Quantum physicists have shrunk and de-censored DeepSeek R1 – MIT Technology Review
Published on: 2025-11-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report:
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
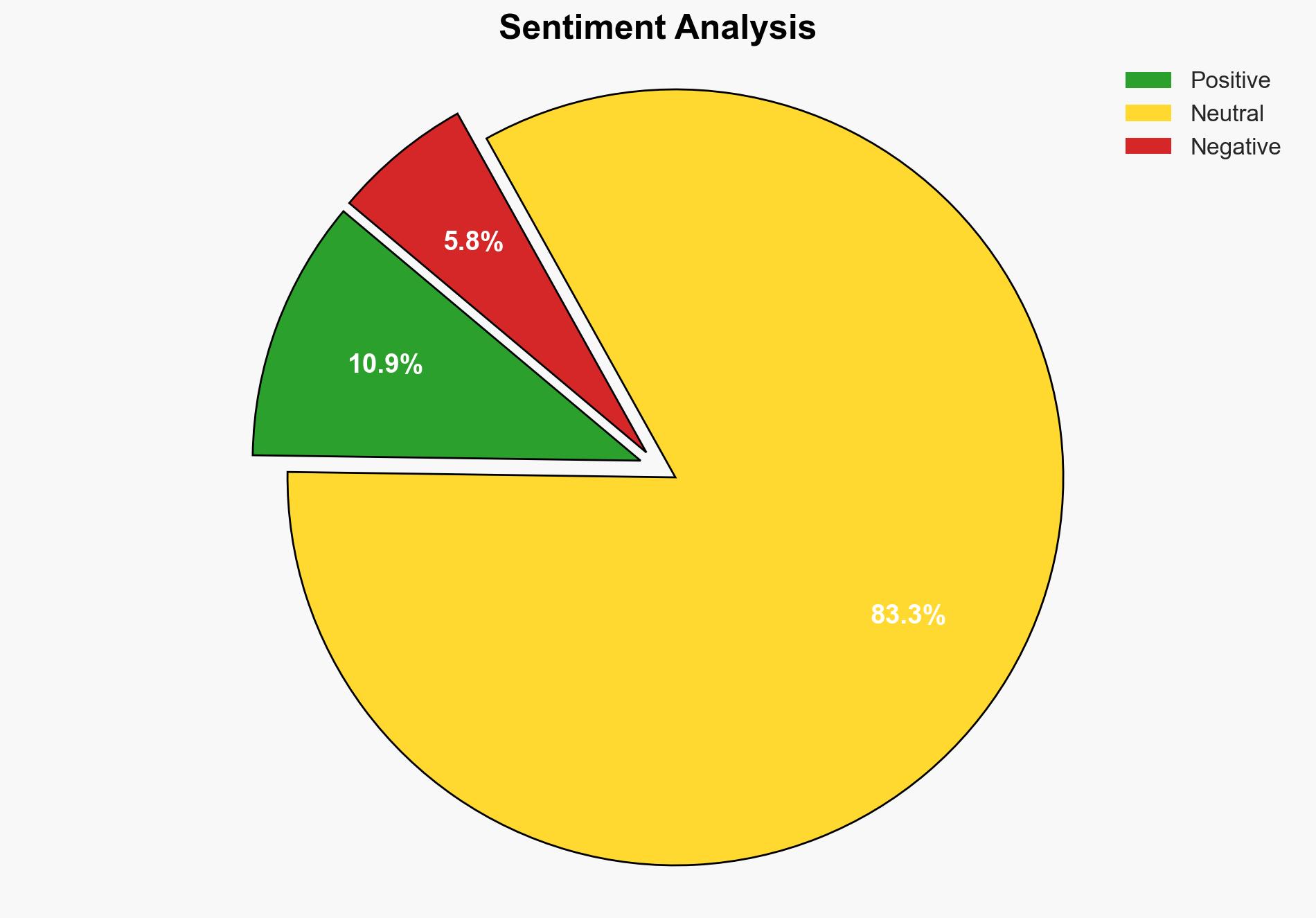
The strategic judgment is that the development of a de-censored and compressed version of the DeepSeek AI model by quantum physicists poses a significant challenge to Chinese AI censorship policies. The most supported hypothesis is that this development will lead to increased scrutiny and potential regulatory actions by Chinese authorities. Confidence Level: Moderate. Recommended action is to monitor Chinese regulatory responses and assess potential impacts on global AI governance and technology transfer.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The de-censored DeepSeek model will lead to increased regulatory scrutiny and potential crackdowns by Chinese authorities on AI research and development that bypasses state censorship.
Hypothesis 2: The development will encourage other international entities to adopt similar techniques, leading to a broader challenge to AI censorship globally, without immediate regulatory backlash from China.
Hypothesis 1 is more likely due to China’s historical precedence of strict control over information technology and the potential threat this poses to state-controlled narratives.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: It is assumed that the Chinese government will perceive this development as a direct challenge to its censorship policies. It is also assumed that the technical capabilities of the de-censored model are on par with existing Western models.
Red Flags: The potential for Chinese authorities to implement stricter regulations on AI research and development. The possibility of misinformation or exaggeration regarding the capabilities of the de-censored model.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The development of a de-censored AI model could lead to political tensions between China and countries advocating for open AI systems. There is a risk of cyber espionage as Chinese entities may attempt to acquire the technology or counteract its effects. Economically, this could impact Chinese AI companies if they face increased restrictions or competition from uncensored models. Informationally, it could lead to a proliferation of uncensored content, challenging state narratives.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Monitor Chinese regulatory responses to this development and assess potential impacts on international AI collaborations.
- Encourage dialogue between international AI developers and Chinese authorities to mitigate potential conflicts.
- Best-case scenario: The development leads to a more open dialogue on AI censorship and governance globally.
- Worst-case scenario: China implements stricter regulations, leading to a fragmented global AI ecosystem.
- Most-likely scenario: Increased scrutiny and regulatory actions by China, with limited immediate global impact.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Roman Orús, co-founder and Chief Scientific Officer of Multiverse. Thomas Cao, Assistant Professor of Technology Policy at Tufts University.
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, AI Censorship, Quantum Computing, International Relations
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Structured challenge to expose and correct biases.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us