Quantum Computing’s Rise Demands Urgent Action on Secure Communications and Post-Quantum Cryptography
Published on: 2026-01-28
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Quantum computing is reshaping secure communications Metadata is now the first line of defence
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
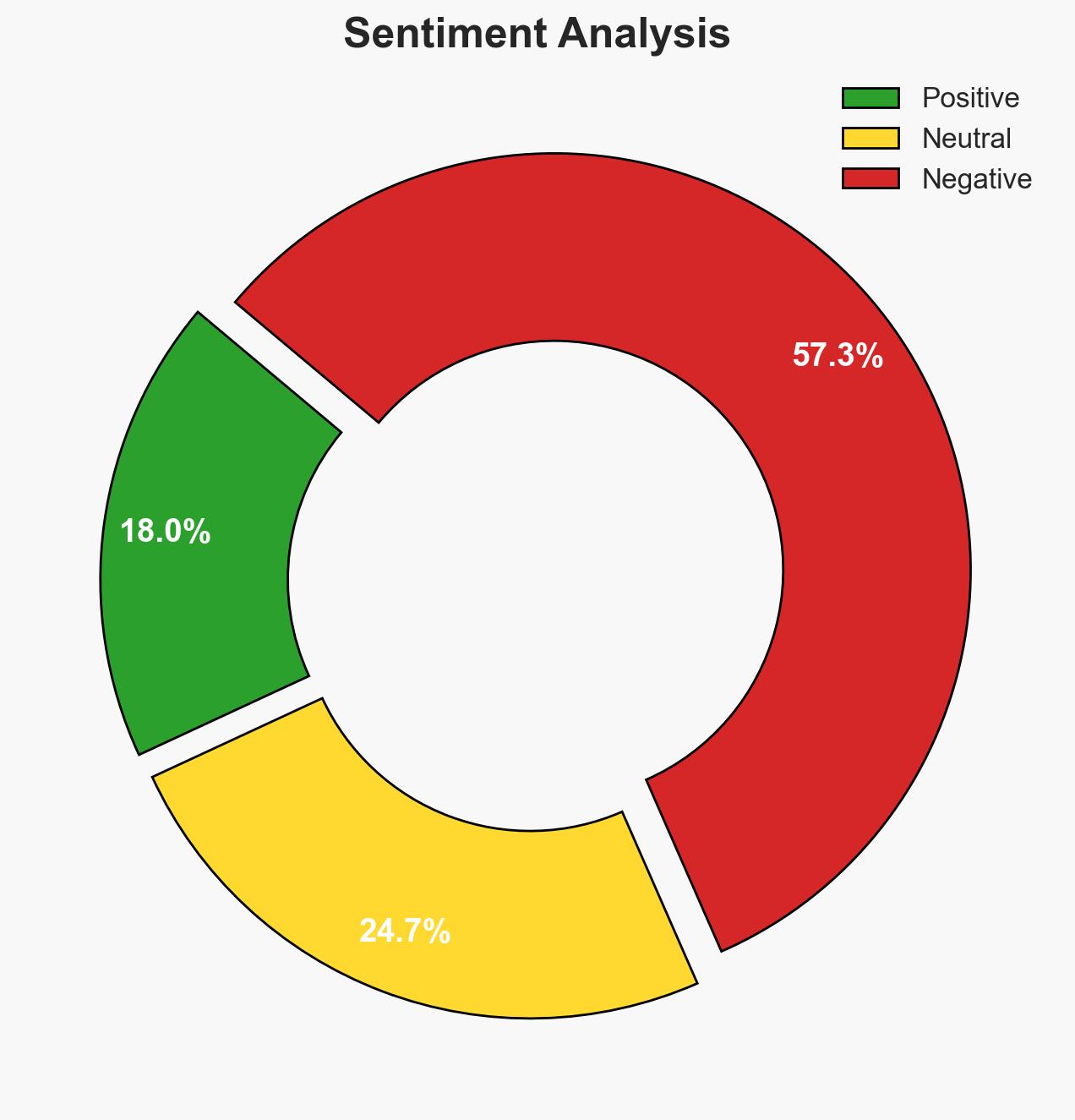
Quantum computing is rapidly advancing, posing a significant threat to current cryptographic systems, with harvest-now-decrypt-later attacks already in progress. The shift towards post-quantum cryptography is urgent, affecting government and critical infrastructure sectors. The focus on metadata as a defensive measure highlights the evolving nature of secure communications. Overall, there is moderate confidence in the assessment due to existing information gaps and the nascent stage of quantum technology deployment.
2. Competing Hypotheses
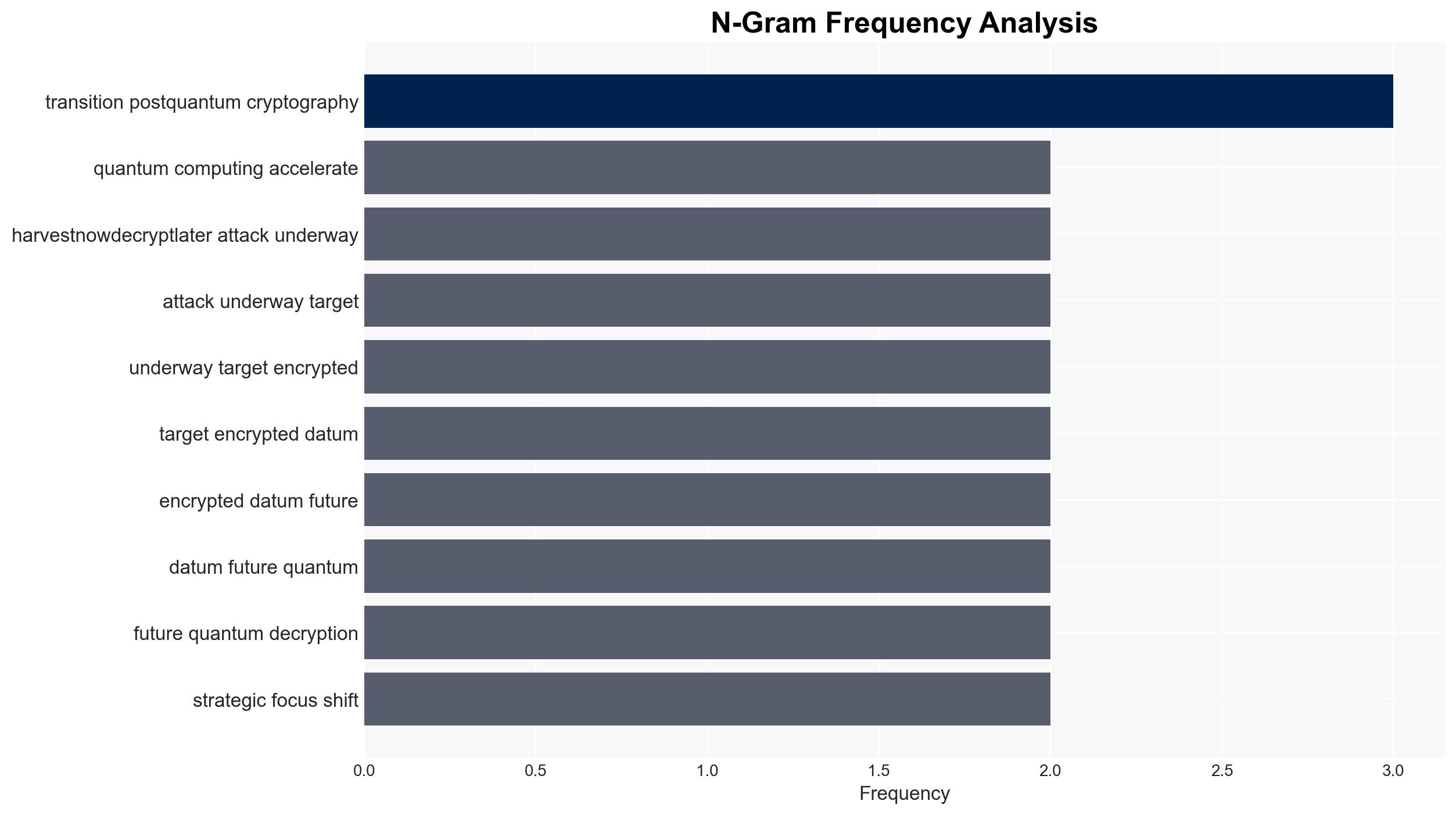
- Hypothesis A: Quantum computing will imminently compromise current cryptographic systems, necessitating immediate transition to post-quantum cryptography. This is supported by the ongoing harvest-now-decrypt-later attacks and the urgency expressed by cybersecurity agencies. However, the timeline for practical quantum attacks remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The threat from quantum computing is overstated, and existing cryptographic systems will remain secure for the foreseeable future. This view is contradicted by the strategic focus on post-quantum readiness and the mandates from cybersecurity agencies for migration plans.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the proactive measures being taken by governments and organizations to transition to post-quantum cryptography. Indicators that could shift this judgment include breakthroughs in quantum-resistant algorithms or delays in quantum computing advancements.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Quantum computing will achieve practical decryption capabilities within the next decade; current cryptographic systems are vulnerable to future quantum attacks; metadata management can effectively mitigate some quantum threats.
- Information Gaps: The exact timeline for quantum computing breakthroughs; the effectiveness of current post-quantum cryptographic solutions; adversaries’ capabilities and intentions regarding quantum decryption.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Over-reliance on optimistic projections of quantum computing capabilities; potential underestimation of adversaries’ current capabilities; possible manipulation of threat assessments by stakeholders with vested interests in quantum technology.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The development of quantum computing could significantly alter the landscape of secure communications, with wide-ranging impacts across multiple domains.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased tension between nations over quantum technology capabilities and control; potential for new international norms and treaties on quantum security.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced capabilities for adversaries to breach secure communications; increased focus on securing critical infrastructure against quantum threats.
- Cyber / Information Space: Shift in cyber defense strategies towards metadata management and post-quantum cryptography; potential for increased cyber espionage activities.
- Economic / Social: Economic impacts from the need to upgrade infrastructure and systems; potential social unrest from perceived vulnerabilities in national security.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive audit of current cryptographic systems; initiate awareness programs on quantum threats; begin developing post-quantum migration plans.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Invest in research and development of quantum-resistant cryptographic solutions; establish partnerships with technology firms specializing in quantum security; enhance metadata management capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful transition to post-quantum cryptography with minimal disruption.
- Worst: Rapid advancement of quantum decryption capabilities leading to widespread data breaches.
- Most-Likely: Gradual implementation of post-quantum solutions with ongoing adjustments based on technological developments.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
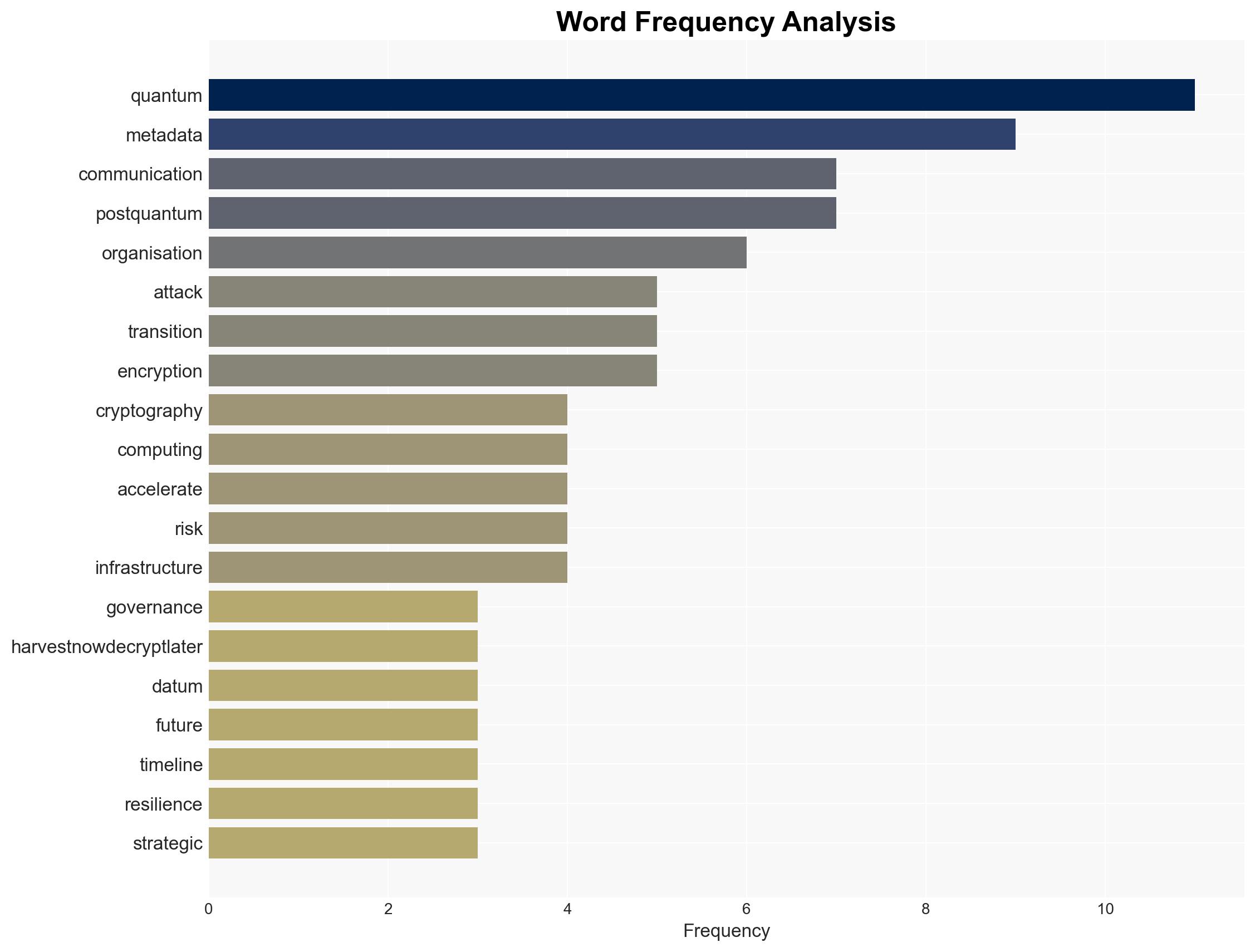
cybersecurity, quantum computing, secure communications, cryptography, metadata management, post-quantum cryptography, national security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us