Quantum Computing Poses Significant Threat to Current Cryptographic Security Systems
Published on: 2025-12-29
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Is quantum about to break security
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
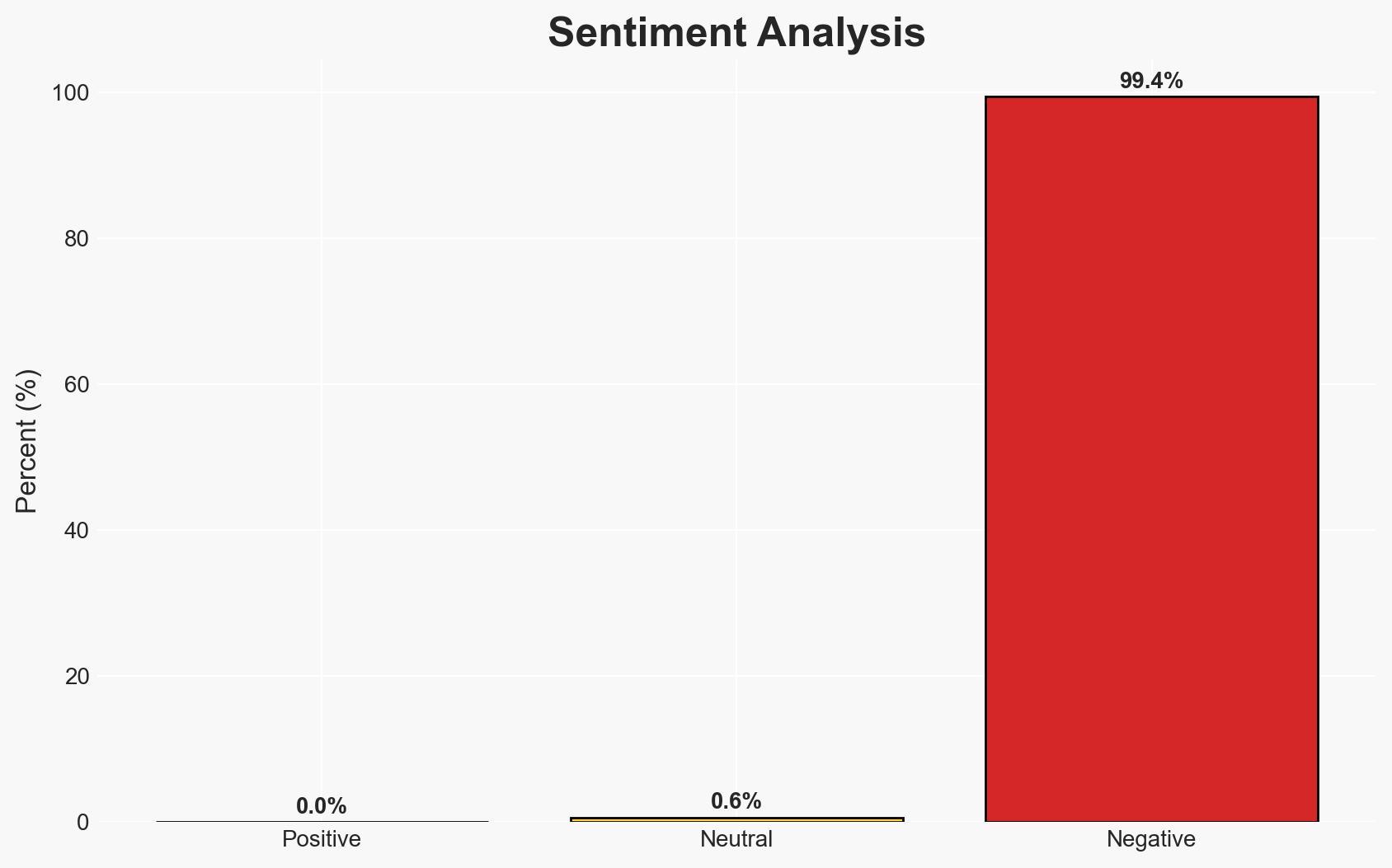
The advent of quantum computing poses a significant threat to current cryptographic systems, potentially compromising the security of sensitive data across banking, government, and critical infrastructure sectors. Crypto4a Technologies is actively developing solutions to mitigate these risks, but widespread adoption remains limited. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to existing information gaps regarding the pace of quantum computing advancements and private sector readiness.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Quantum computing will rapidly advance and disrupt existing cryptographic systems within the next few years. This hypothesis is supported by signals of accelerated timelines and government agency actions, but contradicted by the slow response from the commercial sector. Key uncertainties include the actual pace of quantum computing development and the effectiveness of emerging quantum-safe solutions.
- Hypothesis B: Quantum computing will advance more slowly, allowing sufficient time for the development and implementation of quantum-safe cryptographic solutions. This is supported by the historical pace of technological adoption and the ongoing efforts by companies like Crypto4a. However, it is contradicted by the urgency expressed by government agencies and the founders’ concerns about a dangerous gap in preparedness.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the proactive measures by government agencies and the founders’ direct involvement in national security initiatives. Indicators that could shift this judgment include breakthroughs in quantum-safe algorithms or significant delays in quantum computing advancements.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Quantum computing will achieve significant breakthroughs within a decade; current cryptographic systems will be vulnerable to quantum attacks; private sector adoption of quantum-safe solutions will lag behind government initiatives.
- Information Gaps: Detailed timelines for quantum computing advancements; specific capabilities of emerging quantum-safe technologies; private sector readiness and investment in quantum-safe solutions.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential overestimation of quantum computing timelines due to hype; reliance on limited sources with vested interests in promoting quantum-safe technologies.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The development of quantum computing could fundamentally alter the security landscape, necessitating a reevaluation of cryptographic standards and practices. This evolution will likely intersect with broader technological, economic, and geopolitical dynamics.
- Political / Geopolitical: Nations may accelerate quantum research to gain strategic advantages, potentially leading to an arms race in quantum technology.
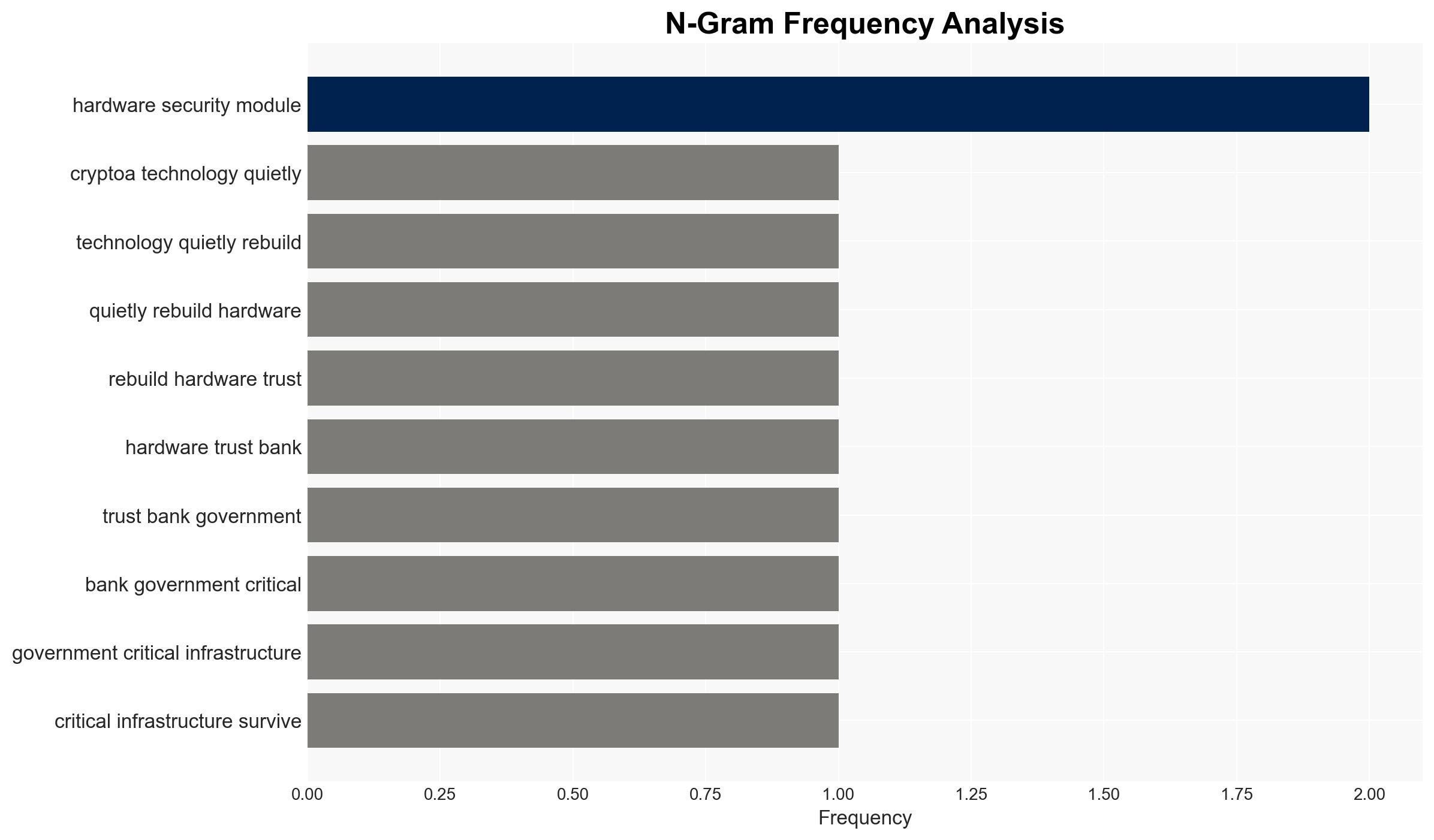
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of data breaches and espionage as adversaries exploit vulnerabilities in outdated cryptographic systems.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened need for robust cyber defenses and updated cryptographic protocols to protect sensitive information.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic disruption if financial systems are compromised; increased public concern over data privacy and security.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor advancements in quantum computing and quantum-safe technologies; engage with key stakeholders to assess readiness and vulnerabilities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with technology firms and research institutions; invest in quantum-safe cryptographic solutions and workforce training.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Quantum-safe solutions are developed and widely adopted before quantum computing becomes a threat.
- Worst: Quantum computing advances rapidly, leading to widespread data breaches and loss of trust in digital systems.
- Most-Likely: Gradual advancements in both quantum computing and quantum-safe technologies, with a transitional period of heightened risk.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Bruno Couillard, Chief Executive and Cofounder of Crypto4a Technologies
- Crypto4a Technologies
- Chrysalis ITS
- United States National Security Agency (NSA)
- Canada’s Communications Security Establishment (CSE)
7. Thematic Tags
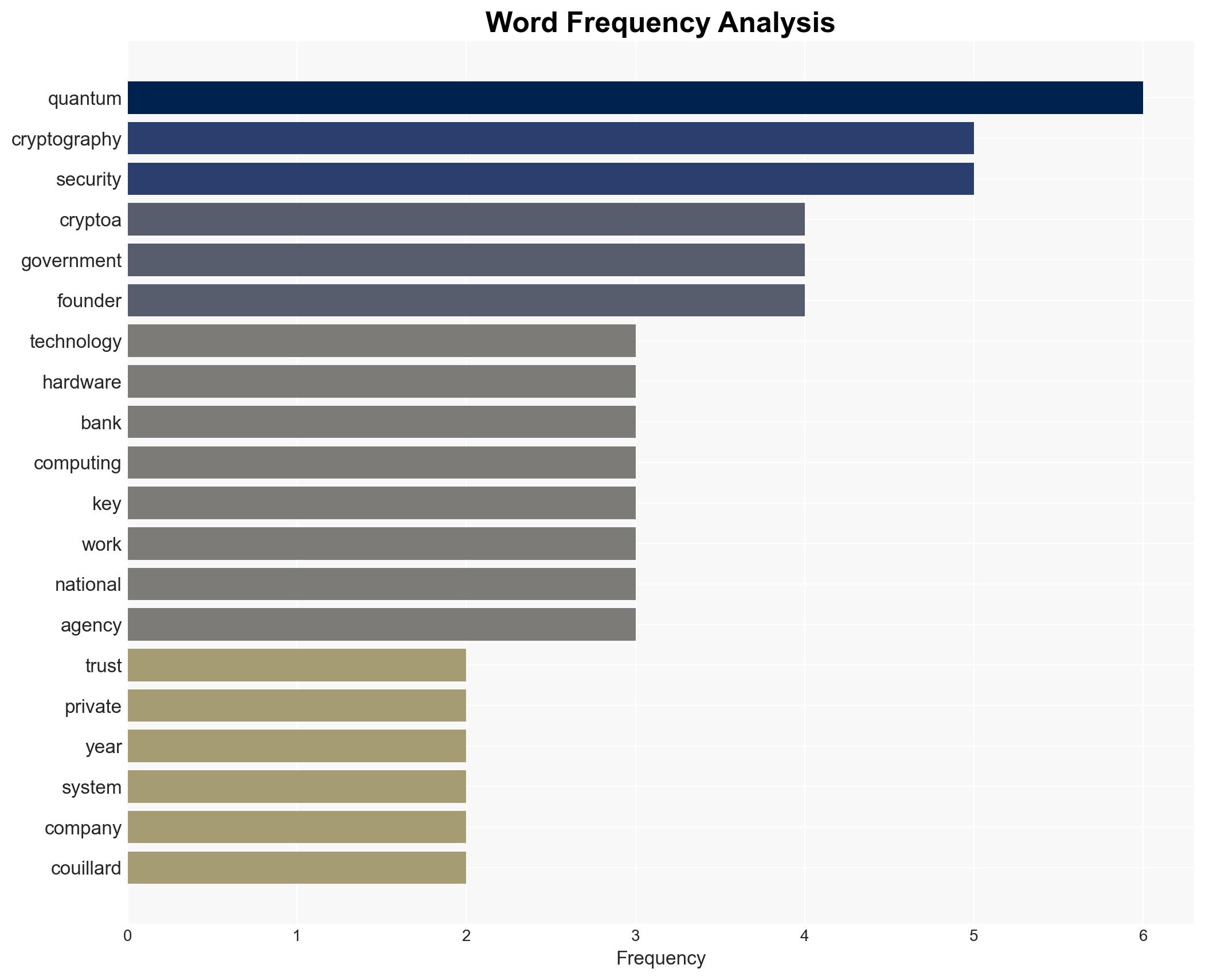
cybersecurity, quantum computing, cryptography, national security, technology innovation, data privacy, critical infrastructure
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us