to identify and neutralize botnet activities preemptively.
- Scenario-based projections:
- Best Case: Increased collaboration leads to improved defenses, deterring future large-scale attacks.
- Worst Case: Failure to adapt results in successful attacks on critical infrastructure, causing widespread disruption.
- Most Likely: Continued sporadic attacks with incremental improvements in defense mechanisms.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Andrey Leskin, Qrator Labs
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, regional focus